#Schizophrenia #Genetics #Psychiatry #PrecisionMedicine #MetaAnalysis
#Schizophrenia #Genetics #Psychiatry #PrecisionMedicine #MetaAnalysis
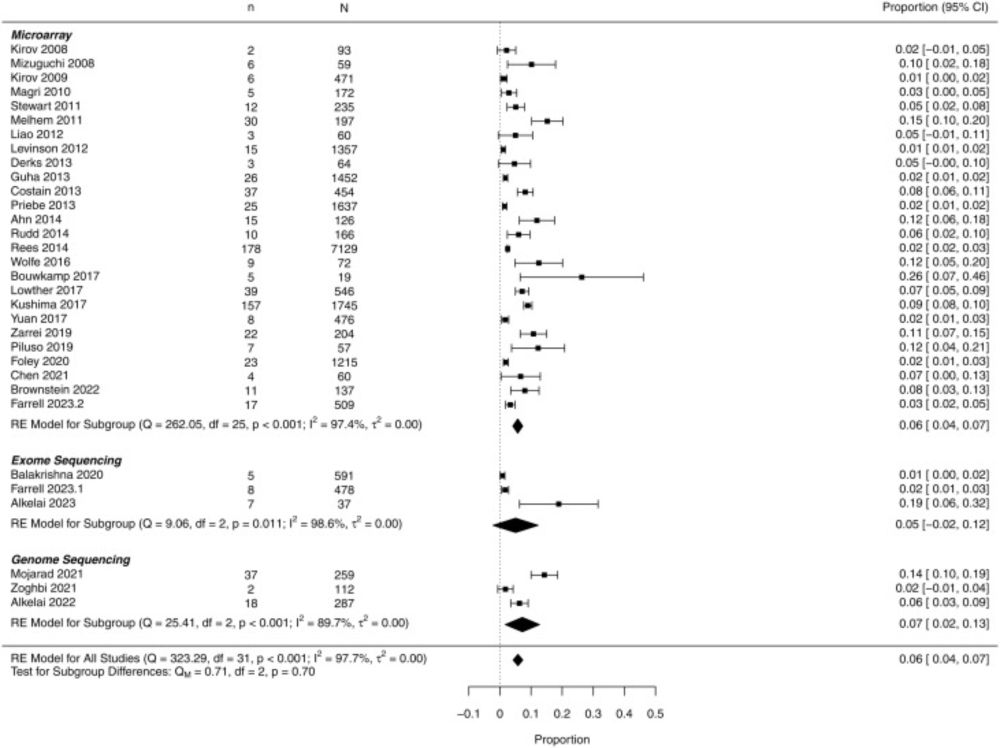
By platform: CMA ~6%, ES ~5%, GS ~7%. (Note: confidence intervals overlap; study methods & reporting varied.) This suggests ~1 in 17 patients may receive clinically informative findings.
By platform: CMA ~6%, ES ~5%, GS ~7%. (Note: confidence intervals overlap; study methods & reporting varied.) This suggests ~1 in 17 patients may receive clinically informative findings.
Dr. Julian Martinez-Agosto (UCLA)
@rarediseasectn.bsky.social @rarediseasesint.bsky.social
@autismspeaks.org
@simonsfoundation.org
Dr. Julian Martinez-Agosto (UCLA)
@rarediseasectn.bsky.social @rarediseasesint.bsky.social
@autismspeaks.org
@simonsfoundation.org
Sensory profiles may provide a window into genetic pathogenicity across OGIDs, but variant scores alone aren’t robust prognostic tools.
Individualized neurobehavioral assessment remains essential for diagnosis, prognosis, and intervention planning.
Sensory profiles may provide a window into genetic pathogenicity across OGIDs, but variant scores alone aren’t robust prognostic tools.
Individualized neurobehavioral assessment remains essential for diagnosis, prognosis, and intervention planning.
Decision tree using behavioral + medical features (e.g., neonatal teeth for PHTS) performed above chance (CV relative error ≈0.67).
Behavioral-only tree also above chance, showing the strength of detailed phenotyping.
Decision tree using behavioral + medical features (e.g., neonatal teeth for PHTS) performed above chance (CV relative error ≈0.67).
Behavioral-only tree also above chance, showing the strength of detailed phenotyping.
• CADD ↗ SSP Low Energy & SSP Total
• CADD ↘ SRS-2 Total T
These were the most consistently stable correlations after 1,000 bootstrap resamples.
• CADD ↗ SSP Low Energy & SSP Total
• CADD ↘ SRS-2 Total T
These were the most consistently stable correlations after 1,000 bootstrap resamples.
• CADD ↗ SSP Low Energy (r=0.72)
• CADD ↘ SRS-2 Total T (r=−0.64)
(both bootstrap-stable; p<0.05 uncorrected)
• CADD ↗ SSP Low Energy (r=0.72)
• CADD ↘ SRS-2 Total T (r=−0.64)
(both bootstrap-stable; p<0.05 uncorrected)
• REVEL ↗ SSP Auditory Filtering (r=0.77)
• AlphaMissense ↗ SSP Visual/Auditory Sensitivity (r=0.74)
• REVEL ↘ DCDQ Control During Movement (r=−0.80)
(all bootstrap-supported; p<0.05 uncorrected)
• REVEL ↗ SSP Auditory Filtering (r=0.77)
• AlphaMissense ↗ SSP Visual/Auditory Sensitivity (r=0.74)
• REVEL ↘ DCDQ Control During Movement (r=−0.80)
(all bootstrap-supported; p<0.05 uncorrected)
Cross-cohort correlations were limited/inconsistent.
CADD showed the most stable associations—especially with sensory processing—supporting the need for deep phenotyping beyond variant scores alone.
Cross-cohort correlations were limited/inconsistent.
CADD showed the most stable associations—especially with sensory processing—supporting the need for deep phenotyping beyond variant scores alone.
PTEN phosphatase-domain variants → more severe social & executive deficits vs C2-domain variants.
MTOR domain differences (FAT vs PI3K) not significant (sample-size limited in SKS).
PTEN phosphatase-domain variants → more severe social & executive deficits vs C2-domain variants.
MTOR domain differences (FAT vs PI3K) not significant (sample-size limited in SKS).

