
🔧 Frankentexts struggle with smooth narrative transitions and grammar, as noted by human annotators.
🔩 Non-fiction versions are coherent and faithful but tend to be overly anecdotal and lack factual accuracy.

🔧 Frankentexts struggle with smooth narrative transitions and grammar, as noted by human annotators.
🔩 Non-fiction versions are coherent and faithful but tend to be overly anecdotal and lack factual accuracy.
👫 Models can follow copy constraints, which is a proxy for % of human writing in co-authored texts.

👫 Models can follow copy constraints, which is a proxy for % of human writing in co-authored texts.
📉 Binary detectors misclassify them as human-written
👨👩👧 Humans can detect AI involvement more often
🔍 Mixed-authorship tools (Pangram) help, but still catch only 59%
We need better tools for this gray zone.

📉 Binary detectors misclassify them as human-written
👨👩👧 Humans can detect AI involvement more often
🔍 Mixed-authorship tools (Pangram) help, but still catch only 59%
We need better tools for this gray zone.
💪 Gemini-2.5-Pro, Claude-3.5-Sonnet, and R1 can generate Frankentexts that are up to 90% relevant, 70% coherent, and 75% traceable to the original human writings.

💪 Gemini-2.5-Pro, Claude-3.5-Sonnet, and R1 can generate Frankentexts that are up to 90% relevant, 70% coherent, and 75% traceable to the original human writings.
1️⃣ Produce a draft by selecting & combining human-written passages.
2️⃣ Iteratively revise the draft while maintaining a copy ratio.

1️⃣ Produce a draft by selecting & combining human-written passages.
2️⃣ Iteratively revise the draft while maintaining a copy ratio.
🧟 You get what we call a Frankentext!
💡 Frankentexts are surprisingly coherent and tough for AI detectors to flag.

🧟 You get what we call a Frankentext!
💡 Frankentexts are surprisingly coherent and tough for AI detectors to flag.
🔩 Larger models (>=70B) may benefit from book-level reasoning—our chapter-level model outperforms the book-level version, indicating that smaller models might struggle with book-level reasoning.
🔩 Fine-tuned models struggle to verify False claims.

🔩 Larger models (>=70B) may benefit from book-level reasoning—our chapter-level model outperforms the book-level version, indicating that smaller models might struggle with book-level reasoning.
🔩 Fine-tuned models struggle to verify False claims.
📍 Source chapter of each event in the claim
🤝 Relationships between these events
📖 Explanation on how this supports/contradicts the claim.

📍 Source chapter of each event in the claim
🤝 Relationships between these events
📖 Explanation on how this supports/contradicts the claim.
📈 The fine-tuned LLaMA model boosts test performance from 28% to 76% and set a new state-of-the-art for <10B on NoCha, a long-form claim verification benchmark!

📈 The fine-tuned LLaMA model boosts test performance from 28% to 76% and set a new state-of-the-art for <10B on NoCha, a long-form claim verification benchmark!
✅ Our claims suffer from fewer errors like misattributions, duplications, and invalid claims compared to naïve approaches.

✅ Our claims suffer from fewer errors like misattributions, duplications, and invalid claims compared to naïve approaches.
1️⃣ Books are compressed into chapter outlines and summaries.
2️⃣ Grounded and complex claims are then generated based on these compressed representations.

1️⃣ Books are compressed into chapter outlines and summaries.
2️⃣ Grounded and complex claims are then generated based on these compressed representations.
We present CLIPPER ✂️, a compression-based pipeline that produces grounded instructions for ~$0.5 each, 34x cheaper than human annotations.
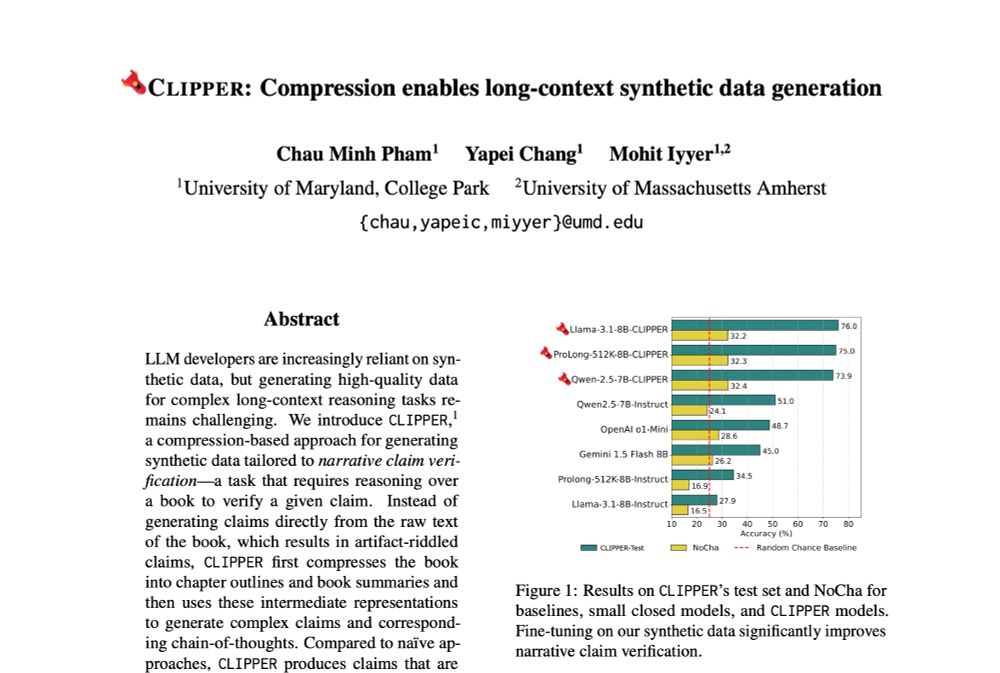
We present CLIPPER ✂️, a compression-based pipeline that produces grounded instructions for ~$0.5 each, 34x cheaper than human annotations.
1️⃣ Long-form text generation/eval
2️⃣ Synthetic data and instruction tuning
3️⃣ Anything else!
Looking forward to meeting old and new friends!

1️⃣ Long-form text generation/eval
2️⃣ Synthetic data and instruction tuning
3️⃣ Anything else!
Looking forward to meeting old and new friends!
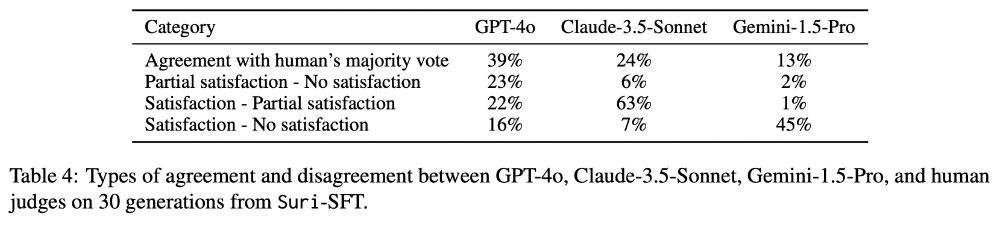




Collecting human preferences on long-form text is costly and hard, so we propose I-ORPO, a variant of the ORPO alignment algorithm that relies on:
3️⃣ Synthetically corrupted instructions.

Collecting human preferences on long-form text is costly and hard, so we propose I-ORPO, a variant of the ORPO alignment algorithm that relies on:
3️⃣ Synthetically corrupted instructions.
1️⃣ Gold responses from 3 existing datasets featuring web text and creative writing.
2️⃣ Backtranslated instructions generated by an LLM based on gold responses.

1️⃣ Gold responses from 3 existing datasets featuring web text and creative writing.
2️⃣ Backtranslated instructions generated by an LLM based on gold responses.
We present Suri 🦙: a dataset of 20K long-form texts & LLM-generated, backtranslated instructions with complex constraints.
📎 arxiv.org/abs/2406.19371

We present Suri 🦙: a dataset of 20K long-form texts & LLM-generated, backtranslated instructions with complex constraints.
📎 arxiv.org/abs/2406.19371

