- identify amenable types of real-world data
- integrate them into data-collection pipelines alongside lab-based tasks
- assess links to mental health
- assess lab-based versus real-world convergent validity of parameters
- expand models to accommodate real-world data
- identify amenable types of real-world data
- integrate them into data-collection pipelines alongside lab-based tasks
- assess links to mental health
- assess lab-based versus real-world convergent validity of parameters
- expand models to accommodate real-world data
⚠️ Noisy data
⚠️ Analytical complexity
⚠️ Data collection burden
⚠️ Ethical considerations
It remains to be seen whether real-world data can better computational psychiatry.
⚠️ Noisy data
⚠️ Analytical complexity
⚠️ Data collection burden
⚠️ Ethical considerations
It remains to be seen whether real-world data can better computational psychiatry.
👍 Testing the generalizability of in-lab computational psychiatry findings to every-day life
👍 Incorporating linguistic behavior into cognitive models using LLMs (see figure)
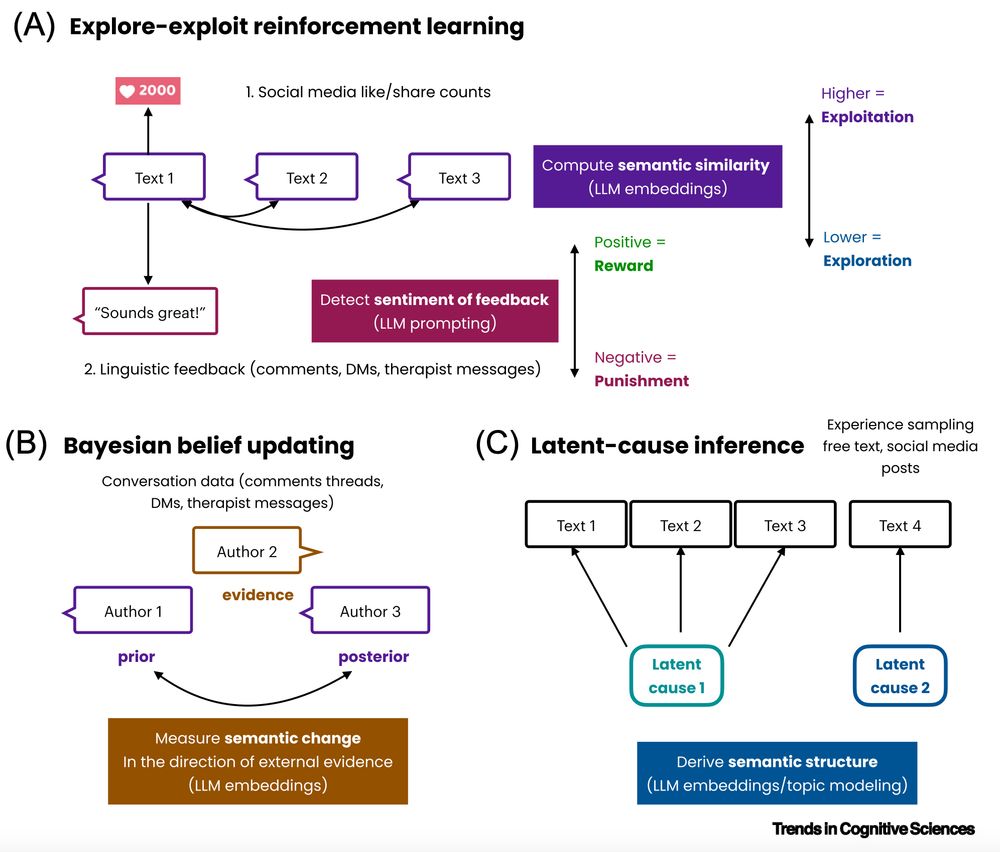
👍 Testing the generalizability of in-lab computational psychiatry findings to every-day life
👍 Incorporating linguistic behavior into cognitive models using LLMs (see figure)

Some of these have uncovered novel links to mental health (e.g. linking depression to blunted reactivity to positive prediction errors, or higher sensitivity to social rewards)

Some of these have uncovered novel links to mental health (e.g. linking depression to blunted reactivity to positive prediction errors, or higher sensitivity to social rewards)
- experience sampling data (active, self-report)
- passive sensing data (e.g. geolocation, physiology, social proximity)
- digital-behavior data (e.g. social media, texting, phone/app navigation)
- experience sampling data (active, self-report)
- passive sensing data (e.g. geolocation, physiology, social proximity)
- digital-behavior data (e.g. social media, texting, phone/app navigation)
By contrast, real-world data have intrinsic ecological validity and allow the continuous assessment of cognition and its variation over time.
By contrast, real-world data have intrinsic ecological validity and allow the continuous assessment of cognition and its variation over time.


