#MedSky #IDSky

#MedSky #IDSky

#idsky

#idsky
#idsky #hivsky #bioconductor #rstats #sierrapy #bioinformatics

#idsky #hivsky #bioconductor #rstats #sierrapy #bioinformatics
#idsky #microsky #rstats #deseq2 #bioconductor

#idsky #microsky #rstats #deseq2 #bioconductor
#idsky #tbsky #microsky #bioinformatics

#idsky #tbsky #microsky #bioinformatics


#idsky #microsky #rstats

#idsky #microsky #rstats
#microsky #idsky #bioconductor #rstats

#microsky #idsky #bioconductor #rstats
Here we describe our investigation and response to the first documented meningococcal conjunctivitis outbreak. 🧫
Contributions by 🌟🌟🌟 fellows @sucroselauren.bsky.social @ogallardo.bsky.social
#IDSky
www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes...

Here we describe our investigation and response to the first documented meningococcal conjunctivitis outbreak. 🧫
Contributions by 🌟🌟🌟 fellows @sucroselauren.bsky.social @ogallardo.bsky.social
#IDSky
www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes...
#microsky #idsky

#microsky #idsky
#idsky #microsky #amr #rstats

#idsky #microsky #amr #rstats
#idsky #medsky #meded

doi.org/10.1093/cid/...
We provide a conceptual overview of HCEs, explain the different associated target parameters and analytic methods.
@steventong.bsky.social @gurujosh.bsky.social

doi.org/10.1093/cid/...
We provide a conceptual overview of HCEs, explain the different associated target parameters and analytic methods.
@steventong.bsky.social @gurujosh.bsky.social
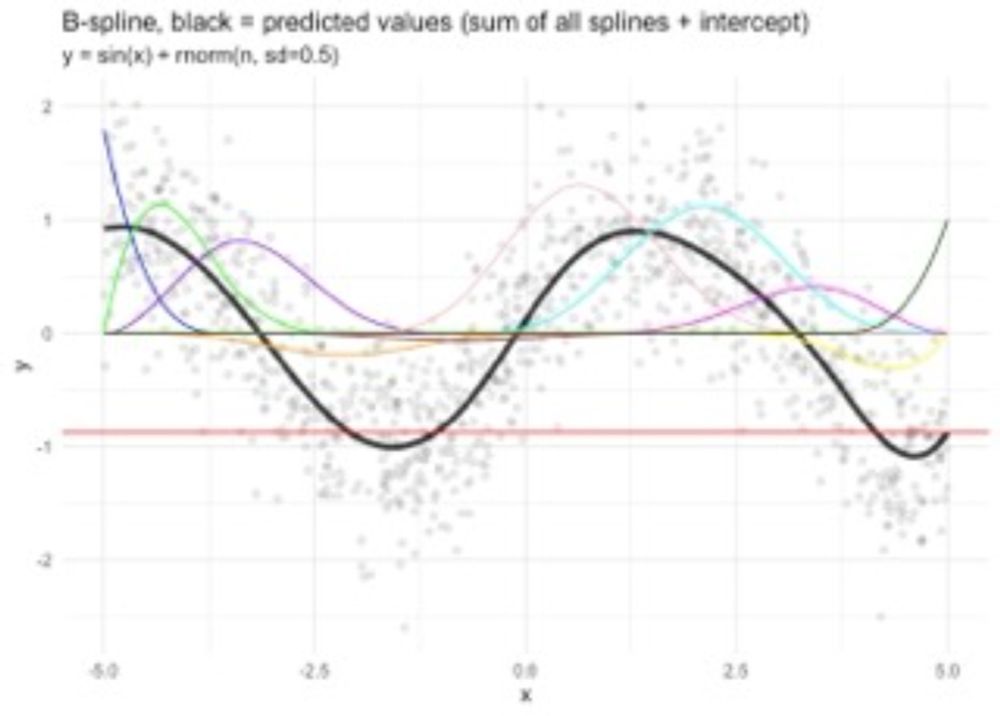
Confusing? Yes! Rewarding? Oh yes!
#rstats

Confusing? Yes! Rewarding? Oh yes!
#rstats
I've been using this package to produce the AGAR Kids reports and can highly recommend.
amr-for-r.org
#Rstats #AMR #IDEpi #MedSky



