https://www.cns.nyu.edu/~saraf/
[email protected]
Different types of tuning diversity reshape population codes in distinct — and beneficial — ways.
Different types of tuning diversity reshape population codes in distinct — and beneficial — ways.
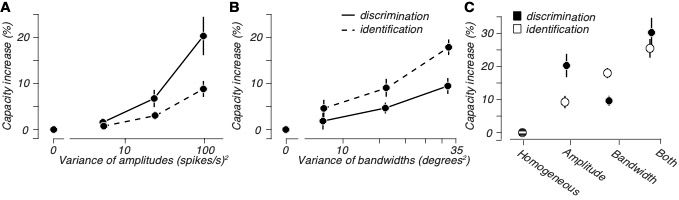
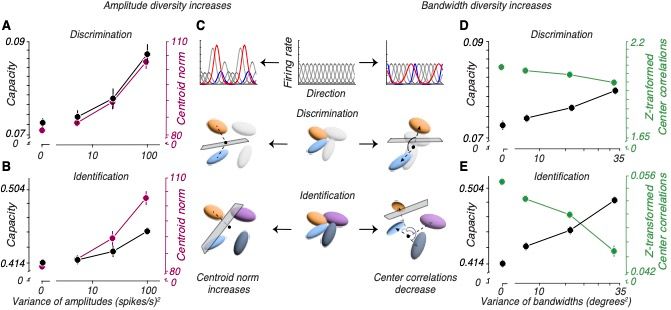
Amp Div: expands distances between the centers of representations for different stimuli
BW Div: decorrelates the centers
Amp Div: expands distances between the centers of representations for different stimuli
BW Div: decorrelates the centers
Different types of tuning diversity reshape population codes in distinct — and beneficial — ways.
Different types of tuning diversity reshape population codes in distinct — and beneficial — ways.



