Paper: arxiv.org/abs/2502.06034
Code: github.com/KempnerInsti...
13/13

Paper: arxiv.org/abs/2502.06034
Code: github.com/KempnerInsti...
13/13
kempnerinstitute.harvard.edu/research/dee...
12/13

kempnerinstitute.harvard.edu/research/dee...
12/13
11/13


11/13
Incredibly, on Multi-MNIST, wave-based models outperformed similarly sized U-Nets, despite having fewer parameters and only local connectivity.
10/13

Incredibly, on Multi-MNIST, wave-based models outperformed similarly sized U-Nets, despite having fewer parameters and only local connectivity.
10/13
9/13
9/13
8/13

8/13
7/13

7/13
We find that wave-based models produce unique dynamics for each shape, resulting in distinct Fourier spectra.
6/13

We find that wave-based models produce unique dynamics for each shape, resulting in distinct Fourier spectra.
6/13
This finding led us to wonder: can we actually learn (via trainable parameters) dynamics for more complex shapes?
5/13
This finding led us to wonder: can we actually learn (via trainable parameters) dynamics for more complex shapes?
5/13
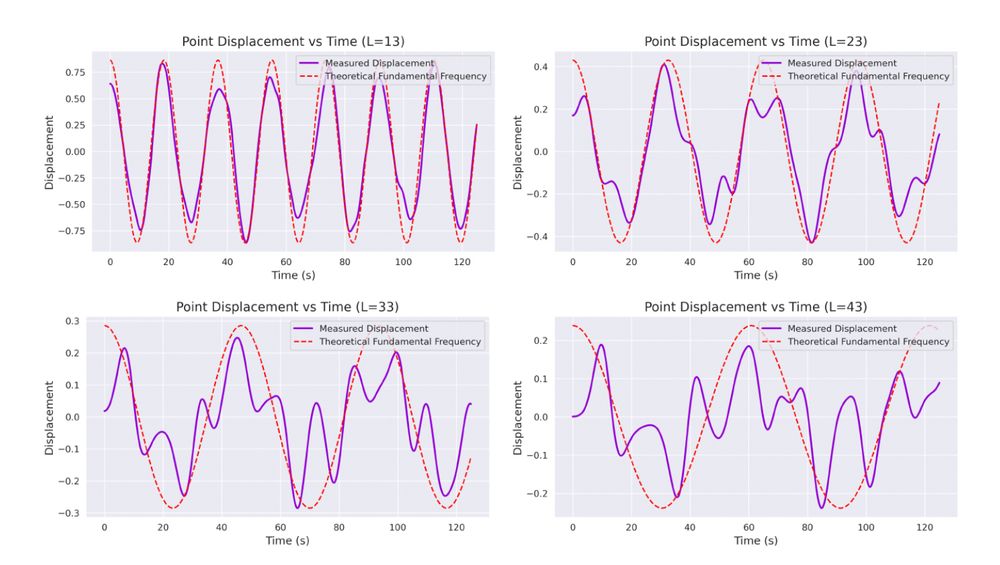
We can see (with fixed RNNs that simulate drums) that different sized drumheads have different dynamics:
4/13


We can see (with fixed RNNs that simulate drums) that different sized drumheads have different dynamics:
4/13
3/13

3/13
Evidence suggests traveling waves could carry this information across space, allowing neurons to “know” what’s happening far away.
2/13

Evidence suggests traveling waves could carry this information across space, allowing neurons to “know” what’s happening far away.
2/13

