
Grateful for funding from the Thiemann Parkinson Foundation, @dfg.de, and many others who made this work possible - not just for the project, but personally for me as well.
Grateful for funding from the Thiemann Parkinson Foundation, @dfg.de, and many others who made this work possible - not just for the project, but personally for me as well.
This was a long-term project developed under @andreashorn.org's guidance, and I couldn’t be more grateful that it marks the conclusion of my time in Boston.
This was a long-term project developed under @andreashorn.org's guidance, and I couldn’t be more grateful that it marks the conclusion of my time in Boston.
To mention just a few colleagues who are here on BlueSky:
@patriciazvarova.bsky.social @bahnebahners.bsky.social @emiddlebrooksmd.bsky.social @jjoutsa.bsky.social @foxmdphd.bsky.social @andreashorn.org
@netstim.org
To mention just a few colleagues who are here on BlueSky:
@patriciazvarova.bsky.social @bahnebahners.bsky.social @emiddlebrooksmd.bsky.social @jjoutsa.bsky.social @foxmdphd.bsky.social @andreashorn.org
@netstim.org
We hope this work helps advance neuromodulation toward guided, symptom-specific treatment.
Full paper: www.nature.com/articles/s41...
We hope this work helps advance neuromodulation toward guided, symptom-specific treatment.
Full paper: www.nature.com/articles/s41...
👉 the dentato-rubro-thalamic tract (DRT).
The best DBS outcomes align closely with its trajectory - regardless of target or disorder.

👉 the dentato-rubro-thalamic tract (DRT).
The best DBS outcomes align closely with its trajectory - regardless of target or disorder.
👉 What influences outcomes after DBS?

👉 What influences outcomes after DBS?
We combined diverse datasets and methods - adding variability.
But this heterogeneity was deliberate, to build a more robust and generalizable network.
And while correlational analysis, the convergence of lesions, DBS, and EMG-fMRI supports causal insight.
We combined diverse datasets and methods - adding variability.
But this heterogeneity was deliberate, to build a more robust and generalizable network.
And while correlational analysis, the convergence of lesions, DBS, and EMG-fMRI supports causal insight.
✅ Different forms of tremor share a common brain network
✅ DBS likely works by modulating this circuit
✅ STN, VIM, GPi may all be access points to the same network
✅ This opens the door to symptom-specific neuromodulation - both invasive and noninvasive
✅ Different forms of tremor share a common brain network
✅ DBS likely works by modulating this circuit
✅ STN, VIM, GPi may all be access points to the same network
✅ This opens the door to symptom-specific neuromodulation - both invasive and noninvasive
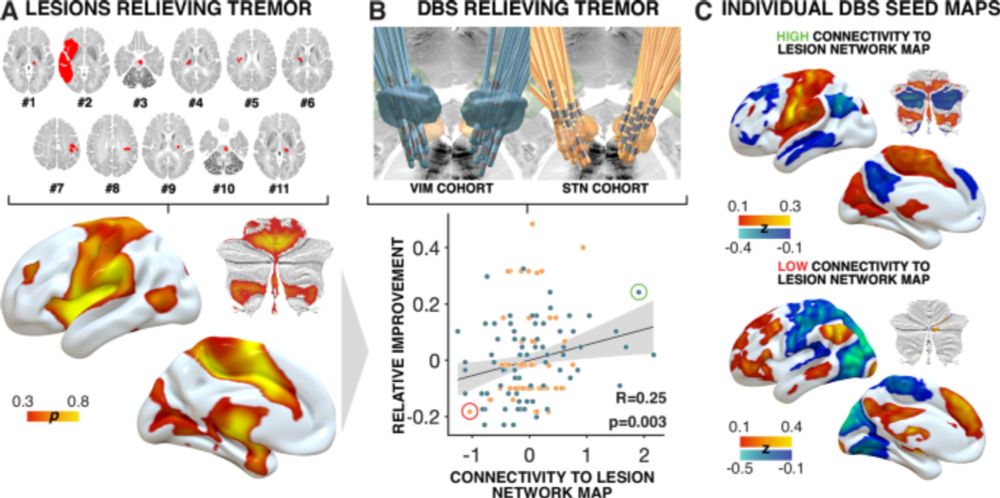
Connectivity between GPi-DBS electrodes and the convergent tremor map explained significant variance in clinical outcomes.

Connectivity between GPi-DBS electrodes and the convergent tremor map explained significant variance in clinical outcomes.
The key test:
Could this convergent map explain tremor outcomes in a new, independent cohort: Parkinson's disease patients with GPi-DBS?
The key test:
Could this convergent map explain tremor outcomes in a new, independent cohort: Parkinson's disease patients with GPi-DBS?
🧠 Based on resting-state fMRI from 1,087 healthy subjects (HCP), 2 mm isotropic voxels
We also replicated results using a Parkinson’s disease-specific connectome from the PPMI cohort. Findings held up across datasets.
🧠 Based on resting-state fMRI from 1,087 healthy subjects (HCP), 2 mm isotropic voxels
We also replicated results using a Parkinson’s disease-specific connectome from the PPMI cohort. Findings held up across datasets.
• Parkinson’s disease patients with subthalamic DBS
• Essential tremor patients with thalamic DBS
Outcome maps from each group could explain outcomes in the other.
Disorder-independent. Target-independent.

• Parkinson’s disease patients with subthalamic DBS
• Essential tremor patients with thalamic DBS
Outcome maps from each group could explain outcomes in the other.
Disorder-independent. Target-independent.
We incorporated a map from the well-known dimmer-switch model of tremor, based on EMG-fMRI:
🔗 academic.oup.com/brain/articl...
Once again, the same core regions emerged:
- Motor cortex
- Motor cerebellum
Three paths. One destination.

We incorporated a map from the well-known dimmer-switch model of tremor, based on EMG-fMRI:
🔗 academic.oup.com/brain/articl...
Once again, the same core regions emerged:
- Motor cortex
- Motor cerebellum
Three paths. One destination.
🔗 doi.org/10.1212/WNL....
This atrophy-based network pointed to cerebellar regions, adding another independent layer of support.

🔗 doi.org/10.1212/WNL....
This atrophy-based network pointed to cerebellar regions, adding another independent layer of support.

As shown by @jjoutsa.bsky.social, these lesions mapped to a distinct functional network:
🔗 doi.org/10.1002/ana....

As shown by @jjoutsa.bsky.social, these lesions mapped to a distinct functional network:
🔗 doi.org/10.1002/ana....
Does a shared tremor treatment network exist across diseases and deep brain stimulation (DBS) targets?
To find out, we combined four independent modalities:
🧠 Lesions
🧠 Atrophy
🧠 EMG-fMRI
🧠 DBS outcomes
Does a shared tremor treatment network exist across diseases and deep brain stimulation (DBS) targets?
To find out, we combined four independent modalities:
🧠 Lesions
🧠 Atrophy
🧠 EMG-fMRI
🧠 DBS outcomes
Read the full study here:
onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/...

Read the full study here:
onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/...
But this cohort is rare: patients who received all three interventions: tDCS, levodopa challenge, and DBS.
That makes these findings hypothesis-generating and worth building on.
But this cohort is rare: patients who received all three interventions: tDCS, levodopa challenge, and DBS.
That makes these findings hypothesis-generating and worth building on.
When we combined both tDCS and levodopa responses in a linear model, they jointly explained a significant amount of the variance in DBS outcomes.

When we combined both tDCS and levodopa responses in a linear model, they jointly explained a significant amount of the variance in DBS outcomes.
(i) Does the levodopa response predict DBS outcome?
(ii) Does it correlate with the tDCS response?
The trends were there - but in this small sample (N = 10), neither reached significance on its own.

(i) Does the levodopa response predict DBS outcome?
(ii) Does it correlate with the tDCS response?
The trends were there - but in this small sample (N = 10), neither reached significance on its own.

