

This means forest ecosystems are being reshaped faster than we expected, requiring adaptive management strategies.
This means forest ecosystems are being reshaped faster than we expected, requiring adaptive management strategies.
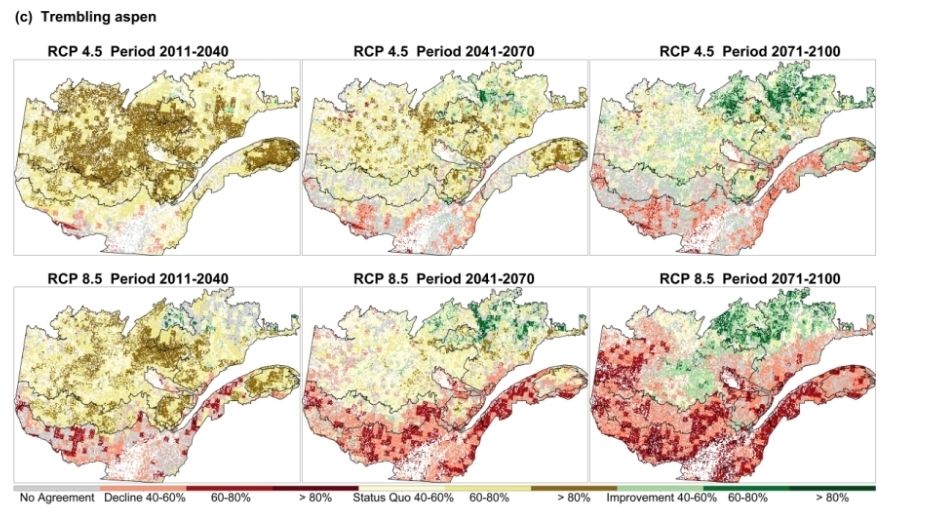
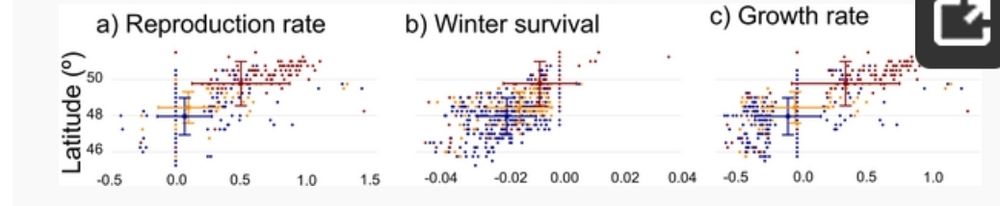
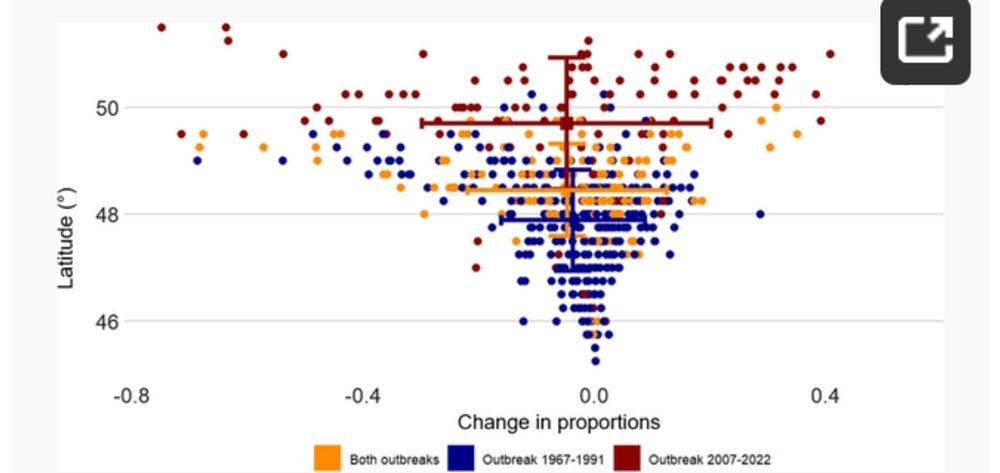
📍 +68 km northward shift of suitable climate conditions (up to 200 km in some areas!)
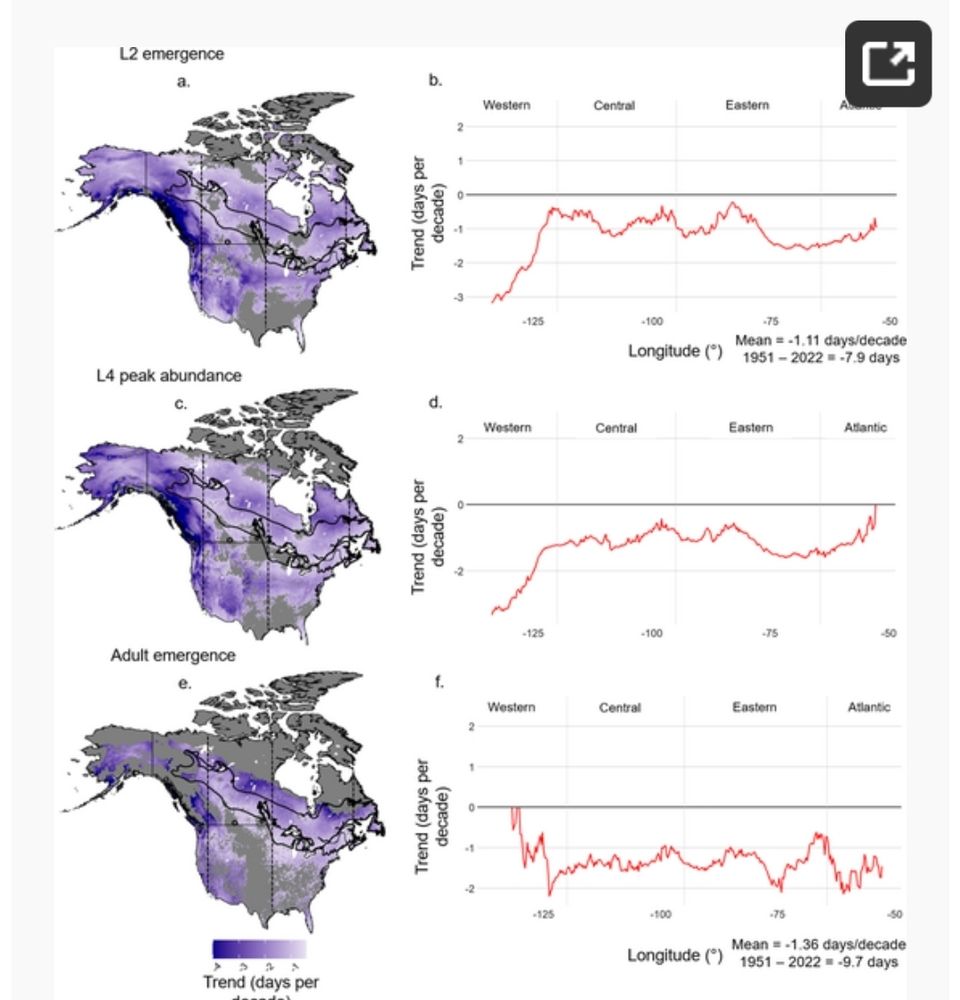
⏳ Earlier phenological events & higher reproduction rates in the north
❄️ Increased winter mortality in the south due to warmer temperatures
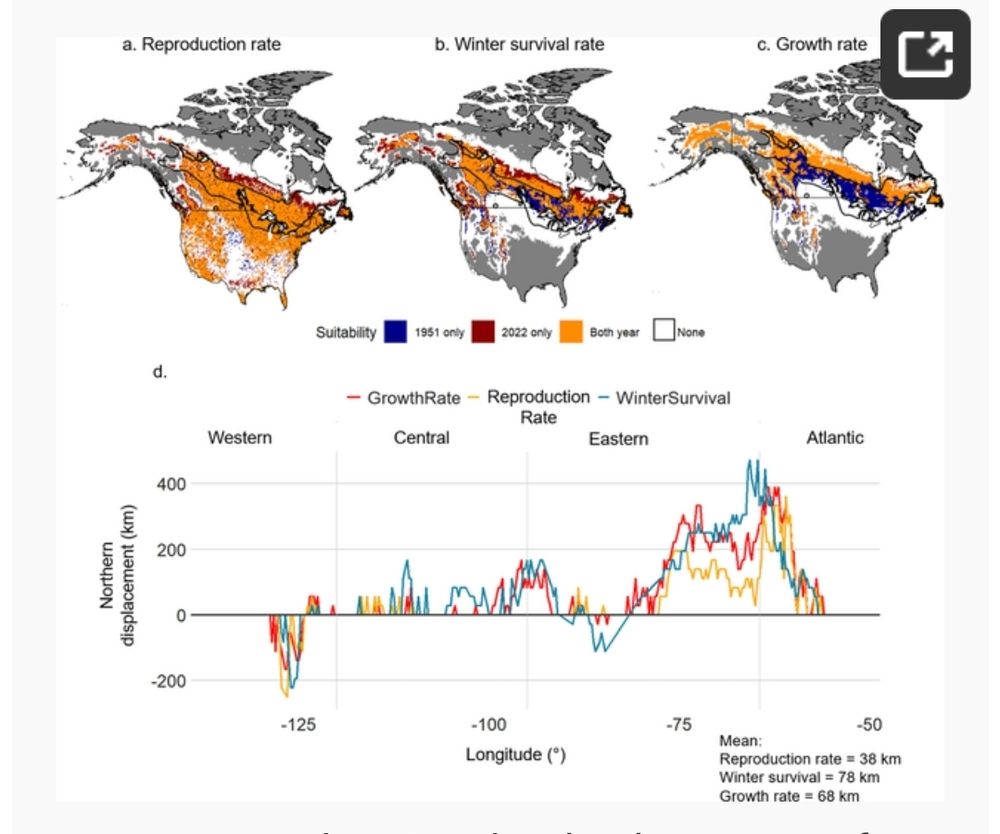
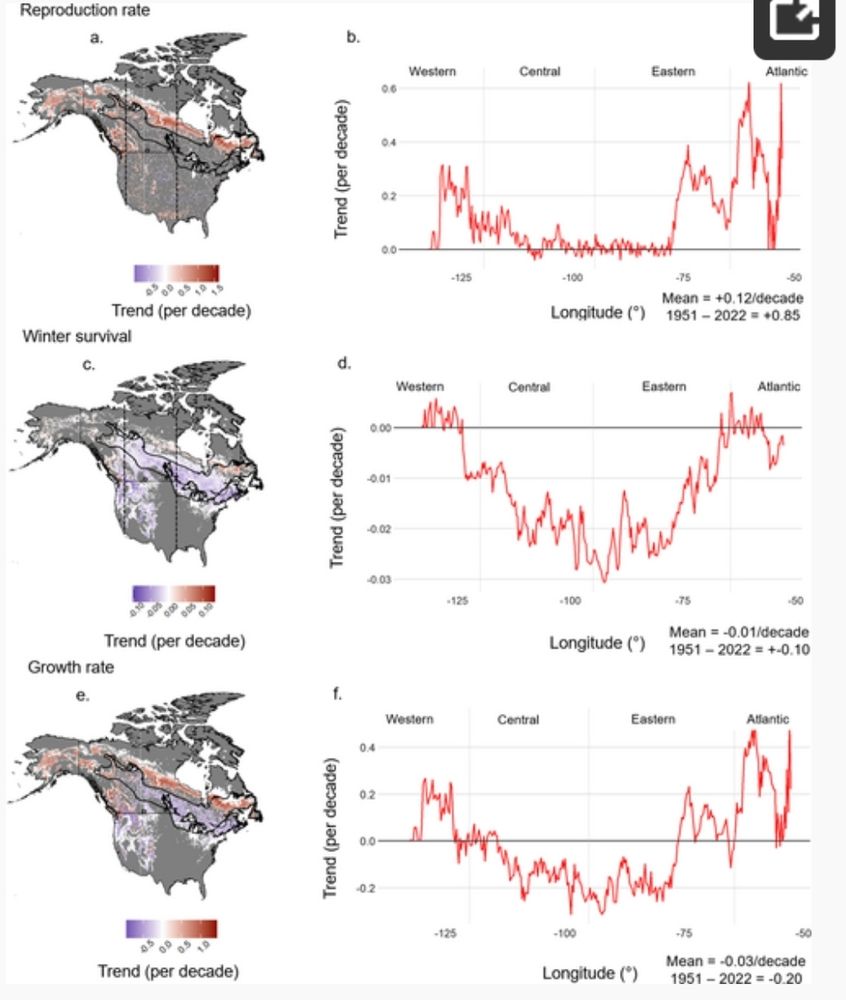
📍 +68 km northward shift of suitable climate conditions (up to 200 km in some areas!)
⏳ Earlier phenological events & higher reproduction rates in the north
❄️ Increased winter mortality in the south due to warmer temperatures
#ClimateChange is reshaping forest ecosystems, and the spruce budworm (Choristoneura fumiferana), a major boreal forest defoliator, is feeling the heat! 🔥
Our latest study in PLOS Climate reveals some striking trends. 🧵👇

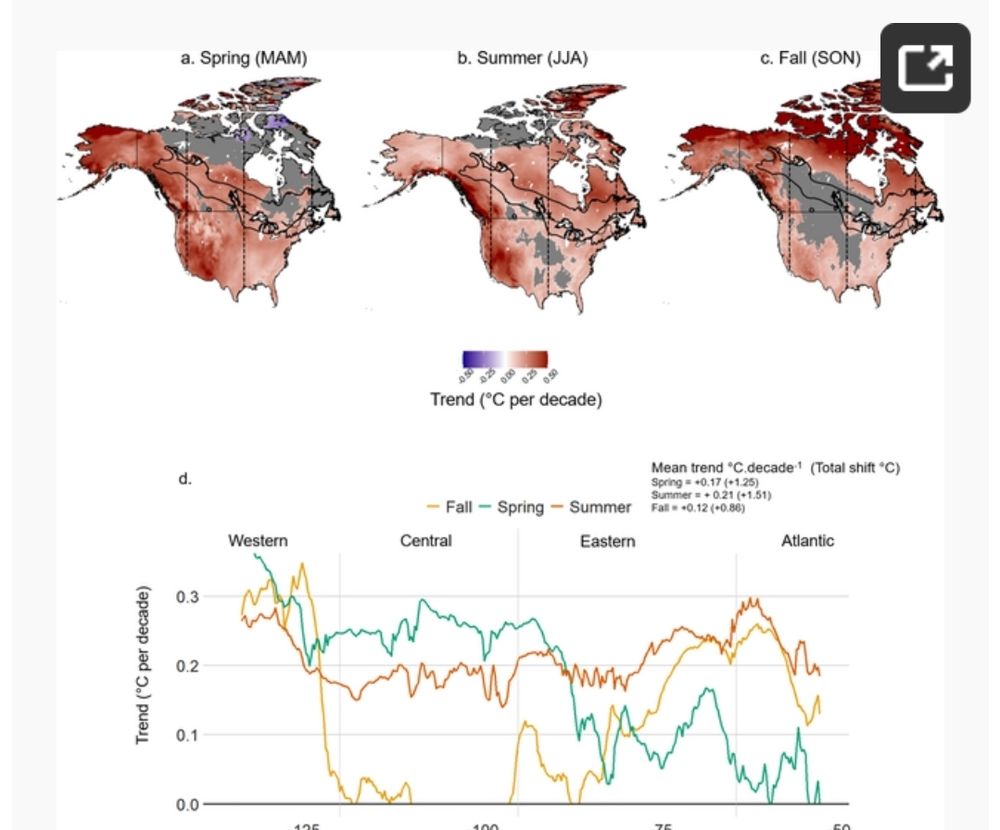
#ClimateChange is reshaping forest ecosystems, and the spruce budworm (Choristoneura fumiferana), a major boreal forest defoliator, is feeling the heat! 🔥
Our latest study in PLOS Climate reveals some striking trends. 🧵👇
Fire exclusion had minimal influence on vegetation composition, indicating that mesophication unfolds over longer timescales.
Modest climate change impacts (1830–2000) pale in comparison to timber harvesting, but future climate shifts could have stronger effects.

Fire exclusion had minimal influence on vegetation composition, indicating that mesophication unfolds over longer timescales.
Modest climate change impacts (1830–2000) pale in comparison to timber harvesting, but future climate shifts could have stronger effects.
Timber harvesting had the most significant impact on forest dynamics:
🌳 Without harvesting, pre-settlement species composition & traits were largely maintained.
🔥 Fire shifts increased aspen, but their effects were secondary.
🌡️ Climate change had a minor role

Timber harvesting had the most significant impact on forest dynamics:
🌳 Without harvesting, pre-settlement species composition & traits were largely maintained.
🔥 Fire shifts increased aspen, but their effects were secondary.
🌡️ Climate change had a minor role
We used the #LANDIS-II forest landscape model for retrospective analysis (1830–2000), integrating:
🔥 Historical #fire reconstructions
🌡️ #Climate reanalysis data
🌲 #Timber harvest records
Counterfactual scenarios helped isolate the impact of each factor.

We used the #LANDIS-II forest landscape model for retrospective analysis (1830–2000), integrating:
🔥 Historical #fire reconstructions
🌡️ #Climate reanalysis data
🌲 #Timber harvest records
Counterfactual scenarios helped isolate the impact of each factor.
#Forests in northeastern #NorthAmerica have undergone massive changes since pre-settlement times
🟩 Loss of conifers
🌲 Decline in taxonomic & functional diversity
We aimed to untangle the individual effects of timber harvesting, fire regimes, and climate on these shifts.

#Forests in northeastern #NorthAmerica have undergone massive changes since pre-settlement times
🟩 Loss of conifers
🌲 Decline in taxonomic & functional diversity
We aimed to untangle the individual effects of timber harvesting, fire regimes, and climate on these shifts.




#wx

#wx
Impacts of time since last #wildfire on forest composition and structure of the Lac Hebecourt islands
#uqat

Impacts of time since last #wildfire on forest composition and structure of the Lac Hebecourt islands
#uqat
Follow him at www.instagram.com/mael_boulang...



Follow him at www.instagram.com/mael_boulang...















