Shivan Shah
@idoncology.bsky.social
980 followers
570 following
93 posts
Transplant /oncology ID at USF. MD Anderson---->Houtston Methodist. Dog enthusiast and more
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Pinned
Shivan Shah
@idoncology.bsky.social
· Nov 19
Reposted by Shivan Shah
Reposted by Shivan Shah
Shivan Shah
@idoncology.bsky.social
· Apr 19
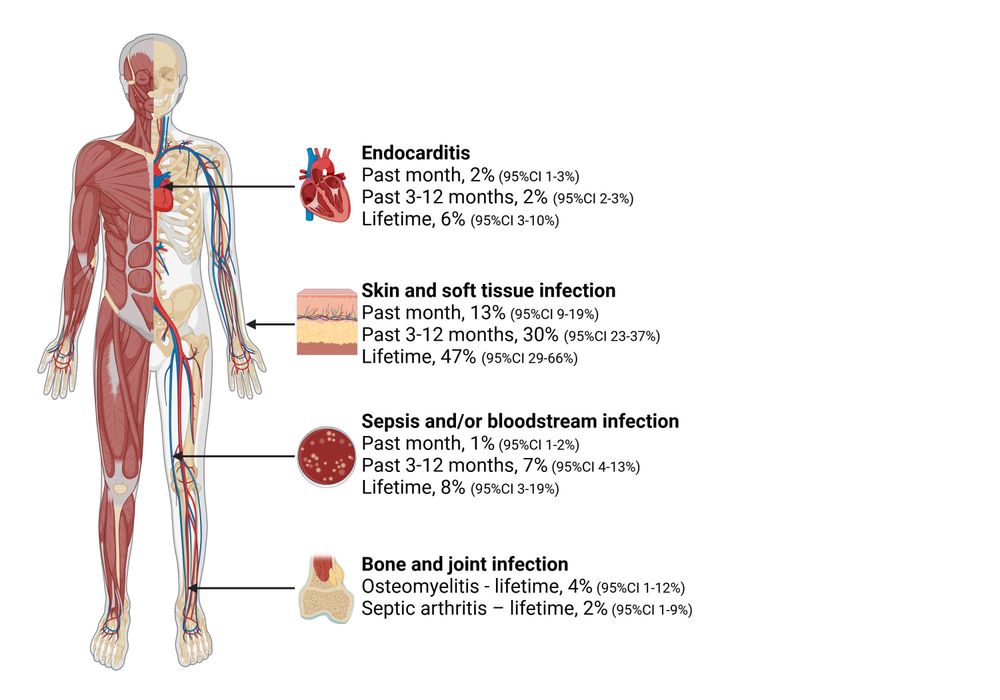
🧪 ISA prophylaxis in 991 patients (69.9% with AML/MDS) showed 7% bIFI incidence (95% CI, 4%-12%). Common pathogens: Aspergillus (43.1%), Candida (22.4%). Mortality >50% in most studies.##idsky
Incidence of Breakthrough Fungal Infections in Patients With Isavuconazole Prophylaxis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Isavuconazole (ISA) is a newer triazole that has activity against most mold species and has been utilized for prophylaxis as well as treatment in patients with hematologic malignancies (HM) and hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT). However, several studies have documented breakthrough invasive fungal infections (bIFIs). Thus, we conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to investigate the incidence of bIFIs among patients receiving ISA prophylaxis.MethodsWe conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of the published literature using the concept of ISA, HSCT, and HM from 5 search engines. In patients with HSCT and HM, the pooled incidence of bIFI while undergoing ISA prophylaxis was calculated via the DerSimonian-Laird random effect model.ResultsThe systematic review and meta-analysis included 35 and 19 studies, respectively. In total, 991 patients were identified as using ISA prophylaxis, and the majority had either acute myeloid leukemia or myelodysplastic syndrome (69.9%). The pooled incidence of proven/probable bIFI was 7% (95% CI, 4%–12%, I2 = 55%). The most common pathogen was Aspergillus species (43.1%), followed by Candida (22.4%) and Mucorales (12.1%). In 19 studies, mortality rates were documented and ranged between 0% and 100%; the majority of which were >50%.ConclusionsIn patients with HM or HSCT, we found a high incidence of bIFI while undergoing ISA prophylaxis, with high mortality. Given the lack of randomized clinical trials evaluating ISA in this indication, its role in prophylaxis remains unclear.
academic.oup.com
Reposted by Shivan Shah
Springer Medicine
@springermedicine.com
· Apr 13

What intensivists need to know about cytomegalovirus infection in immunocompromised ICU patients
Patients with overt immunosuppression are at risk of cytomegalovirus infection, which can lead to, or develop during, ICU admission. Learn more about its broad clinical presentations, risk factors…
buff.ly
Shivan Shah
@idoncology.bsky.social
· Apr 6
Infectious Complications in Patients Treated with T-cell Engagers as Cancer Immunotherapies, A Descriptive Study from the REISAMIC Registry
✅ Just Accepted
#IDSky
✅ Just Accepted
#IDSky

Infectious Complications in Patients Treated with T-cell Engagers as Cancer Immunotherapies, A Descriptive Study from the REISAMIC Registry
We investigated infectious complications and the associated risk factors in 181 patients undergoing T-cell engagers for malignancies. Infections were primarily observed in patients with hematological diseases or heavily pre-treated. Mortality due to infectious complications was 2.8%. Concomitant medications with corticosteroids or tocilizumab did not significantly impact the incidence of infections.
doi.org
Reposted by Shivan Shah
670rv
@670rv.bsky.social
· Mar 30

Deficient Generation of Spike-Specific Long-Lived Plasma Cells in the Bone Marrow After Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection
By studying the bone marrow aspiration samples of 20 individuals with prior coronavirus disease 2019, we showed deficient generation of spike-specific long
academic.oup.com
Shivan Shah
@idoncology.bsky.social
· Mar 25
Epidemiology, Risk Factors and Outcome of Neutropenic Enterocolitis in Onco-Hematological Patients according to Chemotherapy Regimen
✅ Just Accepted
#IDSky
✅ Just Accepted
#IDSky

Epidemiology, Risk Factors and Outcome of Neutropenic Enterocolitis in Onco-Hematological Patients according to Chemotherapy Regimen
While neutropenic enterocolitis (NEC) is a well-known life-threatening complication during intensive chemotherapy, its incidence, impact and outcome on specific at-risk populations remain ill-defined.
doi.org
Reposted by Shivan Shah
Reposted by Shivan Shah
Jake Scott, MD
@jakescottmd.bsky.social
· Mar 13
Reposted by Shivan Shah
Shivan Shah
@idoncology.bsky.social
· Mar 11

Strains of <i>Aspergillus fumigatus</i> Five Times More Likely To Acquire Resistance to Antifungals
Researchers have identified strains of one of the world's most dangerous pathogens that are five times more likely to acquire antifungal resistance.
www.technologynetworks.com
Shivan Shah
@idoncology.bsky.social
· Mar 5
RBL (Rebyota) is FDA-approved for rCDI. In a study of 793, 141 were immunocompromised. TEAEs: 44.7% (immunocompromised) vs. 48.0%. Success: 75.7% (8w), 88.7% (6m). Safe & effective! 💊✨##idsky
Safety and Efficacy of Fecal Microbiota, Live-jslm, in Preventing Recurrent Clostridioides difficile Infection in Mildly to Moderately Immunocompromised Participants in the Phase 3 PUNCH CD3-OLS Study
Fecal microbiota, live-jslm (RBL; Rebyota), is the first FDA-approved, single-dose, microbiota-based live biotherapeutic to prevent recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection (rCDI) in adults following standard-of-care antimicrobials. Patients who are immunocompromised are often considered at higher risk for CDI including recurrence compared to those who are immunocompetent. This subgroup analysis of PUNCH CD3-OLS (NCT03931941) evaluated RBL safety and efficacy in participants with rCDI who were considered mildly to moderately immunocompromised.MethodsParticipants with rCDI who had immunocompromising conditions and/or were taking immunosuppressive medications were included. Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were collected for up to 6 months following RBL administration. Efficacy outcomes included treatment success at 8 weeks and sustained clinical response at 6 months.ResultsOverall, 793 participants were enrolled in PUNCH CD3-OLS and 697 received RBL; 141 were included in the immunocompromised subgroup. TEAEs within 8 weeks were reported by 44.7% and 48.0% of participants in the immunocompromised and non-immunocompromised subgroups, respectively; most events were mild or moderate gastrointestinal disorders. Serious TEAEs within 8 weeks were reported by 4.3% and 3.8% of participants in the immunocompromised and non-immunocompromised subgroups, respectively. No RBL-related systemic infections occurred. In the immunocompromised subgroup, the treatment success rate at 8 weeks was 75.7% and the sustained clinical response rate at 6 months was 88.7%; similar rates were observed in the non-immunocompromised subgroup (73.3% and 91.6%, respectively).ConclusionsResults of this subgroup analysis of PUNCH CD3-OLS suggest that RBL is safe and efficacious for the prevention of rCDI in participants with mild-to-moderate immunocompromising conditions.Trial registrationNCT03931941
academic.oup.com
Shivan Shah
@idoncology.bsky.social
· Mar 4
Levofloxacin to prevent bacterial infection in patients with acute myeloid leukemia treated by venetoclax and azacitidine: a Toulouse-Bordeaux DATAML registry study
✅ Just Accepted
#IDSky
✅ Just Accepted
#IDSky

Levofloxacin to prevent bacterial infection in patients with acute myeloid leukemia treated by venetoclax and azacitidine: a Toulouse-Bordeaux DATAML registry study
Antibiotic prophylaxis for patients with cancer remains a controversial issue and is not broadly recommended for hematological malignancies. The venetoclax (VEN) and azacitidine (AZA) combination allows for high rates of complete remission in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) but enhances the incidence of febrile neutropenia (FN) compared to AZA alone, making primary antibiotic prophylaxis a relevant question.
buff.ly
Reposted by Shivan Shah
After years of falsely claiming that MMR vaccines cause autism, RFK Jr. has published a new op-ed on Fox’s website encouraging people to get the vaccine amid a measles outbreak that has already resulted in the death of a school-aged child.


Shivan Shah
@idoncology.bsky.social
· Mar 1
Shivan Shah
@idoncology.bsky.social
· Mar 1

Inpatient Antibiotic Stewardship Interventions in the Adult Oncology and Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Population: A Review of the Literature - Kelly E. Pillinger, Jeannette Bouchard, Sarah T. Wi...
Objective: To review the use of antibiotic stewardship interventions in the adult oncology and hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) populations. Data Source...
journals.sagepub.com
Shivan Shah
@idoncology.bsky.social
· Mar 1