https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-7917089/latest
https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-7917089/latest
a 🧵 1/n
Drain: arxiv.org/abs/2511.04820
Strain: direct.mit.edu/qss/article/...
Oligopoly: direct.mit.edu/qss/article/...




a 🧵 1/n
Drain: arxiv.org/abs/2511.04820
Strain: direct.mit.edu/qss/article/...
Oligopoly: direct.mit.edu/qss/article/...
While our attention is focused on the security of genomic data storage, this is a strong reminder we have to factor in hardware security as well.
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

While our attention is focused on the security of genomic data storage, this is a strong reminder we have to factor in hardware security as well.
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
New guidelines help: CHART for chatbot health advice, TRIPOD-LLM for model development or prediction, and GAMER for GenAI-assisted manuscript writing.
#MedSky #MedAI #MLSky


www.who.int/news/item/13...
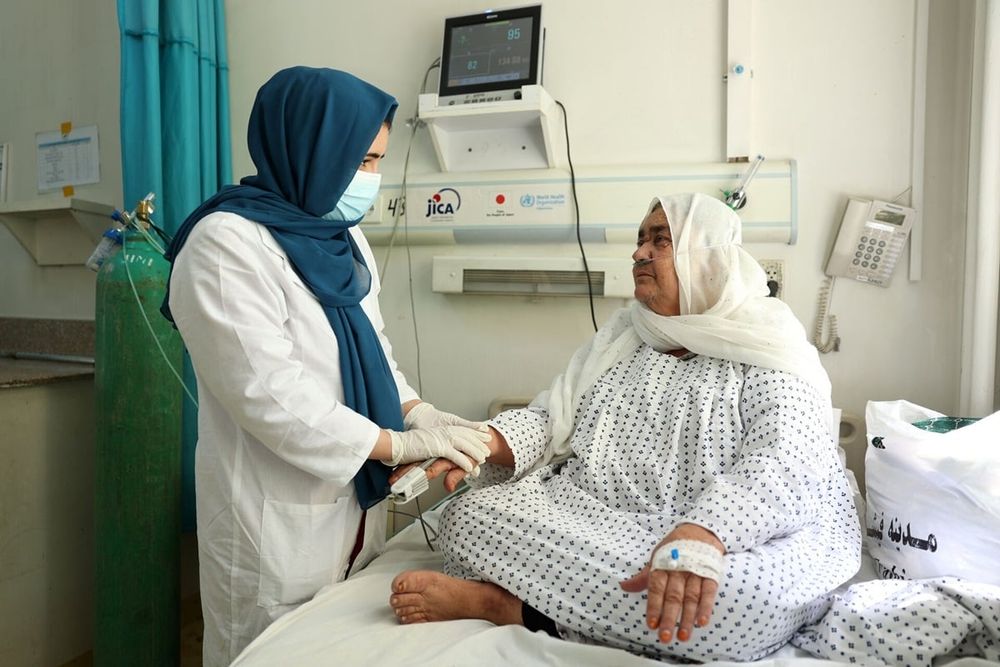
www.who.int/news/item/13...

We found mutually exclusive evolutionary pathways to multidrug resistance in E. coli & P. aeruginosa - some resistance mechanisms actively prevent others from coexisting www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

We found mutually exclusive evolutionary pathways to multidrug resistance in E. coli & P. aeruginosa - some resistance mechanisms actively prevent others from coexisting www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
academic.oup.com/bioinformati...

academic.oup.com/bioinformati...

https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2025.08.06.668843v1
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2025.08.06.668843v1
academic.oup.com/bib/article/...

academic.oup.com/bib/article/...
😎 biology but double whammy for cancer patients
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
🧪
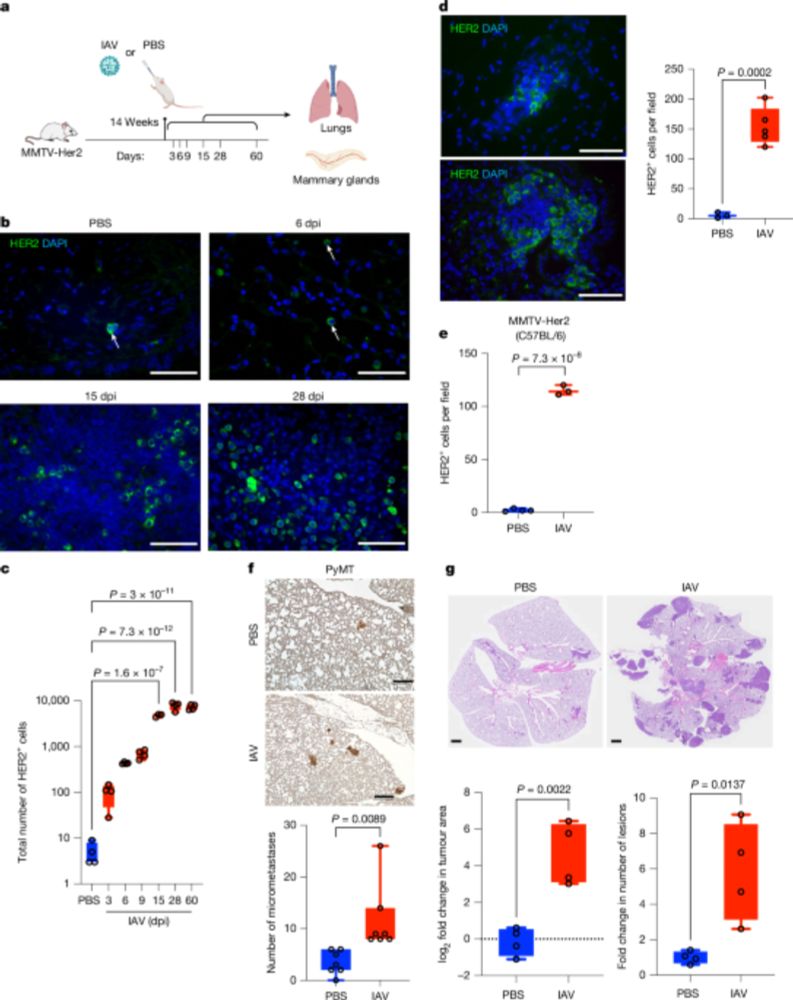
😎 biology but double whammy for cancer patients
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
🧪
We identify risk groups and clusters of transmission and exposure throughout Florida, via a rich database of multi-year contact tracing interviews.
publichealth.jmir.org/2025/1/e65573/
We identify risk groups and clusters of transmission and exposure throughout Florida, via a rich database of multi-year contact tracing interviews.
publichealth.jmir.org/2025/1/e65573/
Success rates ranged from just 15–45%.
Now, the project team reflects on what made replication so hard and what needs to change.
buff.ly/55j9Sax

Success rates ranged from just 15–45%.
Now, the project team reflects on what made replication so hard and what needs to change.
buff.ly/55j9Sax
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
and tell you just a little bit about it in the following 🧵

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
and tell you just a little bit about it in the following 🧵
#InfectiousDisease
www.htfmarketinsights.com/report/41017...

#InfectiousDisease
www.htfmarketinsights.com/report/41017...
Its been a privilege to work with these extraordinary scientists in my lab over the years - all making an incredible impact throughout the world 🙌
We must never give up on #equality #diversity & #inclusion 💪
#WomeninScience #GirlsInSTEM 🧪🔬🔭🚀

Its been a privilege to work with these extraordinary scientists in my lab over the years - all making an incredible impact throughout the world 🙌
We must never give up on #equality #diversity & #inclusion 💪
#WomeninScience #GirlsInSTEM 🧪🔬🔭🚀
"In 1922, he joined the opposition to the Fascist regime of Benito Mussolini and in 1931 he was one of only 12 out of 1,250 professors who refused to take a mandatory oath of loyalty."
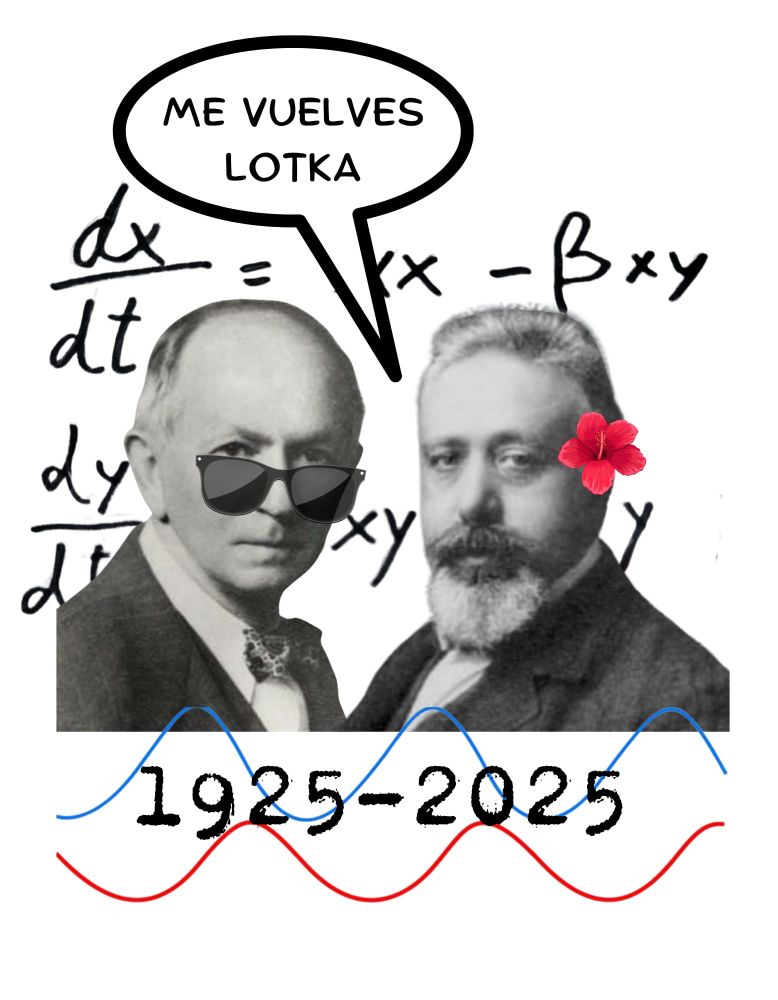
"In 1922, he joined the opposition to the Fascist regime of Benito Mussolini and in 1931 he was one of only 12 out of 1,250 professors who refused to take a mandatory oath of loyalty."


