

We found a gap between algorithmic scoring and real-world usability that may help explain why AI benchmarks feel disconnected from reality.

We found a gap between algorithmic scoring and real-world usability that may help explain why AI benchmarks feel disconnected from reality.

In new research, we find that the CoT is informative about LLM cognition as long as the cognition is complex enough that it can’t be performed in a single forward pass.

In new research, we find that the CoT is informative about LLM cognition as long as the cognition is complex enough that it can’t be performed in a single forward pass.
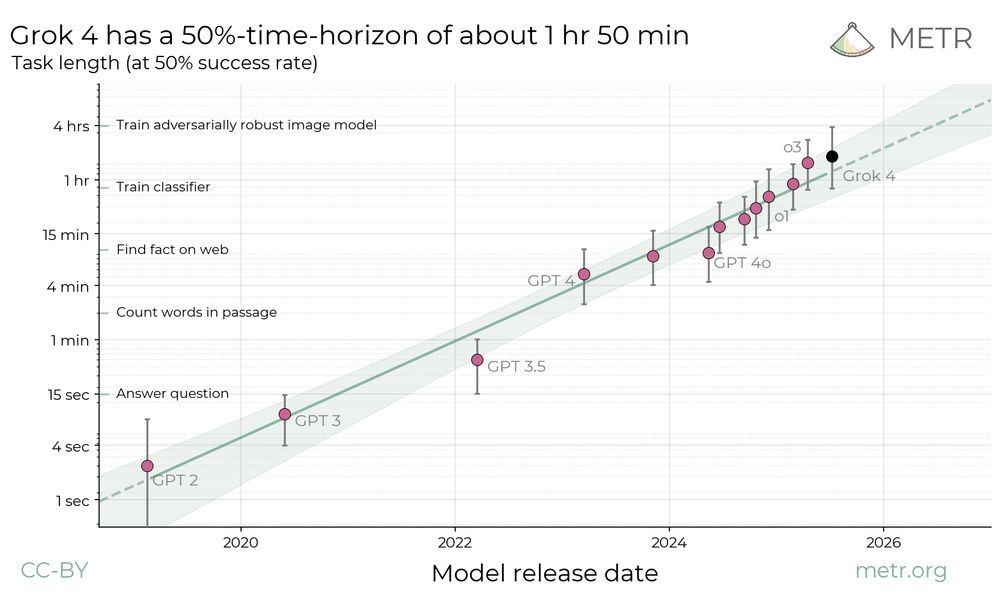
We conclude that this seems unlikely. However, capability trends continue rapidly, and models display increasing eval awareness.

We conclude that this seems unlikely. However, capability trends continue rapidly, and models display increasing eval awareness.
The paper is also live on arXiv, with two new sections: One discussing alternative uncertainty estimation methods, and a new 'bias from developer recruitment' factor that has unclear effect on slowdown.

The paper is also live on arXiv, with two new sections: One discussing alternative uncertainty estimation methods, and a new 'bias from developer recruitment' factor that has unclear effect on slowdown.
We have now analyzed 9 other benchmarks for scientific reasoning, math, robotics, computer use, and self-driving; we observe generally similar rates of improvement.

We have now analyzed 9 other benchmarks for scientific reasoning, math, robotics, computer use, and self-driving; we observe generally similar rates of improvement.
When the results started coming back from this project, we put the survey-only project on ice.
The results surprised us: Developers thought they were 20% faster with AI tools, but they were actually 19% slower when they had access to AI than when they didn't.
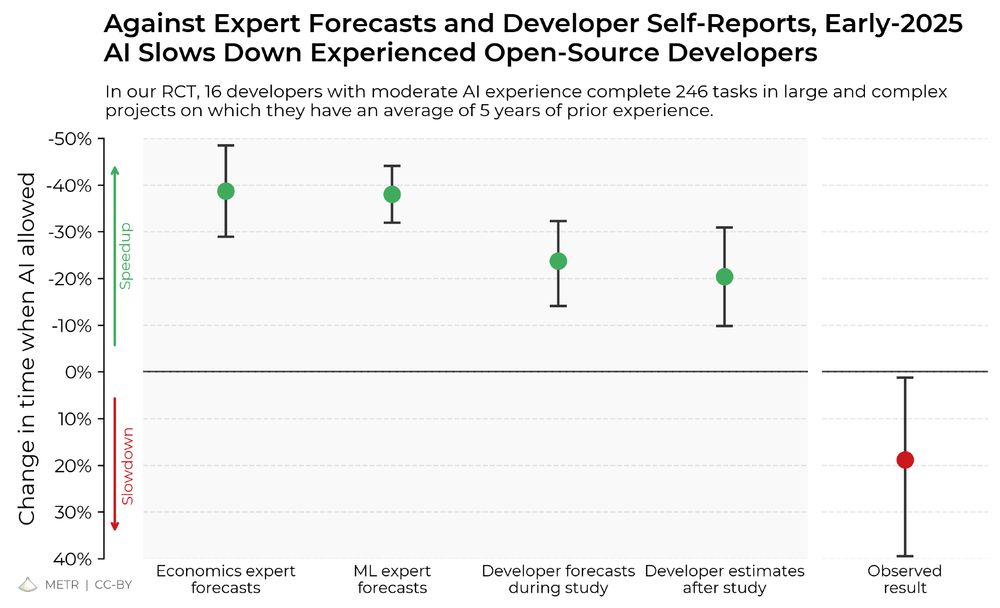
When the results started coming back from this project, we put the survey-only project on ice.
The results surprised us: Developers thought they were 20% faster with AI tools, but they were actually 19% slower when they had access to AI than when they didn't.

The results surprised us: Developers thought they were 20% faster with AI tools, but they were actually 19% slower when they had access to AI than when they didn't.


In new research, we find a kind of “Moore’s Law for AI agents”: the length of tasks that AIs can do is doubling about every 7 months.
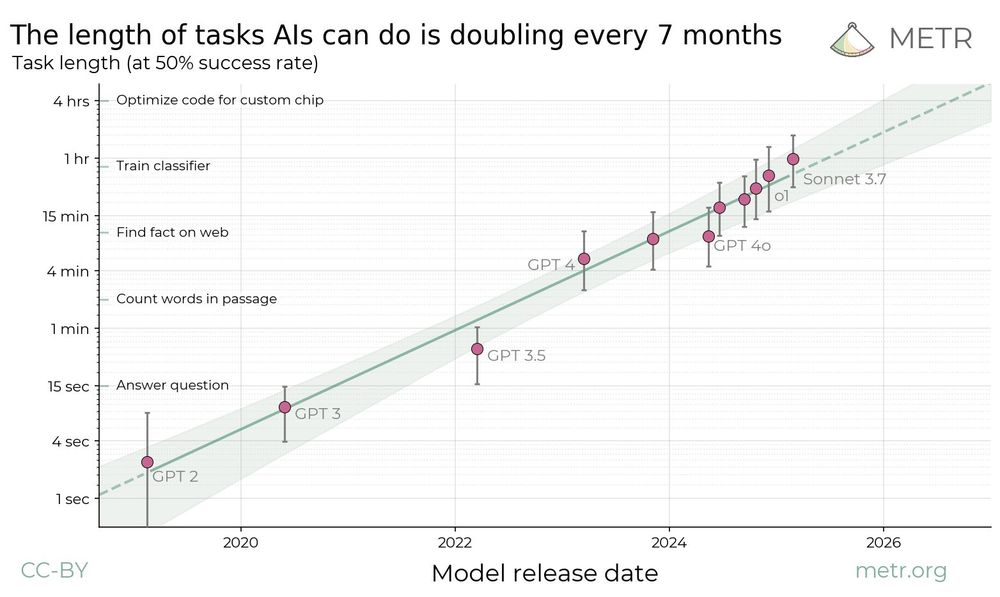
In new research, we find a kind of “Moore’s Law for AI agents”: the length of tasks that AIs can do is doubling about every 7 months.


