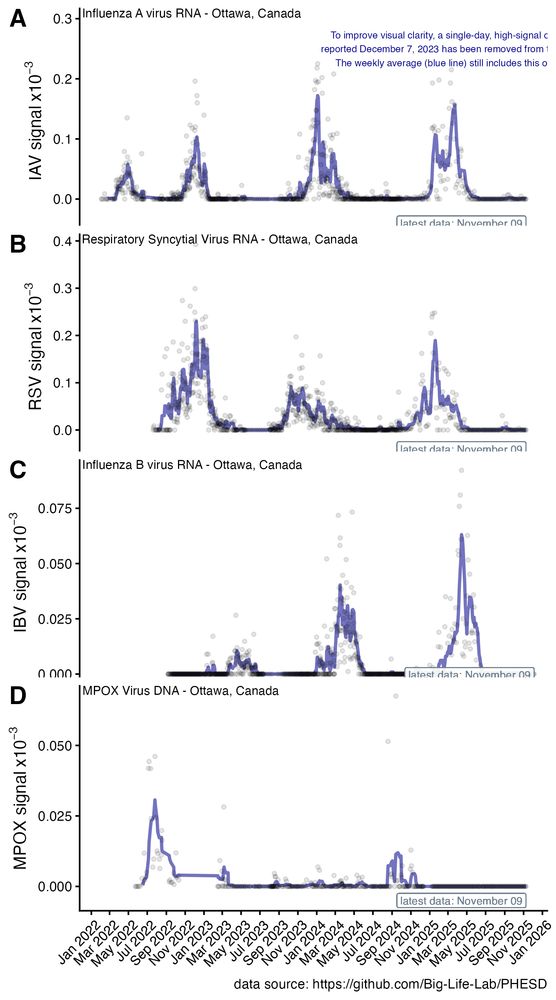
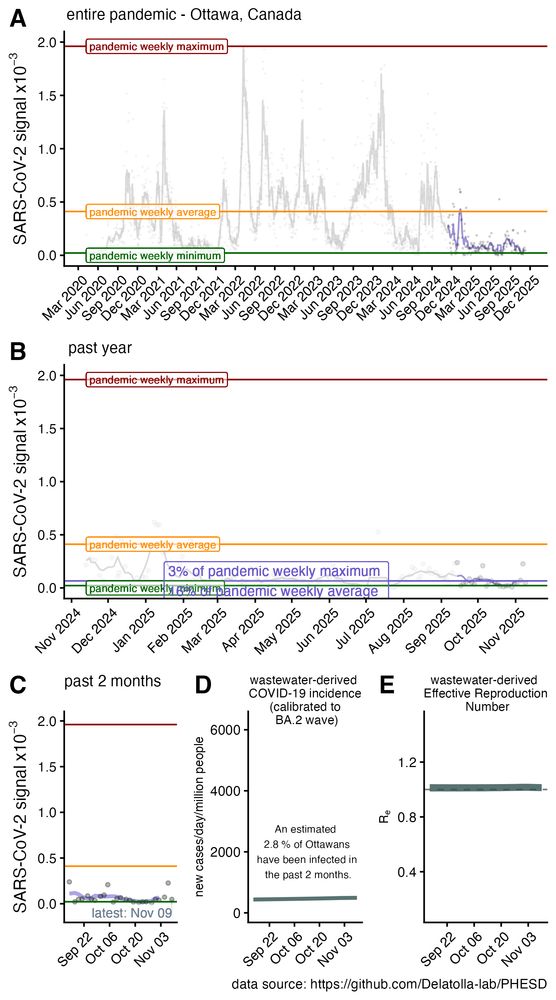
Let's focus on what this means in Ottawa wastewater this past year.
Top: Separated N1 and N2 signals in Ottawa wastewater.
Middle: z-score (N1 vs N2) - negative deviation suggests N1 underestimation.
Bottom: mutation burden in clinical genomes.

Let's focus on what this means in Ottawa wastewater this past year.
Top: Separated N1 and N2 signals in Ottawa wastewater.
Middle: z-score (N1 vs N2) - negative deviation suggests N1 underestimation.
Bottom: mutation burden in clinical genomes.
Looking at it as mutational burden over time.
Across N1+N2, burden is now the highest seen (>2 mutations on average). Yellow marks weeks with <50 sequences. Remember these are clinical seqs based on global *OPEN* data (Genbank) and misses Canadian seqs. But Ottawa tends to follow the trend.

Looking at it as mutational burden over time.
Across N1+N2, burden is now the highest seen (>2 mutations on average). Yellow marks weeks with <50 sequences. Remember these are clinical seqs based on global *OPEN* data (Genbank) and misses Canadian seqs. But Ottawa tends to follow the trend.
Now N2 locus mutations.
A mutation near the start of the forward primer is rising due to a new variant. Its position likely limits impact on assay sensitivity, but it’s something to watch.
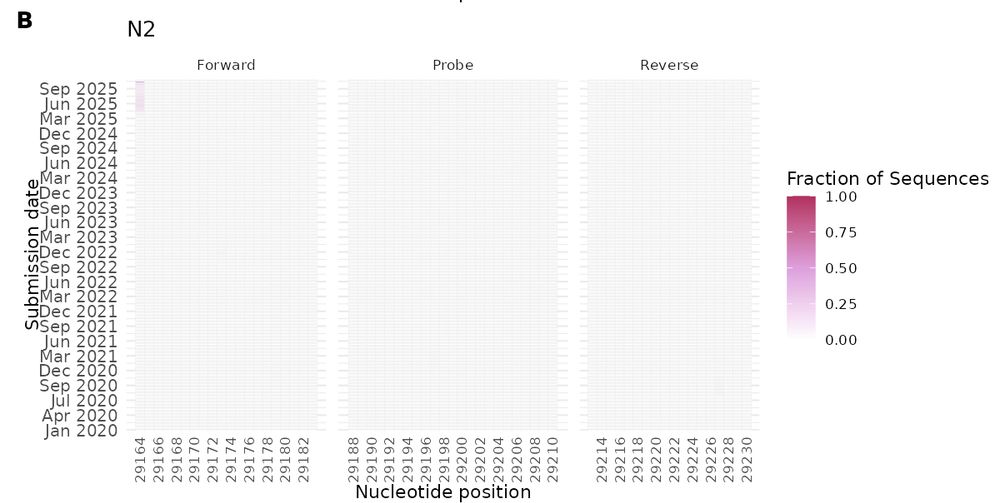
Now N2 locus mutations.
A mutation near the start of the forward primer is rising due to a new variant. Its position likely limits impact on assay sensitivity, but it’s something to watch.
Let's look at the N1 locus.
N1 has gained mutations over the pandemic, especially at nt28311. Researchers have shown that this can slightly lower N1 signal but the effect is small. New mutations have also appeared recently.

Let's look at the N1 locus.
N1 has gained mutations over the pandemic, especially at nt28311. Researchers have shown that this can slightly lower N1 signal but the effect is small. New mutations have also appeared recently.