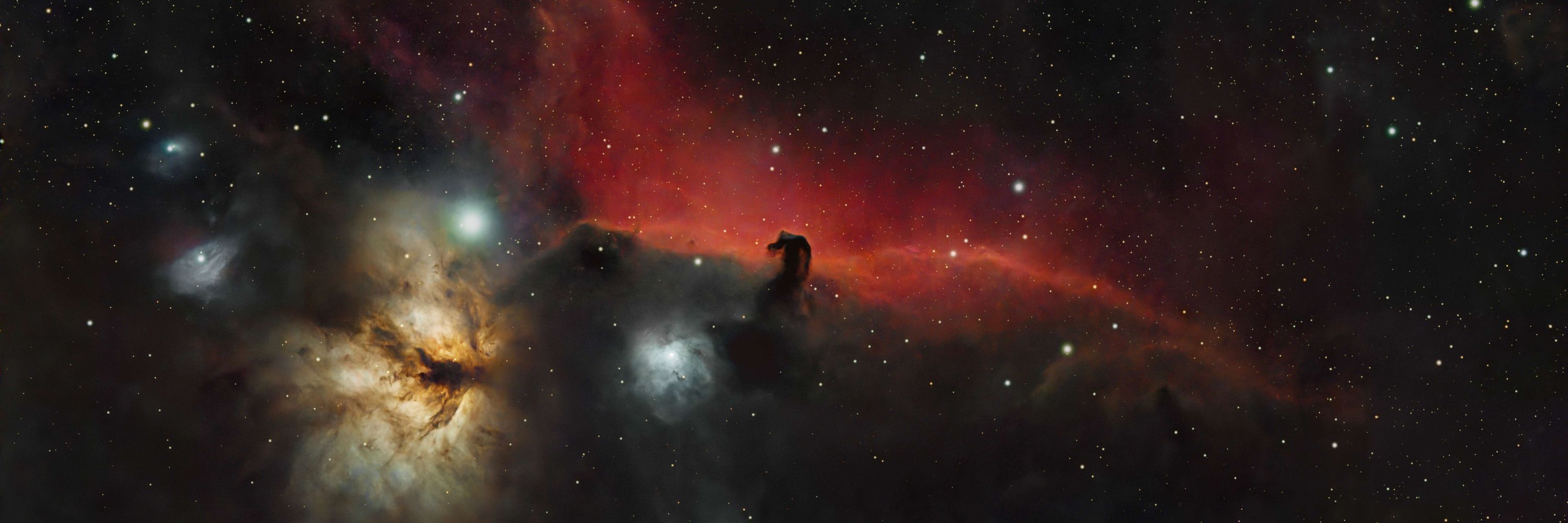

#Astrophotography #DeepSpace #Astronomy
My images: https://telescopius.com/profile/jean_legros
🔭 William Optics RedCat 61
📷 QHY MiniCam8
Total exposure: 2 h 25 min
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy

🔭 William Optics RedCat 61
📷 QHY MiniCam8
Total exposure: 2 h 25 min
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy
The Rosette Nebula (NGC 2238), located near a giant molecular cloud in the Monoceros region of the Milky Way Galaxy.
Shot from my backyard on 2025-12-27.
🔭 William Optics RedCat 61
📷 ZWO ASI 2600
Exposure: 2 h 05 min
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy
![The Rosette Nebula (also known as Caldwell 49) is an H II region located near one end of a giant molecular cloud in the Monoceros region of the Milky Way Galaxy. The open cluster NGC 2244 (Caldwell 50) is closely associated with the nebulosity, the stars of the cluster having been formed from the nebula's matter.The cluster and nebula lie at a distance of 5,000 light-years from Earth[7] and measure roughly 130 light years in diameter. The radiation from the young stars excites the atoms in the nebula, causing them to emit radiation themselves producing the emission nebula we see. The mass of the nebula is estimated to be around 10,000 solar masses.](https://cdn.bsky.app/img/feed_thumbnail/plain/did:plc:dksfsl7lygnhrmfxsxcznf3u/bafkreid3y7vnznj6oi2g7llz2k3nawnlmlbm7ovmdr2vtlgz5atv3s7tai@jpeg)
The Rosette Nebula (NGC 2238), located near a giant molecular cloud in the Monoceros region of the Milky Way Galaxy.
Shot from my backyard on 2025-12-27.
🔭 William Optics RedCat 61
📷 ZWO ASI 2600
Exposure: 2 h 05 min
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy
The Flaming Star Nebula and the Tadpole Nebulae are emission and reflection nebulae located in the constellation Auriga.
Shot from my backyard on 2025-12-25.
🔭 William Optics RedCat 61
📷 ZWO ASI 2600
Exposure: 1 h 10 min
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy
![Bottom object in the image:
IC 405 (also known as the Flaming Star Nebula, SH 2-229, or Caldwell 31) is an emission and reflection nebula[1] in the constellation Auriga north of the celestial equator, surrounding the bluish, irregular variable star AE Aurigae. It shines at magnitude +6.0. Its celestial coordinates are RA 05h 16.2m dec +34° 28′.[2] It is located near the emission nebula IC 410, the open clusters M38 and M36, and the K-class star Iota Aurigae.
The nebula measures approximately 37.0' x 19.0', and lies about 1,500 light-years away from Earth.[2] It is believed that the proper motion of the central star can be traced back to the Orion's Belt area.[2] The nebula is about 5 light-years across.](https://cdn.bsky.app/img/feed_thumbnail/plain/did:plc:dksfsl7lygnhrmfxsxcznf3u/bafkreifpwrj3kms5qgutkgzxfszok2mumelgmxgr4ajnem6rc5524kvele@jpeg)

The Flaming Star Nebula and the Tadpole Nebulae are emission and reflection nebulae located in the constellation Auriga.
Shot from my backyard on 2025-12-25.
🔭 William Optics RedCat 61
📷 ZWO ASI 2600
Exposure: 1 h 10 min
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy
Shot taken on 2025-10-11 from my backyard.
🔭 William Optics Pleiades 111
📷 ZWO ASI 2600
Total exposure: 31 x 30s (15m30s)
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Comet #Astronomy
![C/2025 A6 (Lemmon) is a non-periodic comet discovered by the Mount Lemmon Survey in images obtained on 3 January 2025. It has an inbound orbital period of about 1,350 years and will pass perihelion on 8 November 2025 when it will be 0.53 AU (79 million km; 49 million mi) from the Sun. This perihelion passage will reduce the orbital period to about 1,150 years. It makes its closest approach to Earth on 21 October 2025 and may be visible to the naked eye 42 degrees from the Sun after sunset. As of 24 October 2025, the comet is about apparent magnitude 4.2,[3] and the nucleus and coma are visible in binoculars about 12 degrees above Arcturus and near the magnitude 2.5 star Izar. (The handle of the Big Dipper points towards Arcturus.) Both Arcturus and the comet may be visible in the same field of view using low power binoculars such as 7x35s.](https://cdn.bsky.app/img/feed_thumbnail/plain/did:plc:dksfsl7lygnhrmfxsxcznf3u/bafkreigq6orjub7reelwqiugmdq2kbkoeny3pnqzhwh4jhrqm6kjnoegyu@jpeg)
Shot taken on 2025-10-11 from my backyard.
🔭 William Optics Pleiades 111
📷 ZWO ASI 2600
Total exposure: 31 x 30s (15m30s)
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Comet #Astronomy
Shot taken on 2025-10-11 from my backyard.
🔭 William Optics Pleiades 111
📷 ZWO ASI 2600
Total exposure: 45 x 120s (1h30)
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy

Shot taken on 2025-10-11 from my backyard.
🔭 William Optics Pleiades 111
📷 ZWO ASI 2600
Total exposure: 45 x 120s (1h30)
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy
Shot taken on 2025-10-11 from my backyard.
🔭 William Optics Pleiades 111
📷 ZWO ASI 2600
Total exposure: 31 x 30s (15m30s)
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Comet #Astronomy
![C/2025 A6 (Lemmon) is a non-periodic comet discovered by the Mount Lemmon Survey in images obtained on 3 January 2025. It has an inbound orbital period of about 1,350 years and will pass perihelion on 8 November 2025 when it will be 0.53 AU (79 million km; 49 million mi) from the Sun. This perihelion passage will reduce the orbital period to about 1,150 years. It makes its closest approach to Earth on 21 October 2025 and may be visible to the naked eye 42 degrees from the Sun after sunset. As of 12 October 2025, the comet is about apparent magnitude 5.6,[6] and is visible in binoculars about 15 degrees (approximately one and a half fists) below the cup of the Big Dipper. It is currently about 2 degrees southwest of the star Psi Ursae Majoris.](https://cdn.bsky.app/img/feed_thumbnail/plain/did:plc:dksfsl7lygnhrmfxsxcznf3u/bafkreidp6cmbwr464kygmuzq2f72k6azorsjbssfjpfa5mldh22byia5su@jpeg)
Shot taken on 2025-10-11 from my backyard.
🔭 William Optics Pleiades 111
📷 ZWO ASI 2600
Total exposure: 31 x 30s (15m30s)
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Comet #Astronomy
Shot taken on 2025-10-05 from my backyard.
🔭 William Optics Red Cat 61
📷 ZWO ASI 2600 + L-Extreme
Total exposure: 13 x 600s (2h10)
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy

Shot taken on 2025-10-05 from my backyard.
🔭 William Optics Red Cat 61
📷 ZWO ASI 2600 + L-Extreme
Total exposure: 13 x 600s (2h10)
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy
Shot taken on 2025-09-31 from my backyard.
Moon Distance: 395,789.39 km
Telescope: SCT 8 in
Camera: ZWO 2600 MC OSC
50 best of 500 exposures stacked
#Astrophotography #Space #Moon #MoonHour #Planetary #Astronomy

Shot taken on 2025-09-31 from my backyard.
Moon Distance: 395,789.39 km
Telescope: SCT 8 in
Camera: ZWO 2600 MC OSC
50 best of 500 exposures stacked
#Astrophotography #Space #Moon #MoonHour #Planetary #Astronomy
Shot taken on 2025-09-21 from my backyard.
🔭 William Optics Red Cat 61
📷 ZWO ASI 2600
Total exposure: 30 x 180s (1h30)
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy

Shot taken on 2025-09-21 from my backyard.
🔭 William Optics Red Cat 61
📷 ZWO ASI 2600
Total exposure: 30 x 180s (1h30)
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy
Shot taken on 2025-09-19 from my backyard.
🔭 William Optics Red Cat 61
📷 ZWO ASI 2600 + L-Extreme
Total exposure: 45 x 300s (3h45)
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy
![IC 1396 is a large emission nebulae, a region of ionized gas, located in the constellation Cepheus about 2,400 light years away from Earth.[1]
IC 1396 is illuminated and ionized by a very bright, massive multiple star HD 206267 at its center, except for dense globules that can protect themselves from the star's harsh ultraviolet rays. This hierarchical triple star system has two members that form a spectroscopic binary that orbit each other with a period of 3.7 days, while a third member lies further away—it is unclear whether this third member is gravitationally bound to the pair. The system is emitting a stellar wind that reaches an exceptional velocity of 3,225 km/s, among the highest measured for stars of this type.[2]
Jutting from the rim of the nebula is IC 1396A, commonly called the Elephant's Trunk Nebula, a dark, dense globule with a bright, sinuous rim being illuminated by HD 206267.[3]](https://cdn.bsky.app/img/feed_thumbnail/plain/did:plc:dksfsl7lygnhrmfxsxcznf3u/bafkreigbv6j4j3ns5ibvn4xsbzkau5lsaoe63wmy4jqgkwmplduvir6s2y@jpeg)
Shot taken on 2025-09-19 from my backyard.
🔭 William Optics Red Cat 61
📷 ZWO ASI 2600 + L-Extreme
Total exposure: 45 x 300s (3h45)
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy
Shot taken on 2025-09-16 from my backyard.
🔭 William Optics Red Cat 61
📷 ZWO ASI 2600
Total exposure: 32 x 300s (2h40)
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy

Shot taken on 2025-09-16 from my backyard.
🔭 William Optics Red Cat 61
📷 ZWO ASI 2600
Total exposure: 32 x 300s (2h40)
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy
Shot taken on 2025-08-31 from my backyard.
🔭 William Optics Pleiades 111
📷 ZWO ASI 2600
Total exposure: 42 x 300s (3h30)
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy
![Westerhout 5 (Sharpless 2-199, LBN 667, Soul Nebula) is an emission nebula located in Cassiopeia. Several small open clusters are embedded in the nebula: CR 34, 632, and 634[citation needed] (in the head) and IC 1848 (in the body). The object is more commonly called by the cluster designation IC 1848.
Small emission nebula IC 1871 is present just left of the top of the head, and small emission nebulae 670 and 669 are just below the lower back area.
The galaxies Maffei 1 and Maffei 2 are both nearby the nebula, although light extinction from the Milky Way makes them very hard to see. Once thought to be part of the Local Group, they are now known to belong to their own group- the IC 342/Maffei Group.
This complex is the eastern neighbour of IC1805 (Heart Nebula) and the two are often mentioned together as the "Heart and Soul".](https://cdn.bsky.app/img/feed_thumbnail/plain/did:plc:dksfsl7lygnhrmfxsxcznf3u/bafkreiecflvg52e6rorjtjcfrp66jd2oafhpl77n3ab7oux75ppsjsuyki@jpeg)
Shot taken on 2025-08-31 from my backyard.
🔭 William Optics Pleiades 111
📷 ZWO ASI 2600
Total exposure: 42 x 300s (3h30)
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy
Shot taken on 2025-08-15 from my backyard.
🔭 William Optics Pleiades 111
📷 ZWO ASI 2600
Total exposure: 42 x 300s (3h30)
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy

Shot taken on 2025-08-15 from my backyard.
🔭 William Optics Pleiades 111
📷 ZWO ASI 2600
Total exposure: 42 x 300s (3h30)
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy
Shot taken on 2025-08-11 from my backyard
🔭: William Optics Pleiades 111
📷: ZWO ASI 2600
Total exposure: 26 x 300 sec (2h10)
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy
![NGC 7380 is a young open cluster of stars in the northern circumpolar constellation of Cepheus, discovered by Caroline Herschel in 1787. The surrounding emission nebulosity is known colloquially as the Wizard Nebula, which spans an angle of 25′. German-born astronomer William Herschel included his sister's discovery in his catalog, and labelled it H VIII.77. The nebula is known as S 142 in the 1959 Sharpless catalog (Sh2-142).It is extremely difficult to observe visually, usually requiring very dark skies and an O-III filter. The NGC 7380 complex is located at a distance of approximately 8.5 kilolight-years from the Sun, in the Perseus Arm of the Milky Way.
The cluster spans ~20 light-years (6 pc) with an elongated shape and an extended tail.[2] Age estimates range from 4[2] to 11.9 million years. At the center of the cluster lies DH Cephei, a close, double-lined spectroscopic binary system consisting of two massive O-type stars. This pair are the primary ionizing source for the surrounding H II region, and are driving out the surrounding gas and dust while triggering star formation in the neighboring region. Of the variable stars that have been identified in the cluster, 14 have been identified as pre-main sequence stars while 17 are main sequence stars that are primarily B-type variables.
Shot taken on 2025-08-01 from my backyard
🔭: William Optics Pleiades 111
📷: ZWO ASI 2600
Total exposure: 26 x 300 sec (2h10)
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy](https://cdn.bsky.app/img/feed_thumbnail/plain/did:plc:dksfsl7lygnhrmfxsxcznf3u/bafkreice3vhh5xxnvtzjdpycyr22wpfsbi542sqqtmgyouxhtmjylfqwhu@jpeg)
Shot taken on 2025-08-11 from my backyard
🔭: William Optics Pleiades 111
📷: ZWO ASI 2600
Total exposure: 26 x 300 sec (2h10)
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy
Shot taken on 2025-08-01 from my backyard
🔭: William Optics Pleiades 111
📷: ZWO ASI 2600
Total exposure: 56 x 120 sec (1h52)
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy
![The Iris Nebula (also known as NGC 7023 and Caldwell 4) is a bright reflection nebula in the constellation Cepheus. The designation NGC 7023 refers to the open cluster within the larger reflection nebula designated LBN 487.
The nebula, which shines at magnitude +6.8, is illuminated by a magnitude +7.4 star designated HD 200775.[1] It is located near the Mira-type variable star T Cephei, and near the bright magnitude +3.23 variable star Beta Cephei (Alfirk). It lies 1,300 light-years away and is six light-years across.](https://cdn.bsky.app/img/feed_thumbnail/plain/did:plc:dksfsl7lygnhrmfxsxcznf3u/bafkreievpmay3ykkqeiyjbwiaw7d75tinwpqueoeqlnpo3ofhuduligghq@jpeg)
Shot taken on 2025-08-01 from my backyard
🔭: William Optics Pleiades 111
📷: ZWO ASI 2600
Total exposure: 56 x 120 sec (1h52)
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy
Shot taken on 2025-07-18 from my backyard
🔭: William Optics Pleiades 111
📷: ZWO ASI 2600
Total exposure: 4 x 8 x 180 sec (1h05)
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy
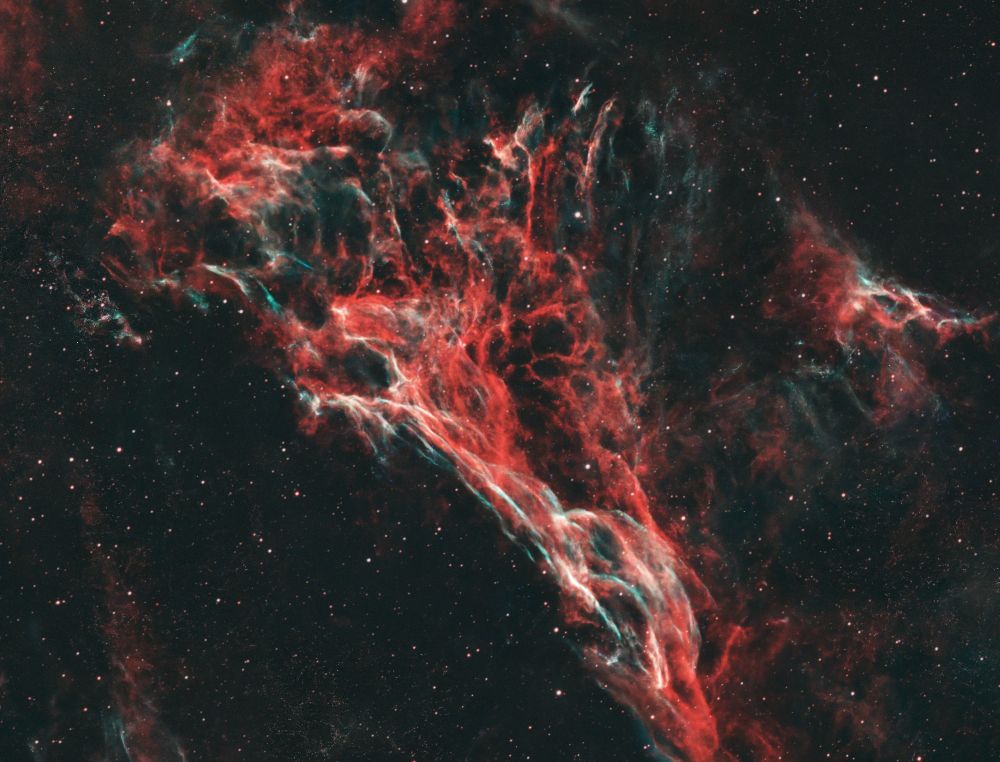
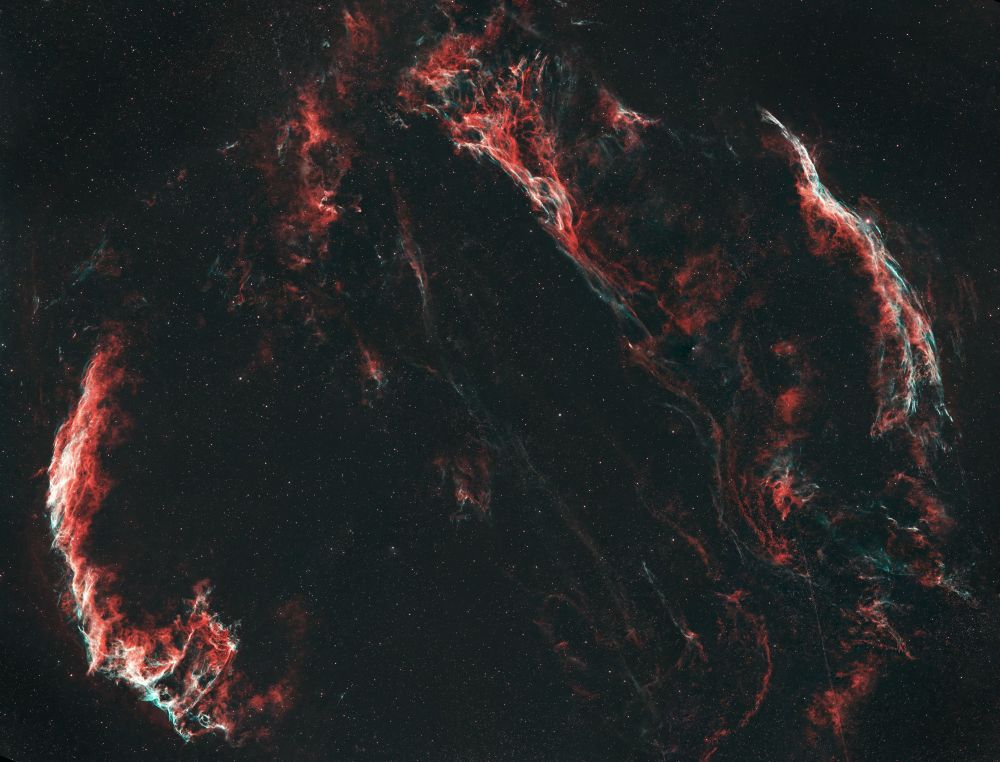

Shot taken on 2025-07-18 from my backyard
🔭: William Optics Pleiades 111
📷: ZWO ASI 2600
Total exposure: 4 x 8 x 180 sec (1h05)
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy
Shot taken on 2025-06-22 from my backyard.
🔭: William Optics Pleiades 111
📷: ZWO ASI 2600
Total exposure: 13 x 300 sec (1h05)
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy
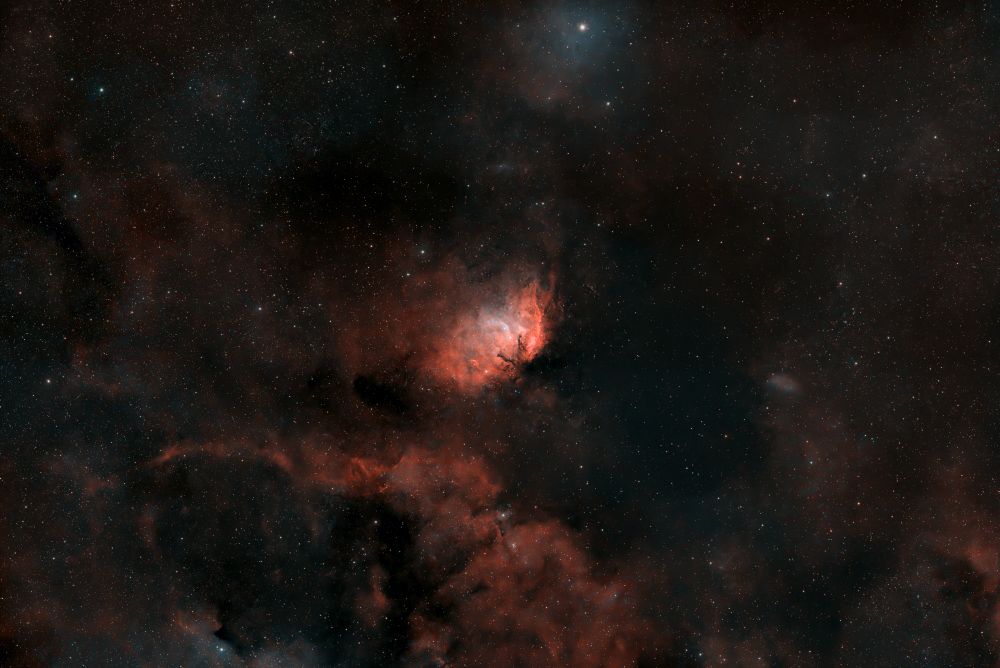
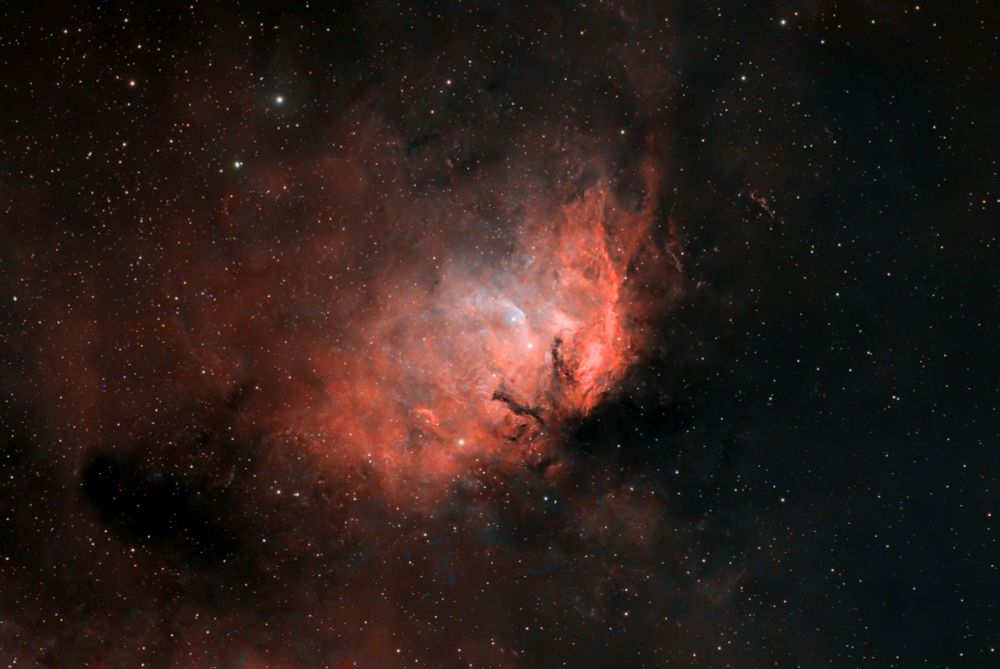


Shot taken on 2025-06-22 from my backyard.
🔭: William Optics Pleiades 111
📷: ZWO ASI 2600
Total exposure: 13 x 300 sec (1h05)
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy
Shot taken on 2025-06-22 from my backyard.
🔭: William Optics Pleiades 111
📷: ZWO ASI 2600 + Filter L-Extreme
Total exposure: 1200 sec
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy
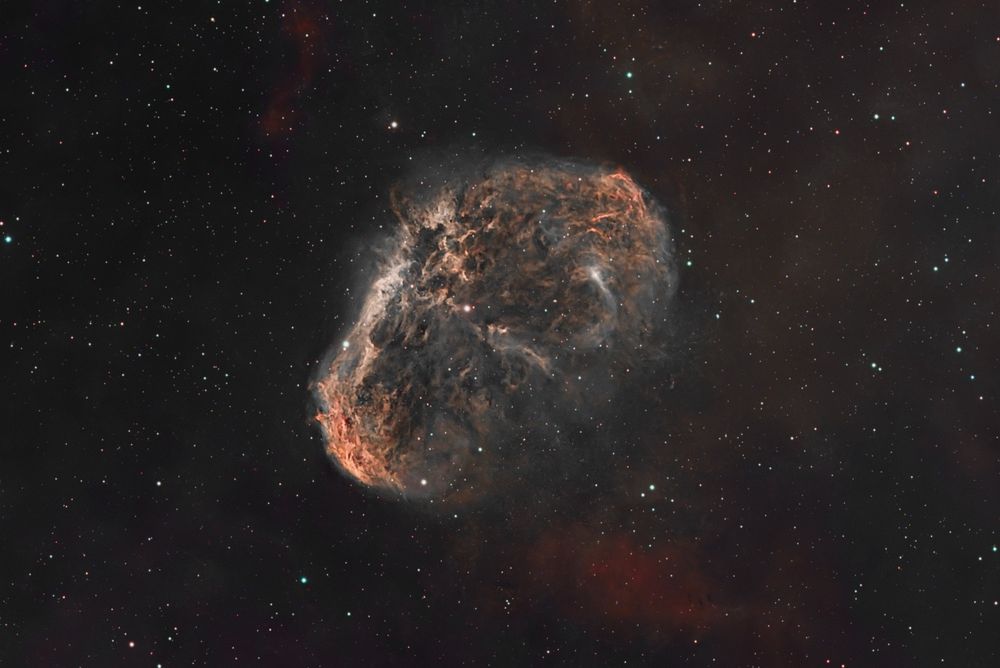


Shot taken on 2025-06-22 from my backyard.
🔭: William Optics Pleiades 111
📷: ZWO ASI 2600 + Filter L-Extreme
Total exposure: 1200 sec
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy
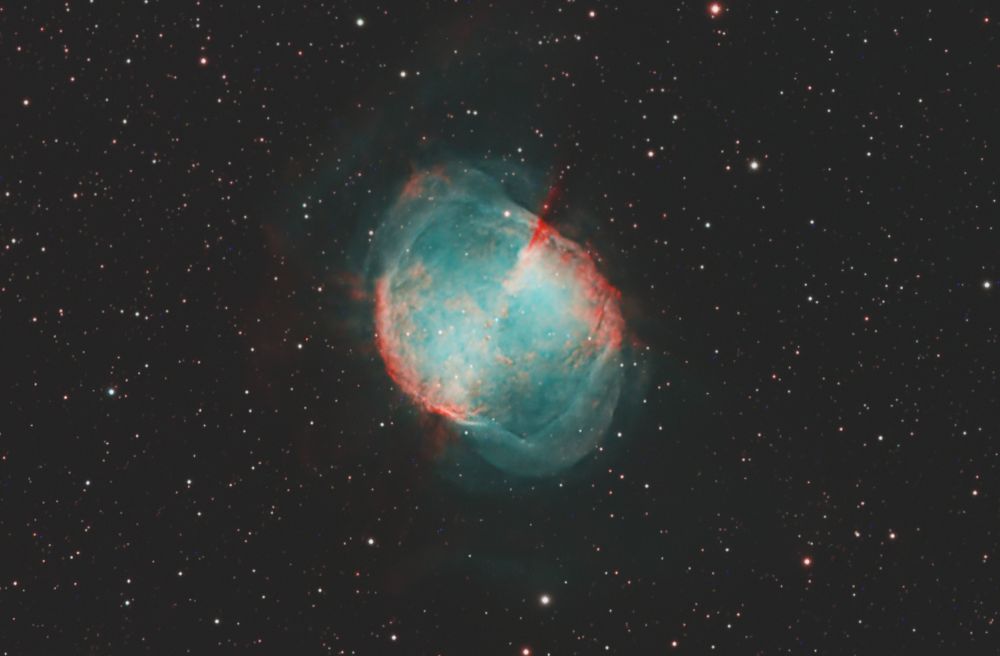
Messier 27, The Dumbbell Nebula (also known as the Apple Core Nebula). Retaken with more exposure
Shot taken on 2025-07-4 from my backyard
Telescope: William Optics Pleiades 111
Camera: ZWO ASI 2600 + L-Extreme Filter
Total exposure: 85 minutes
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy

Messier 27, The Dumbbell Nebula (also known as the Apple Core Nebula). Retaken with more exposure
Shot taken on 2025-07-4 from my backyard
Telescope: William Optics Pleiades 111
Camera: ZWO ASI 2600 + L-Extreme Filter
Total exposure: 85 minutes
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy
Shot taken on 2025-06-29 from my backyard.
Telescope : William Optics Pleiades 111
Camera : ZWO ASI 2600
Exposure: best 50% of (5000 x 4 millisec)
#Astrophotography #Space #Planetary #Astronomy
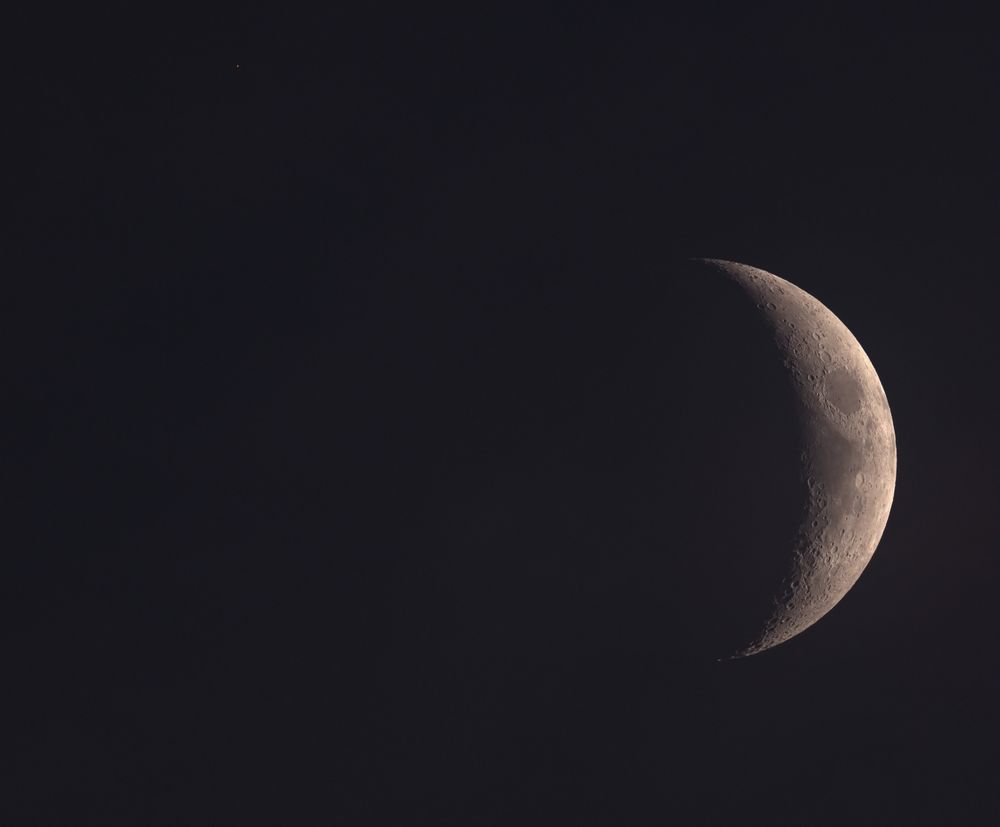
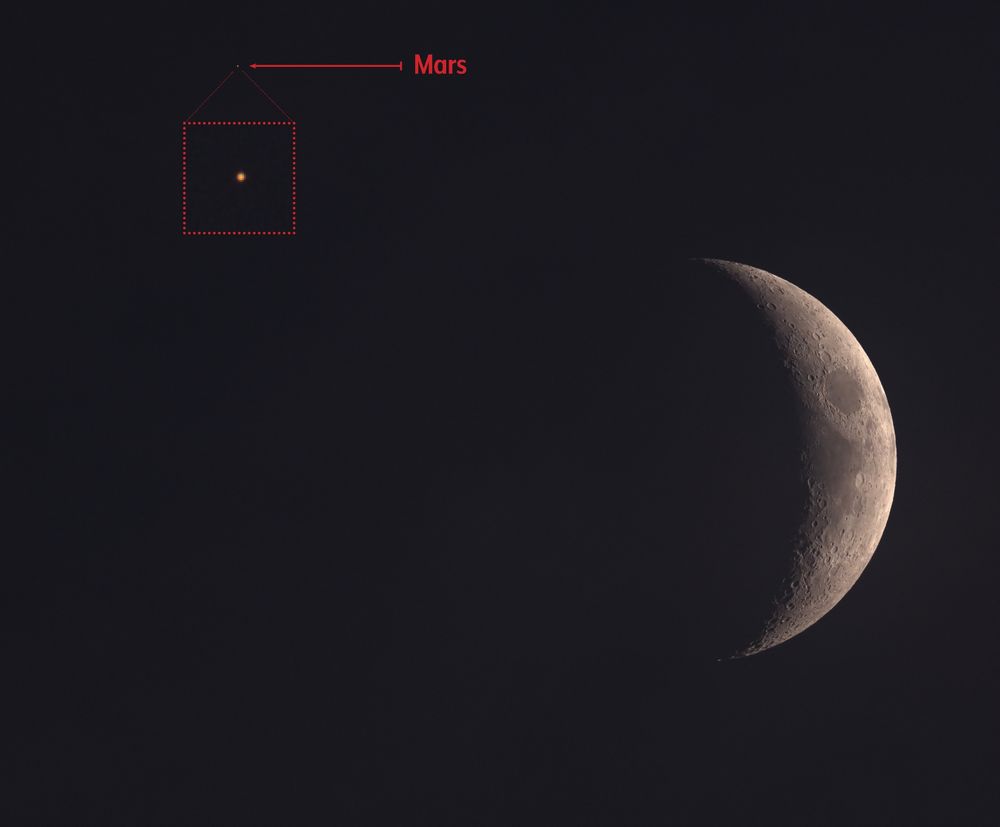



Shot taken on 2025-06-29 from my backyard.
Telescope : William Optics Pleiades 111
Camera : ZWO ASI 2600
Exposure: best 50% of (5000 x 4 millisec)
#Astrophotography #Space #Planetary #Astronomy
Shot taken on 2025-06-22 from my backyard.
🔭: William Optics Pleiades 111
📷: ZWO ASI 2600
Total exposure: 13x300 sec (1h05)
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy
![Sharpless 101 (Sh 2-101) is a H II region[1] emission nebula located in the constellation Cygnus. It is sometimes also called the Tulip Nebula because it appears to resemble the outline of a tulip when imaged photographically. It was catalogued by astronomer Stewart Sharpless in his 1959 catalog of nebulae. It lies at a distance of about 6,000 light-years (5.7×1016 km; 3.5×1016 mi) from Earth.
Sh 2-101, at least in the field seen from Earth, is in close proximity to microquasar Cygnus X-1, site of one of the first suspected black holes. Cygnus X-1 is located about 15′ west of Sh 2-101. The companion star of Cygnus X-1 is a spectral class O9.7 Iab supergiant with a mass of 21 solar masses and 20 times the radius of the Sun. The period of the binary system is 5.8 days and the pair is separated by 0.2 astronomical units. The black hole has a mass of 15 solar masses and a Schwarzschild radius of 45 km.](https://cdn.bsky.app/img/feed_thumbnail/plain/did:plc:dksfsl7lygnhrmfxsxcznf3u/bafkreifdielc2mm25gh5yktm4wh6riabzxul7ddqb5ojo3iduh3ehvy4ou@jpeg)

Shot taken on 2025-06-22 from my backyard.
🔭: William Optics Pleiades 111
📷: ZWO ASI 2600
Total exposure: 13x300 sec (1h05)
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy
Shot taken on 2025-06-22 from my backyard.
🔭: William Optics Pleiades 111
📷: ZWO ASI 2600
Total exposure: 1200 sec
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy


Shot taken on 2025-06-22 from my backyard.
🔭: William Optics Pleiades 111
📷: ZWO ASI 2600
Total exposure: 1200 sec
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy
Shot taken on 2025-06-20 from my backyard.
Telescope : William Optics Pleiades 111
Camera : ZWO ASI 2600
Total exposure: 25 x 300 sec (2h05)
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy
![NGC 7635, also known as the Bubble Nebula is an emission nebula in the constellation Cassiopeia. It lies close to the open cluster Messier 52. The "bubble" is created by the stellar wind from a massive hot, 8.7[1] magnitude young central star. The nebula is near a giant molecular cloud which contains the expansion of the bubble nebula while itself being excited by the hot central star, causing it to glow. It was discovered in November 1787 by William Herschel.
Shot taken on 2025-06-20 from my backyard.
Telescope : William Optics Pleiades 111
Camera : ZWO ASI 2600
Total exposure: 25 x 300 sec (2h05)
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy](https://cdn.bsky.app/img/feed_thumbnail/plain/did:plc:dksfsl7lygnhrmfxsxcznf3u/bafkreigl4ihealue6slnaxczzjvtahcz6f77j57jcwtn3nvxsezqid7uei@jpeg)
Shot taken on 2025-06-20 from my backyard.
Telescope : William Optics Pleiades 111
Camera : ZWO ASI 2600
Total exposure: 25 x 300 sec (2h05)
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy
Shot taken on 2025-06-15 from my backyard.
Before the clouds.
Telescope : William Optics Pleiades 111
Camera : ZWO ASI 2600
Total exposure: 1 x 120 sec
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy
![The Dumbbell Nebula (also known as the Apple Core Nebula, Messier 27, and NGC 6853) is a planetary nebula (nebulosity surrounding a white dwarf) in the constellation Vulpecula, at a distance of about 1360 light-years.[1] It was the first such nebula to be discovered, by Charles Messier in 1764. At its brightness of visual magnitude 7.5 and diameter of about 8 arcminutes, it is easily visible in binoculars[4] and is a popular observing target in amateur telescopes.
The Dumbbell Nebula appears shaped like a prolate spheroid and is viewed from our perspective along the plane of its equator. In 1992, Moreno-Corral et al. computed that its rate of expansion angularly was, viewed from our distance, no more than 2.3 arcseconds (″) per century. From this, an upper limit to the age of 14,600 years may be determined. In 1970, Bohuski, Smith, and Weedman found an expansion velocity of 31 km/s. Given its semi-minor axis radius of 1.01 ly, this implies that the kinematic age of the nebula is 9,800 years.[](https://cdn.bsky.app/img/feed_thumbnail/plain/did:plc:dksfsl7lygnhrmfxsxcznf3u/bafkreibrzrptjr5cyltbz7icrbmciqoxboiii5zxs4jty6mpk5xbxcdhfm@jpeg)
Shot taken on 2025-06-15 from my backyard.
Before the clouds.
Telescope : William Optics Pleiades 111
Camera : ZWO ASI 2600
Total exposure: 1 x 120 sec
#Astrophotography #Space #DeepSpace #Astronomy
Shot taken on 2025-06-02 from my backyard.
Telescope: William Optics Pleiades 111
Camera: ZWO 2600 MC OSC
50% best of 5000 4 millisec exposures stacked
#Astrophotography #Space #Moon #MoonHour #Planetary #Astronomy

Shot taken on 2025-06-02 from my backyard.
Telescope: William Optics Pleiades 111
Camera: ZWO 2600 MC OSC
50% best of 5000 4 millisec exposures stacked
#Astrophotography #Space #Moon #MoonHour #Planetary #Astronomy

