We show that this is the case for various learning objectives, explore when it is optimal, provide empirical evidence, and propose a practically useful metric.
We show that this is the case for various learning objectives, explore when it is optimal, provide empirical evidence, and propose a practically useful metric.
Paper: arxiv.org/abs/2208.12764
Poster: West Ballroom A-D #5000 Wed 4.30pm
Joint work w/ @atajer.bsky.social, Karthikeyan Shanmugam, and Prasanna Sattigeri

Paper: arxiv.org/abs/2208.12764
Poster: West Ballroom A-D #5000 Wed 4.30pm
Joint work w/ @atajer.bsky.social, Karthikeyan Shanmugam, and Prasanna Sattigeri
Joint work w/ @atajer.bsky.social, Dmitriy Katz, Dennis Wei, and Prasanna Sattigeri

Joint work w/ @atajer.bsky.social, Dmitriy Katz, Dennis Wei, and Prasanna Sattigeri
Paper: arxiv.org/abs/2406.08666
Poster: West Ballroom A-D #5006 Thu 4.30pm

Paper: arxiv.org/abs/2406.08666
Poster: West Ballroom A-D #5006 Thu 4.30pm
Both CRL papers are joint worth w/ @atajer.bsky.social , Emre Acartürk, and Karthikeyan Shanmugam.
Both CRL papers are joint worth w/ @atajer.bsky.social , Emre Acartürk, and Karthikeyan Shanmugam.
2) 𝗦𝗮𝗺𝗽𝗹𝗲 𝗰𝗼𝗺𝗽𝗹𝗲𝘅𝗶𝘁𝘆 𝗼𝗳 𝗖𝗥𝗟: In the paper led by Emre Acartürk, we look into Sample Complexity of Interventional CRL.
Paper: openreview.net/forum?id=XL9...
Poster: West Ballroom A-D #5002 Wed 11am

2) 𝗦𝗮𝗺𝗽𝗹𝗲 𝗰𝗼𝗺𝗽𝗹𝗲𝘅𝗶𝘁𝘆 𝗼𝗳 𝗖𝗥𝗟: In the paper led by Emre Acartürk, we look into Sample Complexity of Interventional CRL.
Paper: openreview.net/forum?id=XL9...
Poster: West Ballroom A-D #5002 Wed 11am
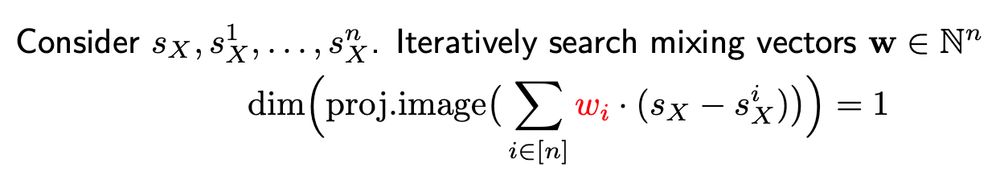

Paper: arxiv.org/abs/2406.05937
Poster: West Ballroom A-D #5005 Wed 11am

Paper: arxiv.org/abs/2406.05937
Poster: West Ballroom A-D #5005 Wed 11am

