A version of this warhol-inspired image has been in my head almost since we first conceived this Tfh diversity project (many, many years ago) @wehi-research.bsky.social

A version of this warhol-inspired image has been in my head almost since we first conceived this Tfh diversity project (many, many years ago) @wehi-research.bsky.social



This suggested cytokine pathways are a stronger driver of specific heterogeneous Tfh cell phenotypes than pathogen class.

This suggested cytokine pathways are a stronger driver of specific heterogeneous Tfh cell phenotypes than pathogen class.
This allowed us to establish a core Tfh signature that is conserved regardless of pathogen type.

This allowed us to establish a core Tfh signature that is conserved regardless of pathogen type.

We hypothesized that pathogen-specific cues result in functionally distinct Tfh phenotypes with the capacity to tailor B cell responses.

We hypothesized that pathogen-specific cues result in functionally distinct Tfh phenotypes with the capacity to tailor B cell responses.
Check out the Tfh “circle of influence” from @profshanecrotty.bsky.social

Check out the Tfh “circle of influence” from @profshanecrotty.bsky.social
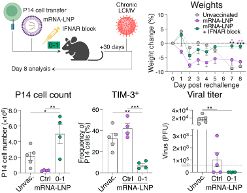
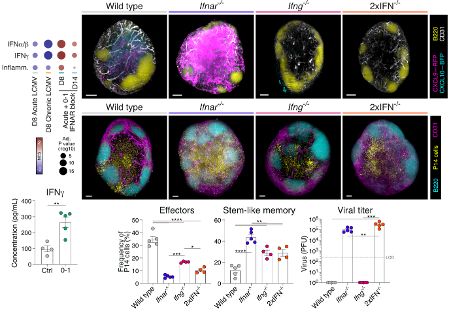
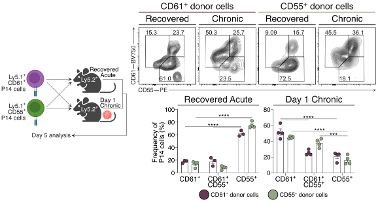
To our surprise, they were increased when IFN-I signaling was inhibited. Yet, CD8+ T cells were retained in the lymph node paracortex due to receptor desensitization.
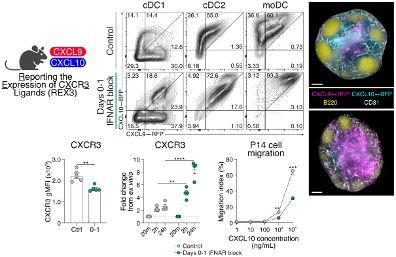
To our surprise, they were increased when IFN-I signaling was inhibited. Yet, CD8+ T cells were retained in the lymph node paracortex due to receptor desensitization.
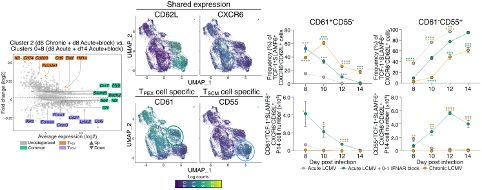
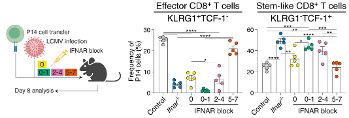
The key here is early and transient IFN-I blockade. While delayed, we see total viral clearance with stem-like CD8+ T cell accumulation being distinct from that seen in chronic infection.

The key here is early and transient IFN-I blockade. While delayed, we see total viral clearance with stem-like CD8+ T cell accumulation being distinct from that seen in chronic infection.
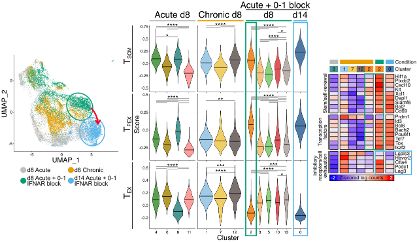
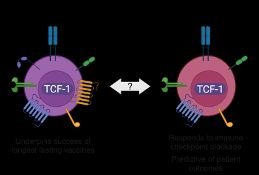
1. Tscm cells – seen in vaccine and acute infection
2. Tpex cells – seen in chronic infection and cancer
But their developmental relationship and how to individually define or promote them is lacking.
1. Tscm cells – seen in vaccine and acute infection
2. Tpex cells – seen in chronic infection and cancer
But their developmental relationship and how to individually define or promote them is lacking.
Feel incredibly proud and privileged to work with this crew @wehi-research.bsky.social
Credits:
Creative vision and execution: @benjbroom.bsky.social
Wardrobe: @brigetteduckworth.bsky.social
Best pose (always): @raymondqin.bsky.social

Feel incredibly proud and privileged to work with this crew @wehi-research.bsky.social
Credits:
Creative vision and execution: @benjbroom.bsky.social
Wardrobe: @brigetteduckworth.bsky.social
Best pose (always): @raymondqin.bsky.social

