https://sites.socsci.uci.edu/~dagrawa4/
and all the authors who contributed @jeffreypclemens.bsky.social @stanveuger.bsky.social @s-stantcheva.bsky.social @mariusbrulhart.bsky.social @kurtschmidheiny.bsky.social & many others not on here!
and all the authors who contributed @jeffreypclemens.bsky.social @stanveuger.bsky.social @s-stantcheva.bsky.social @mariusbrulhart.bsky.social @kurtschmidheiny.bsky.social & many others not on here!
econtheory.org/ojs/index.ph...
econtheory.org/ojs/index.ph...
Highly recommend the process at
@econtheory.bsky.social
Highly recommend the process at
@econtheory.bsky.social
Finally, we discussion how our results might be applicable to spatial price competition with multiple firms, to spatial voting models, or to border effects in trade.
Finally, we discussion how our results might be applicable to spatial price competition with multiple firms, to spatial voting models, or to border effects in trade.
With three jurisdictions, the distribution of moving costs for firms plays the same role as population density.
Again bigger jurisdiction can set lower rates!
With three jurisdictions, the distribution of moving costs for firms plays the same role as population density.
Again bigger jurisdiction can set lower rates!
We generalize to three jurisdictions with a more general convex cost function for profit shifting.
The higher derivatives of the cost function play the same role as population density.
We generalize to three jurisdictions with a more general convex cost function for profit shifting.
The higher derivatives of the cost function play the same role as population density.
Wilson).
Wilson).
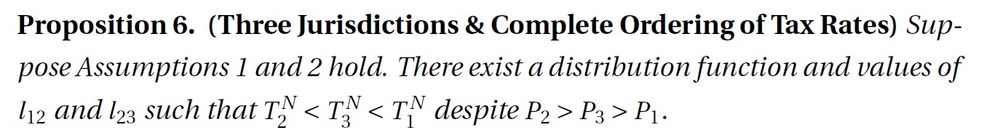
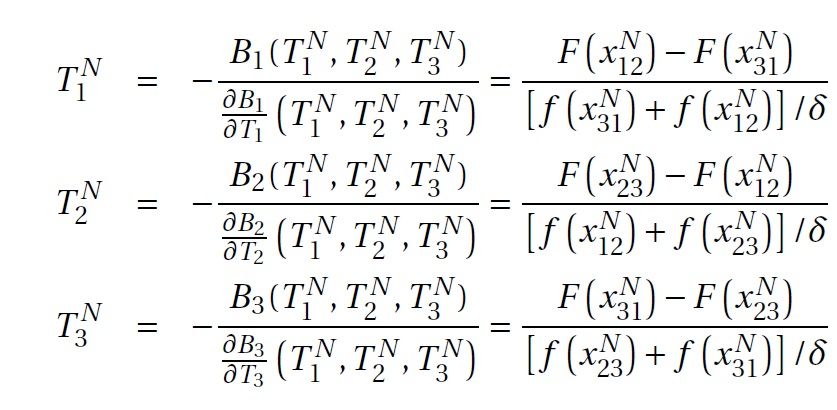
Thus, tax base sensitivities are no longer equal
Elasticities in Ramsey rule depend on size and on the average base change at 2 borders!
Thus, tax base sensitivities are no longer equal
Elasticities in Ramsey rule depend on size and on the average base change at 2 borders!
That is, a smaller jurisdiction can set a higher
tax rate than the next largest jurisdiction.
That is, a smaller jurisdiction can set a higher
tax rate than the next largest jurisdiction.

