I am really excited to share our recently published manuscript, where we tried to contribute to addressing this question!
🌱https://tinyurl.com/2vz23ck6


Plant pathology community at @bspp.bsky.social and @britmycolsoc.org.uk please take the time to complete the Phytopathogen Genomics Resources Survey:-
🔗 zurl.co/gKjC1
Your input is important for FungiDB/@veupathdb.org
& Ensembl @ebi.embl.org.

Plant pathology community at @bspp.bsky.social and @britmycolsoc.org.uk please take the time to complete the Phytopathogen Genomics Resources Survey:-
🔗 zurl.co/gKjC1
Your input is important for FungiDB/@veupathdb.org
& Ensembl @ebi.embl.org.
dx.plos.org/10.1371/jour...

dx.plos.org/10.1371/jour...


➡️ ufr.link/dataplant-foerderung
@fz-juelich.de

➡️ ufr.link/dataplant-foerderung
@fz-juelich.de
www.science.org/doi/full/10....
#ScienceAdvances #PlantScience #IDRs
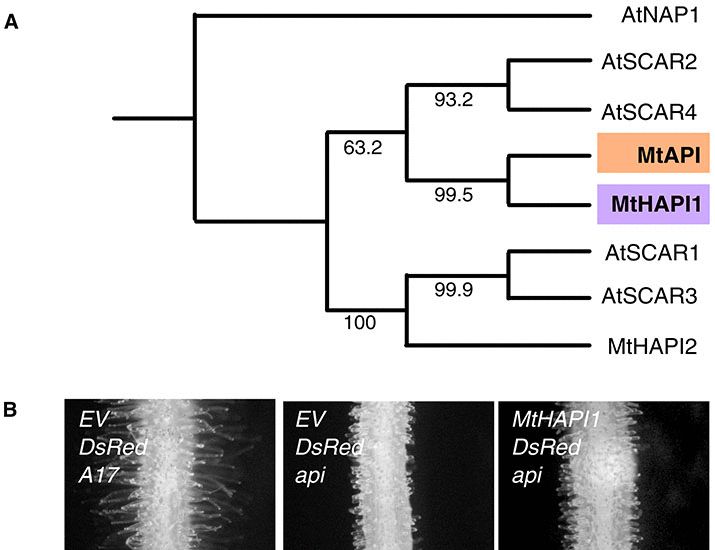
www.science.org/doi/full/10....
#ScienceAdvances #PlantScience #IDRs
academic.oup.com/mbe/article/...
and A. thaliana academic.oup.com/plcell/artic...

academic.oup.com/mbe/article/...
and A. thaliana academic.oup.com/plcell/artic...
🧑🔬 Shideh Mojerlou, @schwessinger.bsky.social, Julian Rodriguez-Algaba
📔 @plos.org Pathogens
🔗 journals.plos.org/plospathogen...
#️⃣ #PlantScience #PlantImmunity

🧑🔬 Shideh Mojerlou, @schwessinger.bsky.social, Julian Rodriguez-Algaba
📔 @plos.org Pathogens
🔗 journals.plos.org/plospathogen...
#️⃣ #PlantScience #PlantImmunity

2025 marks the 20th anniversary of filamentous plant pathogen genomics. In our new review, we present lessons we learned over the past 2 decades and discuss the future of plant pathogen genomics. Take a first look!
apsjournals.apsnet.org/doi/10.1094/...


They are also highly difficult to study….
It is truely remarkable how well described the barley and what powdery mildews are.
Here you find an overview on the current knowledge and summary of great resources. Enjoy!
👇
🌱🌾Technical Advances Drive the Molecular Understanding of Effectors from Wheat and Barley Powdery Mildew Fungi doi.org/10.1094/MPMI...
@izzysaurlab.bsky.social

They are also highly difficult to study….
It is truely remarkable how well described the barley and what powdery mildews are.
Here you find an overview on the current knowledge and summary of great resources. Enjoy!
🧑🔬 Yueqiang Leng, Florian Kümmel, Paul Schulze-Lefert, Shaobin Zhong, et al.
📔 @newphyt.bsky.social
🔗 nph.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/...
#️⃣ #PlantScience #PlantImmunity #Barley
🧑🔬 Yueqiang Leng, Florian Kümmel, Paul Schulze-Lefert, Shaobin Zhong, et al.
📔 @newphyt.bsky.social
🔗 nph.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/...
#️⃣ #PlantScience #PlantImmunity #Barley
Read more about how SBT5.2 releases and inactivates flg22: www.nature.com/articles/s41...
rdcu.be/d1UsT
Congratulations to all involved!
#PlantImmunity #PlantPathology #PlantChemeticsLab

Read more about how SBT5.2 releases and inactivates flg22: www.nature.com/articles/s41...
rdcu.be/d1UsT
Congratulations to all involved!
#PlantImmunity #PlantPathology #PlantChemeticsLab
Soohyun Oh et al. 2024 rdcu.be/d1f33
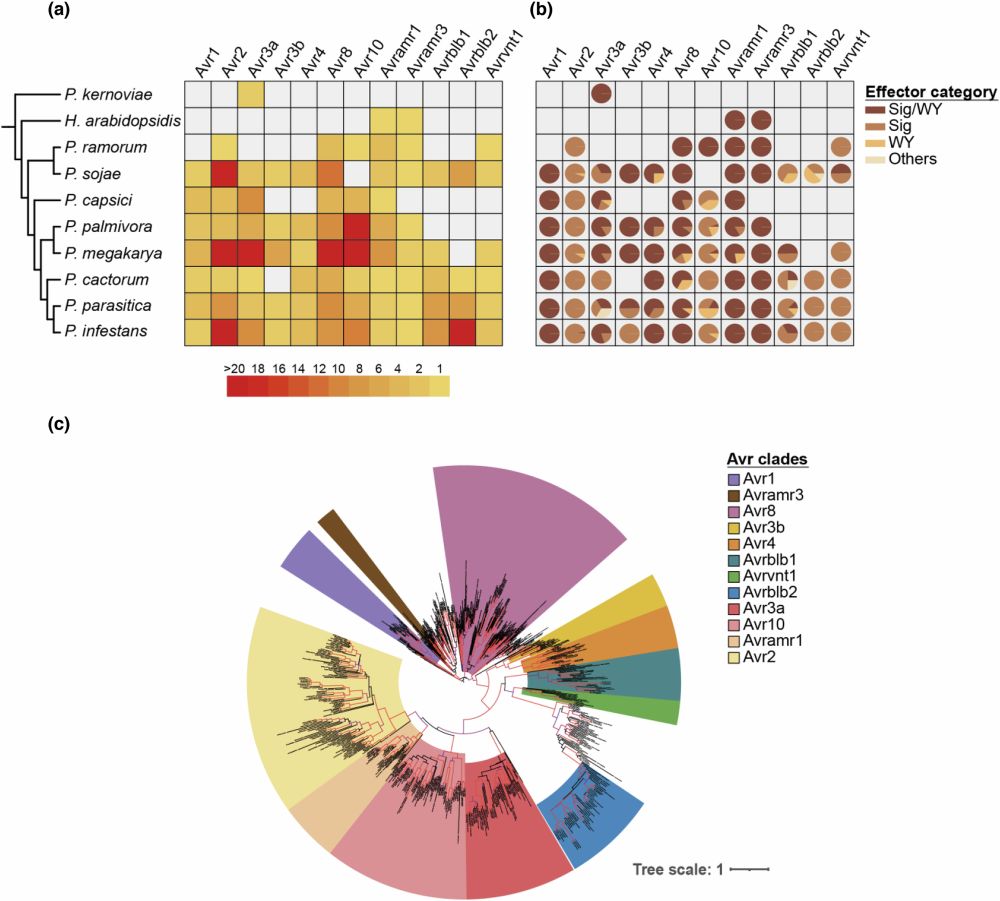
Soohyun Oh et al. 2024 rdcu.be/d1f33
doi.org/10.1371/jour...

doi.org/10.1371/jour...
PTGS is dispensable for the initiation of epigenetic silencing of an active transposon in Arabidopsis.
www.embopress.org/doi/full/10....

PTGS is dispensable for the initiation of epigenetic silencing of an active transposon in Arabidopsis.
www.embopress.org/doi/full/10....
#PlantScience

#PlantScience
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

