


❌ Slower germination in E. palustris
❌ Reduced germination, growth and biomass in both species
❌ Lower total seed production in J. bufonius (6/10)

❌ Slower germination in E. palustris
❌ Reduced germination, growth and biomass in both species
❌ Lower total seed production in J. bufonius (6/10)
Gut passage alone wasn’t harmful, sometimes it even helped.
✔️ It sped up germination for J. bufonius (when no faeces were present).
✔️ It increased the final height of E. palustris. (5/10)

Gut passage alone wasn’t harmful, sometimes it even helped.
✔️ It sped up germination for J. bufonius (when no faeces were present).
✔️ It increased the final height of E. palustris. (5/10)
🌱 Juncus bufonius (annual mudflat plant)
🌱 Eleocharis palustris (perennial aquatic plant) (3/10)

🌱 Juncus bufonius (annual mudflat plant)
🌱 Eleocharis palustris (perennial aquatic plant) (3/10)
👉 doi.org/qfrv
@drandygreen.bsky.social
#PlantDispersal #SeedEcology #Endozoochory #AoBpapers

👉 doi.org/qfrv
@drandygreen.bsky.social
#PlantDispersal #SeedEcology #Endozoochory #AoBpapers

🐝 Bee visitation was >50× higher than bat visitation.
Higher nectar sugar content = more bees.
And diurnal visitors, especially large bees, significantly boosted fruit and seed set. (5/7)

🐝 Bee visitation was >50× higher than bat visitation.
Higher nectar sugar content = more bees.
And diurnal visitors, especially large bees, significantly boosted fruit and seed set. (5/7)
• smaller flowers
• anthesis later at night, extending into early morning
• nectar peaking at dawn
• sucrose-enriched, hexose-dominant nectar (4/7)

• smaller flowers
• anthesis later at night, extending into early morning
• nectar peaking at dawn
• sucrose-enriched, hexose-dominant nectar (4/7)
🌼 flower size
⏰ anthesis timing
💧 nectar production
🧪 nectar chemical composition
They also ran pollinator exclusion experiments and measured genome size and chromosome number. (3/7)

🌼 flower size
⏰ anthesis timing
💧 nectar production
🧪 nectar chemical composition
They also ran pollinator exclusion experiments and measured genome size and chromosome number. (3/7)

👉 doi.org/qfdp
#AoBpapers

👉 doi.org/qfdp
#AoBpapers
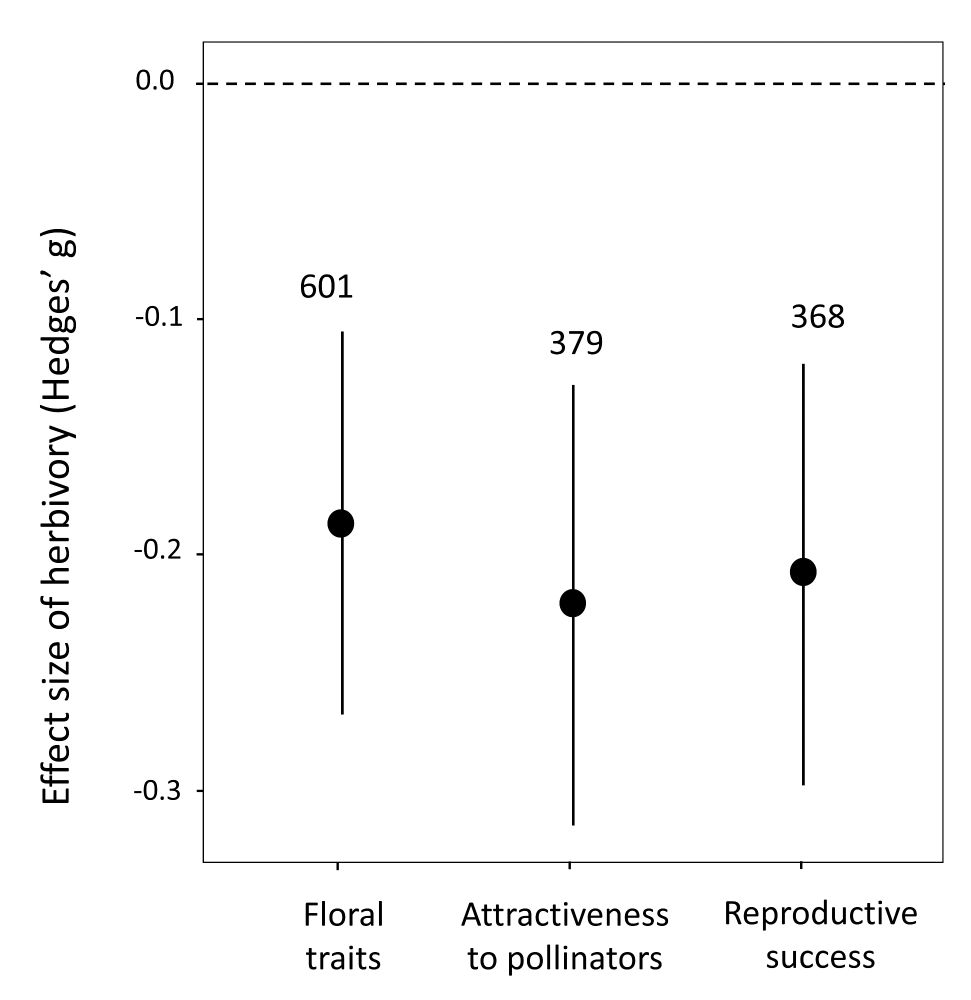
• Damage to flowers and stems reduced only floral traits.
• Simulated leaf damage decreased pollinator attraction.
This contrasts with earlier syntheses that suggested simulated herbivory had no effect. (7/9)

• Damage to flowers and stems reduced only floral traits.
• Simulated leaf damage decreased pollinator attraction.
This contrasts with earlier syntheses that suggested simulated herbivory had no effect. (7/9)
• Damage to leaves or flowers usually reduces floral traits, visitation and reproduction.
• Exception: natural flower damage did not reduce floral traits.
• Root and mixed damage showed no significant effects (6/9)

• Damage to leaves or flowers usually reduces floral traits, visitation and reproduction.
• Exception: natural flower damage did not reduce floral traits.
• Root and mixed damage showed no significant effects (6/9)


👉 doi.org/qd2p
@xmoreira.bsky.social
#FloralBiology #PollinationEcology #Plantscience #AoBpapers

👉 doi.org/qd2p
@xmoreira.bsky.social
#FloralBiology #PollinationEcology #Plantscience #AoBpapers
Get quarterly updates on Calls for Papers, Special Issues, author interviews and much more.
Subscribe 👉 buff.ly/3Xqdyac

Get quarterly updates on Calls for Papers, Special Issues, author interviews and much more.
Subscribe 👉 buff.ly/3Xqdyac




👉 doi.org/qc69
#PlantReproduction #AoBpapers

👉 doi.org/qc69
#PlantReproduction #AoBpapers

