

Protein assembly in membranes is crucial yet elusive. Why steer when you can just observe? We introduce a bias-free simulation method that captures the full picture of transmembrane dimerization—free energies, mechanisms, and rates!
pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/...
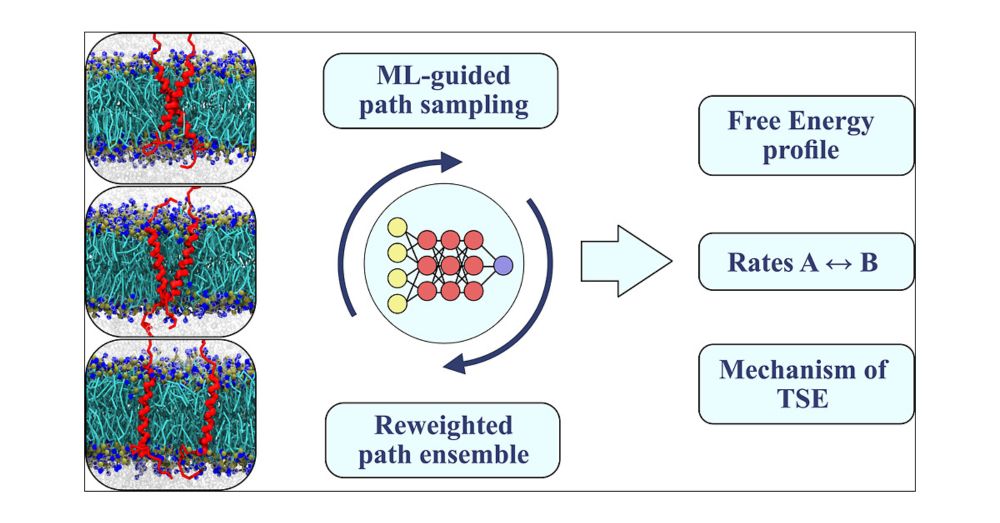
Protein assembly in membranes is crucial yet elusive. Why steer when you can just observe? We introduce a bias-free simulation method that captures the full picture of transmembrane dimerization—free energies, mechanisms, and rates!
pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/...
Here comes my "not so elegant but so far only" solution as a Christmas gift 🎄
1. Build correct structure with glycam.org
2. Reorder and rename atoms to fit CHARMM convention topology from Charmm-gui
3. Use topology & FF files from Charmm-gui with corrected structure
Here comes my "not so elegant but so far only" solution as a Christmas gift 🎄
1. Build correct structure with glycam.org
2. Reorder and rename atoms to fit CHARMM convention topology from Charmm-gui
3. Use topology & FF files from Charmm-gui with corrected structure


