Senior researcher at Microsoft Research, PhD from UC Berkeley, https://csinva.io/


cc: Sen. Bill Cassidy

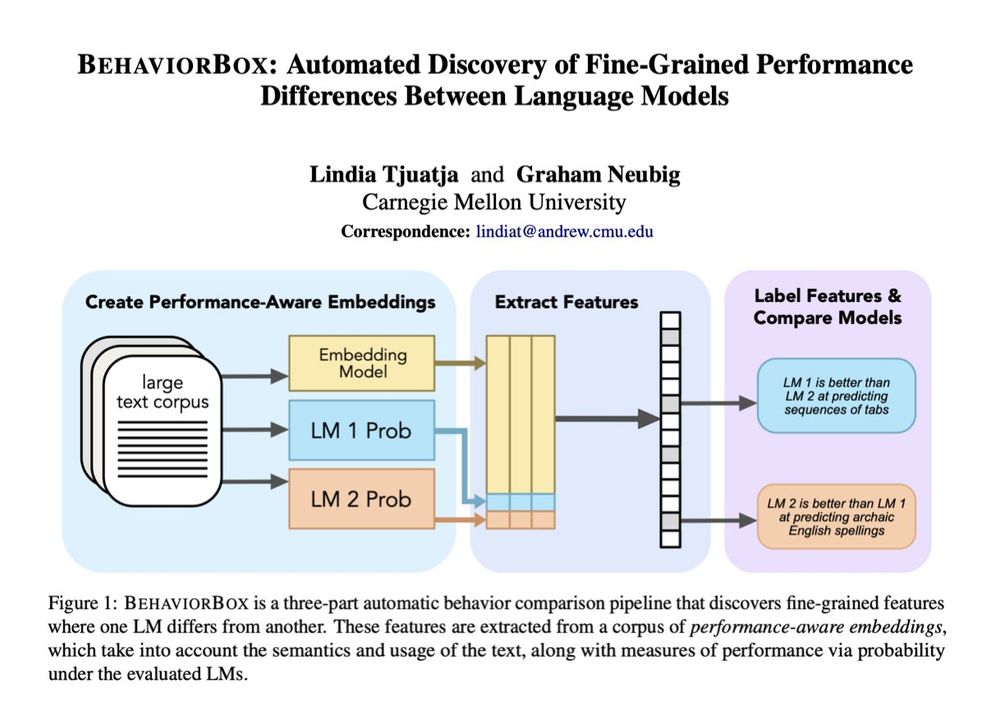
SPIRAL: models learn via self-competition. Kuhn Poker → +8.7% math, +18.1 Minerva Math! 🃏
Paper: huggingface.co/papers/2506....
Code: github.com/spiral-rl/spiral
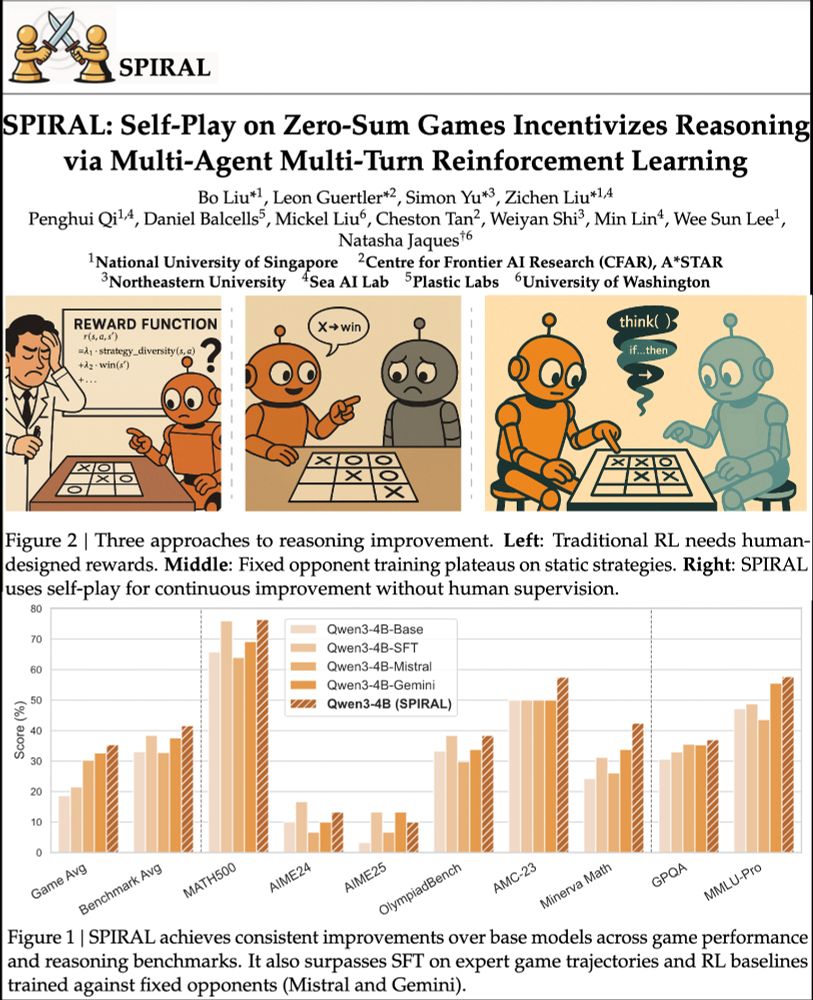
SPIRAL: models learn via self-competition. Kuhn Poker → +8.7% math, +18.1 Minerva Math! 🃏
Paper: huggingface.co/papers/2506....
Code: github.com/spiral-rl/spiral
Prior work has mapped how the brain encodes concepts: If you see fire and smoke, your brain will represent the fire (hot, bright) and smoke (gray, airy). But how do you encode features of the fire-smoke relation? We analyzed fMRI with embeddings extracted from LLMs to find out 🧵
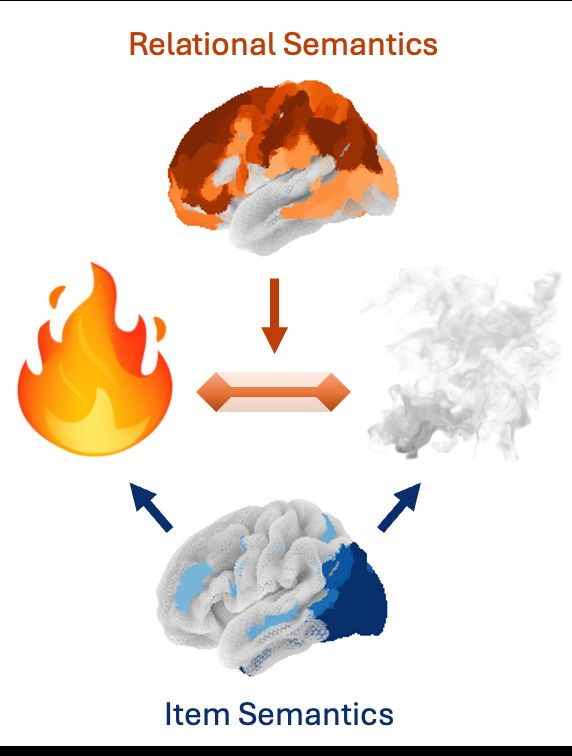
Prior work has mapped how the brain encodes concepts: If you see fire and smoke, your brain will represent the fire (hot, bright) and smoke (gray, airy). But how do you encode features of the fire-smoke relation? We analyzed fMRI with embeddings extracted from LLMs to find out 🧵
www.nature.com/articles/s42...
www.nature.com/articles/s42...
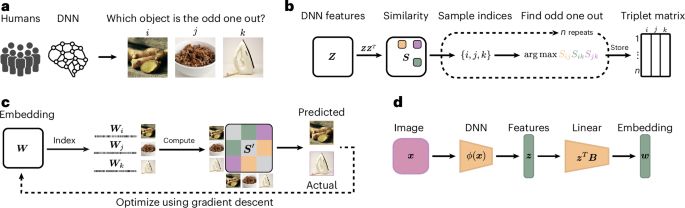
TL;DR first: We used a pre-trained deep neural network to model fMRI data and to generate images predicted to elicit a large response for each many different parts of the brain. We aggregate these into an awesome interactive brain viewer: piecesofmind.psyc.unr.edu/activation_m...
TL;DR first: We used a pre-trained deep neural network to model fMRI data and to generate images predicted to elicit a large response for each many different parts of the brain. We aggregate these into an awesome interactive brain viewer: piecesofmind.psyc.unr.edu/activation_m...
We show that voxel responses during comprehension are organized along 2 main axes: processing difficulty & meaning abstractness—revealing an interpretable, topographic representational basis for language processing shared across individuals
We show that voxel responses during comprehension are organized along 2 main axes: processing difficulty & meaning abstractness—revealing an interpretable, topographic representational basis for language processing shared across individuals
🧵1/9
🧵1/9
Learn more in #ScienceAdvances: scim.ag/442Hjn6
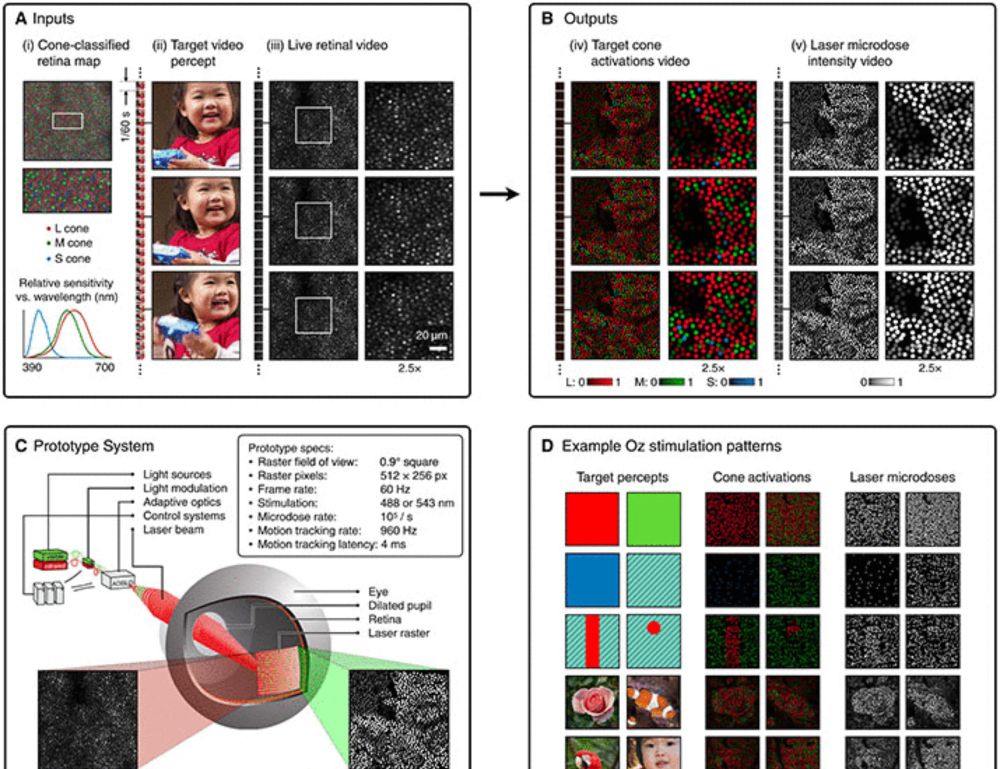
Learn more in #ScienceAdvances: scim.ag/442Hjn6
go.nature.com/4jfSRYX 🧪
go.nature.com/4jfSRYX 🧪

Led by Colin Conwell with @emaliemcmahon.bsky.social Akshay Jagadeesh, Kasper Vinken @amrahs-inolas.bsky.social @jacob-prince.bsky.social George Alvarez @taliakonkle.bsky.social & Marge Livingstone 1/n

Led by Colin Conwell with @emaliemcmahon.bsky.social Akshay Jagadeesh, Kasper Vinken @amrahs-inolas.bsky.social @jacob-prince.bsky.social George Alvarez @taliakonkle.bsky.social & Marge Livingstone 1/n
A dream study of mine for nearly 20 yrs not possible until now thanks to NIH 🧠 funding & 1st-author lead @seeber.bsky.social
We tracked hippocampal activity as people walked memory-guided paths & imagined them again. Did brain patterns reappear?🧵👇
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
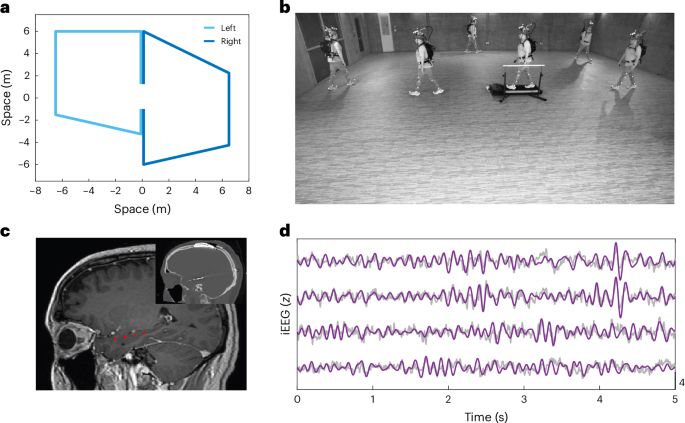
A dream study of mine for nearly 20 yrs not possible until now thanks to NIH 🧠 funding & 1st-author lead @seeber.bsky.social
We tracked hippocampal activity as people walked memory-guided paths & imagined them again. Did brain patterns reappear?🧵👇
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
2025: SAEs give plausible interpretations of random weights, triggering skepticism and ...


2025: SAEs give plausible interpretations of random weights, triggering skepticism and ...

Turns out: yes!
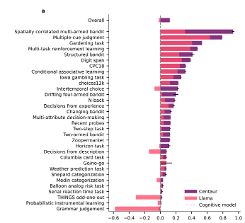
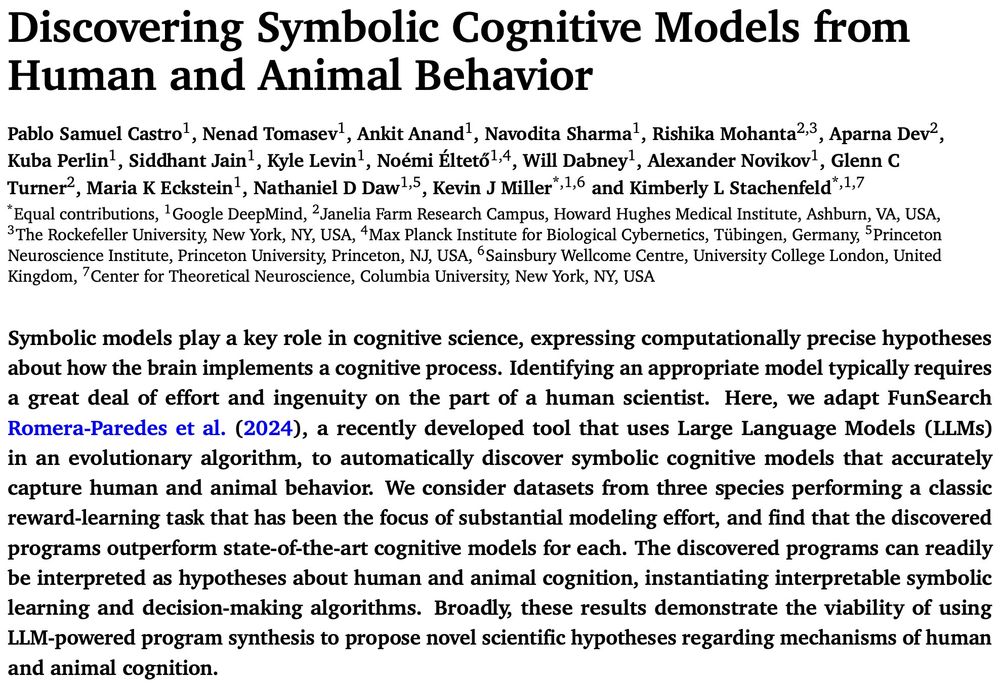
Thrilled to share our latest preprint where we used FunSearch to automatically discover symbolic cognitive models of behavior.
1/12
Turns out: yes!
Thrilled to share our latest preprint where we used FunSearch to automatically discover symbolic cognitive models of behavior.
1/12
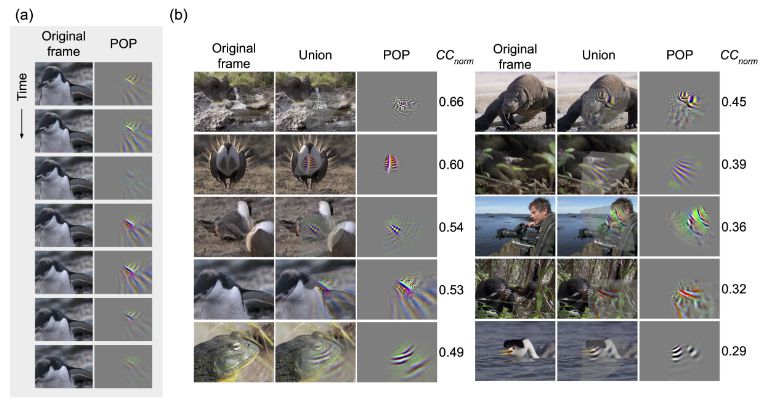
#NeuroAI
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

#NeuroAI
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Drop me a message if you want to chat about interpretability/language neuroscience!
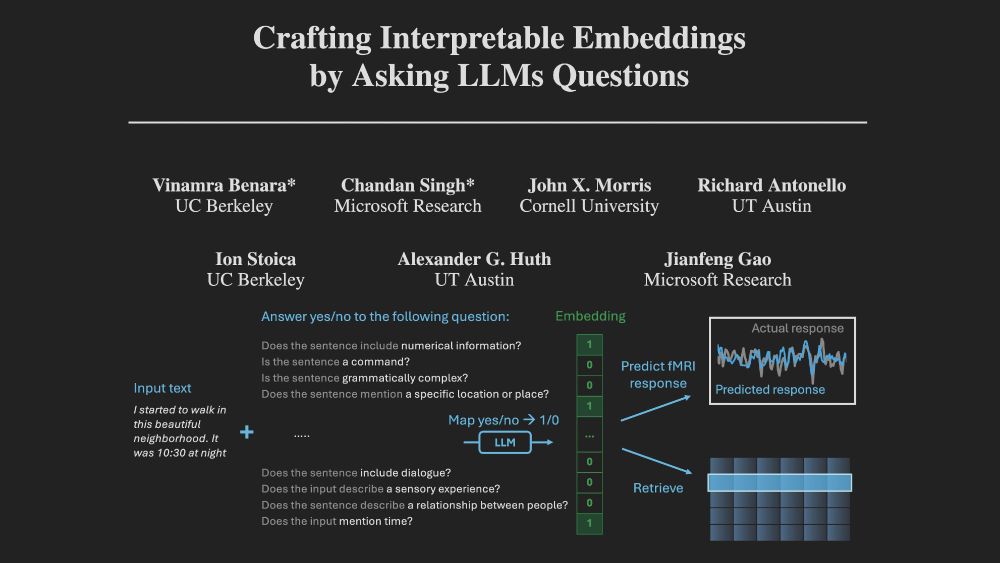
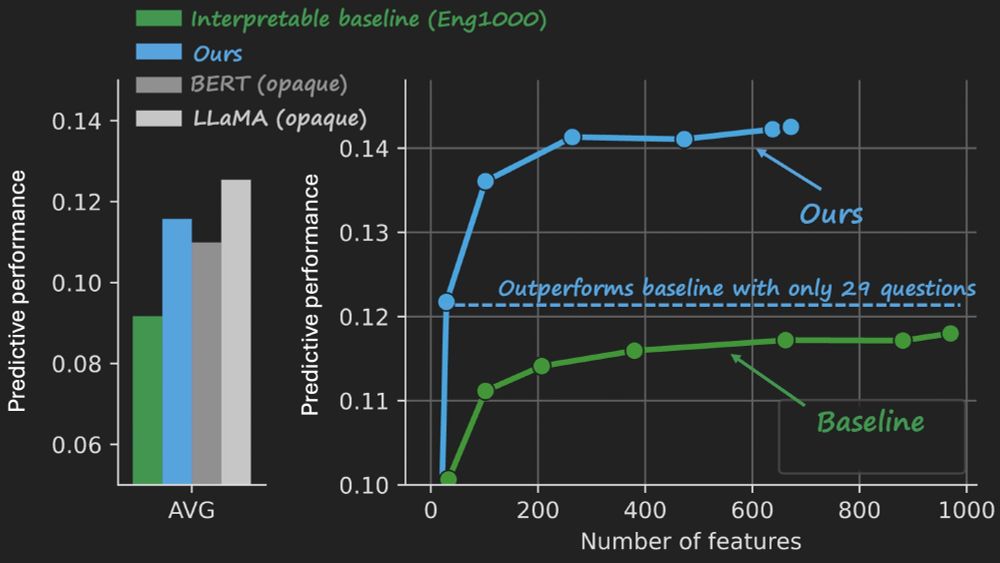
Drop me a message if you want to chat about interpretability/language neuroscience!
go.bsky.app/BYkRryU
go.bsky.app/BYkRryU
We tackle this issue in language neuroscience by using LLMs to generate *and validate* explanations with targeted follow-up experiments

We tackle this issue in language neuroscience by using LLMs to generate *and validate* explanations with targeted follow-up experiments
We show that "induction heads" found in LLMs can be reverse-engineered to yield accurate & interpretable next-word prediction models

We show that "induction heads" found in LLMs can be reverse-engineered to yield accurate & interpretable next-word prediction models

