This was a true team effort with @domenicnarducci.bsky.social, Simon Grosse-Holz,
@jessematthias.bsky.social & @andersshansen.bsky.social. I’m grateful and proud to have worked together. Huge thanks to AICF for their fellowship support. Check out the preprint:
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

This was a true team effort with @domenicnarducci.bsky.social, Simon Grosse-Holz,
@jessematthias.bsky.social & @andersshansen.bsky.social. I’m grateful and proud to have worked together. Huge thanks to AICF for their fellowship support. Check out the preprint:
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
However, as distance increases search times become progressively more challenging. At ~1µm (1-3 Mb), EP can take ~5-24 h to randomly find each other – potentially too long for a cell cycle → distant EP need help (e.g. loop extrusion)
However, as distance increases search times become progressively more challenging. At ~1µm (1-3 Mb), EP can take ~5-24 h to randomly find each other – potentially too long for a cell cycle → distant EP need help (e.g. loop extrusion)
We ran simulations to estimate EP search times based on 1) measured subdiffusion, 2) physical/genomic distance. Within 300nm (~<200 kb), a gene can find 1000s of enhancers in minutes. Such encounters can’t be selective → EP selectivity needs other mechanisms, e.g. biochemical
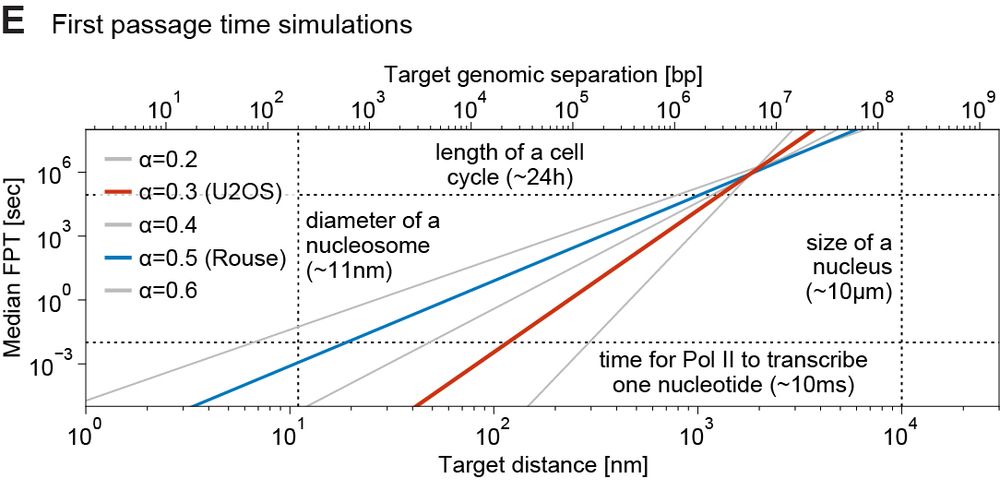
We ran simulations to estimate EP search times based on 1) measured subdiffusion, 2) physical/genomic distance. Within 300nm (~<200 kb), a gene can find 1000s of enhancers in minutes. Such encounters can’t be selective → EP selectivity needs other mechanisms, e.g. biochemical
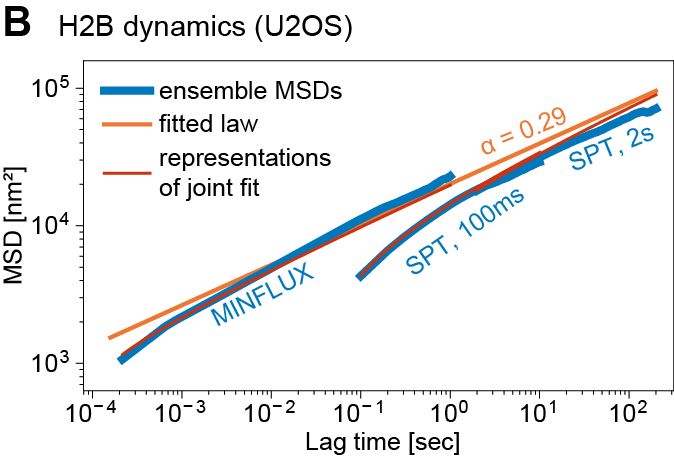
Such fast and long chromatin tracking is key to understanding how distal genomic elements (e.g. enhancers and promoters – EP) find each other. We found chromatin is highly subdiffusive (α ~ 0.3) -> loci are great at exploring the neighborhoods but rarely reach distant regions
Such fast and long chromatin tracking is key to understanding how distal genomic elements (e.g. enhancers and promoters – EP) find each other. We found chromatin is highly subdiffusive (α ~ 0.3) -> loci are great at exploring the neighborhoods but rarely reach distant regions

