
Site notice: http://bit.ly/2oAyLi1 https://www.nature.com/ngeo/

www.nature.com/ngeo/volumes...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

www.nature.com/articles/s41...
go.nature.com/3Kv3Gu3

go.nature.com/3Kv3Gu3
go.nature.com/4pWdKeD

go.nature.com/4pWdKeD
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
(1/4)

www.nature.com/articles/s41...
(1/4)
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.nature.com/ngeo/volumes...

www.nature.com/ngeo/volumes...
go.nature.com/3YcD2ZS

go.nature.com/3YcD2ZS
#geobiology #astrobiology @earthscista.bsky.social
@earlylife.bsky.social
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

#geobiology #astrobiology @earthscista.bsky.social

#earthscience #geoscience ⚒️

#earthscience #geoscience ⚒️
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
@earlylife.bsky.social
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

@earlylife.bsky.social
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

www.nature.com/articles/s41...
go.nature.com/3XjAk4G ⚒️ 🧪

go.nature.com/3XjAk4G ⚒️ 🧪
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

www.nature.com/articles/s41...
go.nature.com/48rQi1s

go.nature.com/48rQi1s
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

www.nature.com/articles/s41...
go.nature.com/4oj1wLF

go.nature.com/4oj1wLF
go.nature.com/3JZGdku 🧪

go.nature.com/3JZGdku 🧪
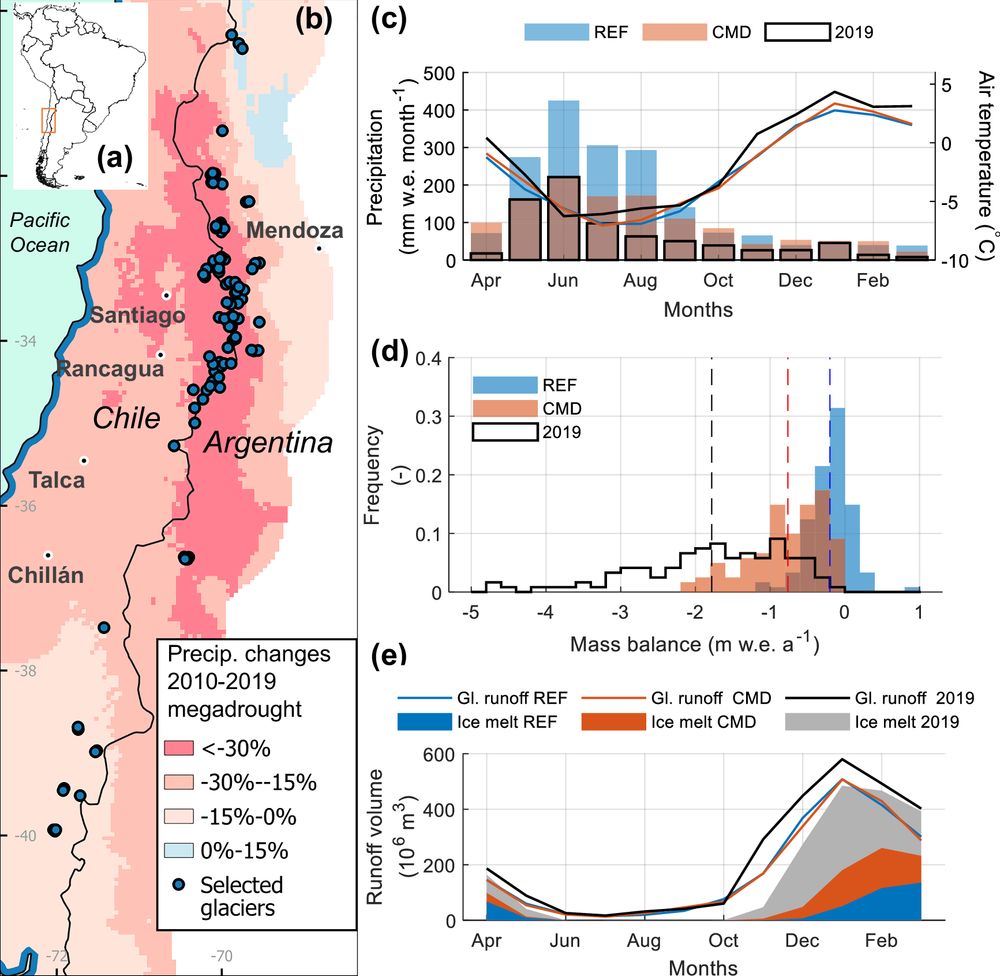
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

www.nature.com/articles/s41...

A new #PKUResearch has uncovered this hidden driver:
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
#ClimateScience #Ecology #PekingUniversity #AcademicSky @natgeosci.nature.com

A new #PKUResearch has uncovered this hidden driver:
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
#ClimateScience #Ecology #PekingUniversity #AcademicSky @natgeosci.nature.com
📸 Explore the full picture story: @natgeosci.nature.com 👇
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

📸 Explore the full picture story: @natgeosci.nature.com 👇
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

