https://www.anti-sense.org/

@science.org
science.org/doi/10.1126/...

@science.org
science.org/doi/10.1126/...
#Review by @carolinamonzo.bsky.social, Tianyuan Liu & @anaconesa.bsky.social @conesalab.bsky.social @csic.es
Free to read here: rdcu.be/efBjP

#Review by @carolinamonzo.bsky.social, Tianyuan Liu & @anaconesa.bsky.social @conesalab.bsky.social @csic.es
Free to read here: rdcu.be/efBjP

We uncover an unexpected role for endogenous Xist RNA in regulating X-linked genes that escape X-inactivation.

We uncover an unexpected role for endogenous Xist RNA in regulating X-linked genes that escape X-inactivation.

Yes, one can. with CUT&ID ✂️🪪
Spearheaded — singlehandedly — by @annanordin.bsky.social
No need of transgenesis, cloning and overexpression.
Check it out, it's fast and its works.

Yes, one can. with CUT&ID ✂️🪪
Spearheaded — singlehandedly — by @annanordin.bsky.social
No need of transgenesis, cloning and overexpression.
Check it out, it's fast and its works.
The Expanding Histone Universe: Histone-Based DNA Organization in Noneukaryotic Organisms - www.annualreviews.org/content/jour...

The Expanding Histone Universe: Histone-Based DNA Organization in Noneukaryotic Organisms - www.annualreviews.org/content/jour...
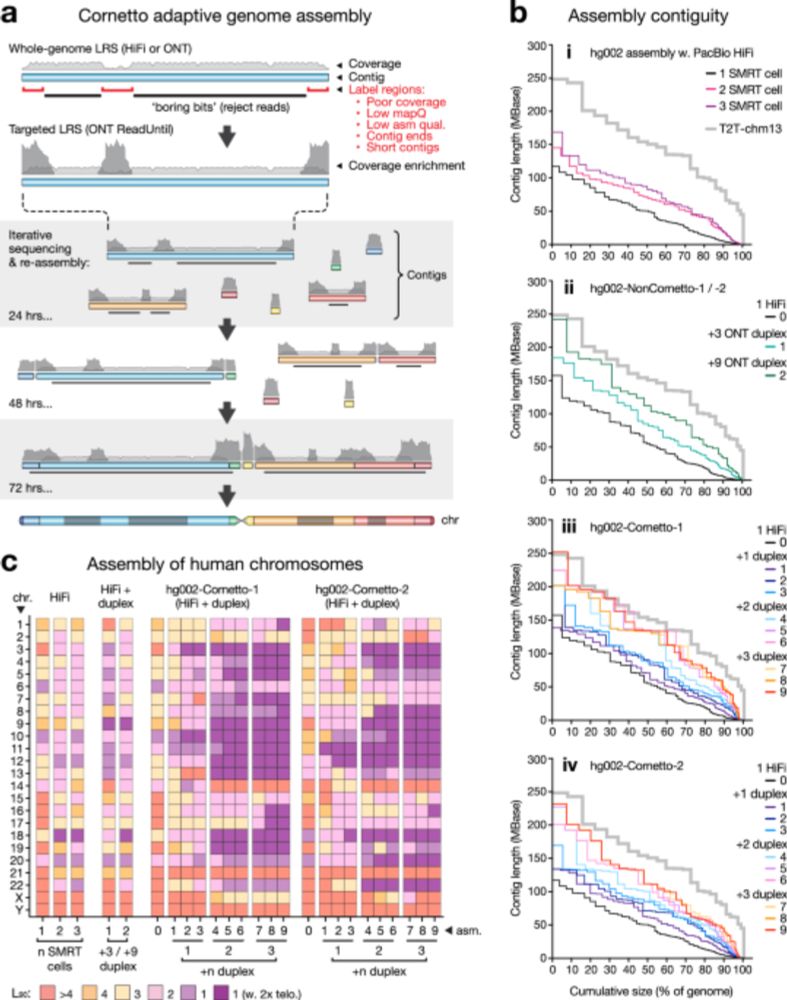
It can do near-T2T assembly using @nanoporetech.com adaptive sampling
- with less 💸
- reference agnostic, so works for non-humans
- not just blood, even saliva
Just presented at #abacbs2025 yesterday.
It can do near-T2T assembly using @nanoporetech.com adaptive sampling
- with less 💸
- reference agnostic, so works for non-humans
- not just blood, even saliva
Just presented at #abacbs2025 yesterday.
www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/...

www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/...

You shall know a gene by the company it keeps!

You shall know a gene by the company it keeps!

Here we investigated the adaptive remodeling of a protein-protein interaction surface essential for telomere protection.
Congrats to whole team!
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...

Here we investigated the adaptive remodeling of a protein-protein interaction surface essential for telomere protection.
Congrats to whole team!
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
@natsmb.nature.com. A wonderful team effort across the centromere community, across @jansenlab.bsky.social @naltemose.bsky.social @dfachinetti.bsky.social and Giunta labs. Happy reading! 1/4
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

@natsmb.nature.com. A wonderful team effort across the centromere community, across @jansenlab.bsky.social @naltemose.bsky.social @dfachinetti.bsky.social and Giunta labs. Happy reading! 1/4
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Fight the drain of scientific publishing.
arxiv.org/abs/2511.04820

Fight the drain of scientific publishing.
arxiv.org/abs/2511.04820
Free to read here: rdcu.be/eR4zx

Free to read here: rdcu.be/eR4zx
Selfish genes are found across the tree of life. They can disrupt inheritance patterns and at the same time act as units for molecular innovation. Here we tried to answer one big question: how do selfish genes emerge in the first place?
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

Selfish genes are found across the tree of life. They can disrupt inheritance patterns and at the same time act as units for molecular innovation. Here we tried to answer one big question: how do selfish genes emerge in the first place?
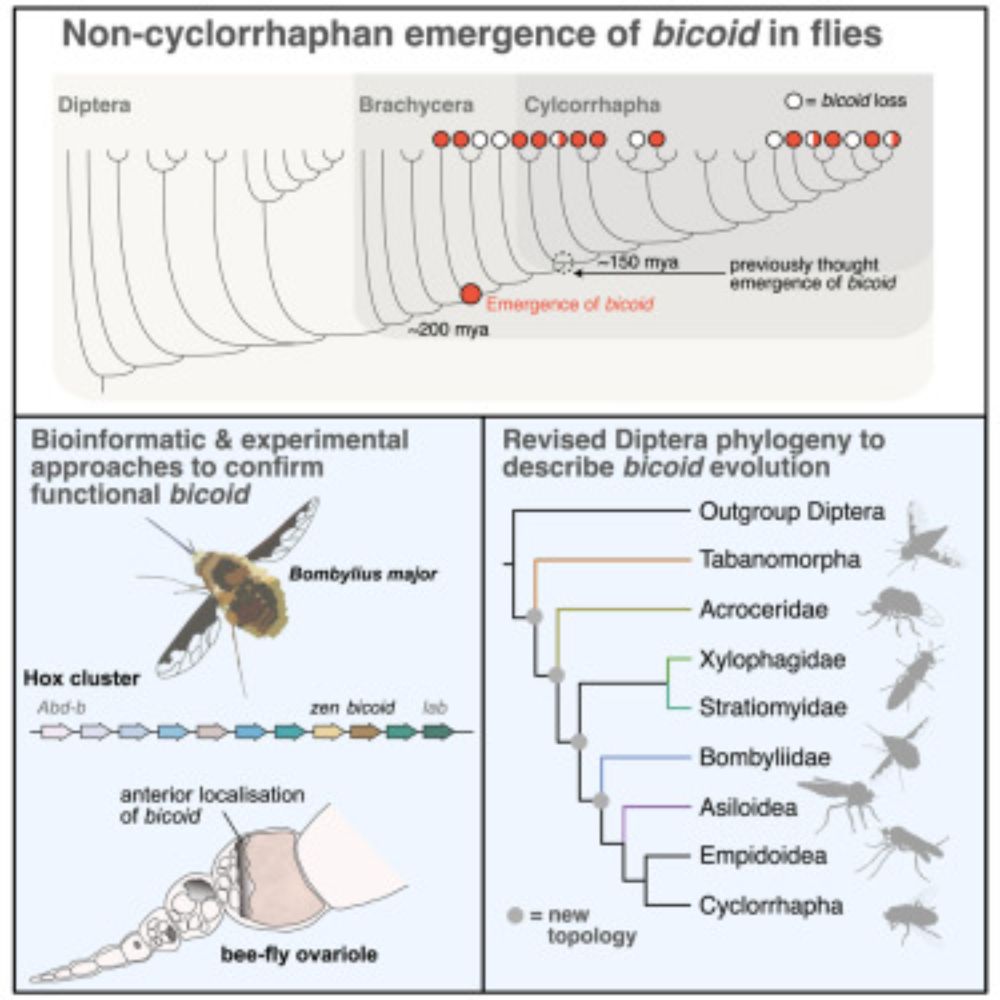
We find the fly development gene bicoid is much older than previously thought (~20 million yrs older!) 🪰🧬
To pinpoint its origins we tackled the Diptera phylogeny, providing some resolution (many open questions remain).
🔗 tinyurl.com/2vyuevpy
We find the fly development gene bicoid is much older than previously thought (~20 million yrs older!) 🪰🧬
To pinpoint its origins we tackled the Diptera phylogeny, providing some resolution (many open questions remain).
🔗 tinyurl.com/2vyuevpy
#PlantScience
Paper here: www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
Perspective here:
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...

#PlantScience
Paper here: www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
Perspective here:
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
"We must also continue to deepen and refine our understanding of fundamental biological processes because these details frequently hold the keys to major advances in applied research."
elifesciences.org/articles/102...
"We must also continue to deepen and refine our understanding of fundamental biological processes because these details frequently hold the keys to major advances in applied research."
elifesciences.org/articles/102...


