
bit.ly/44b5e3L

bit.ly/44b5e3L
bit.ly/49xgb0D
bit.ly/49xgb0D
bit.ly/45GznYv
#STS #MedSky
bit.ly/45GznYv
#STS #MedSky
#MedSky

#MedSky
#MedSky
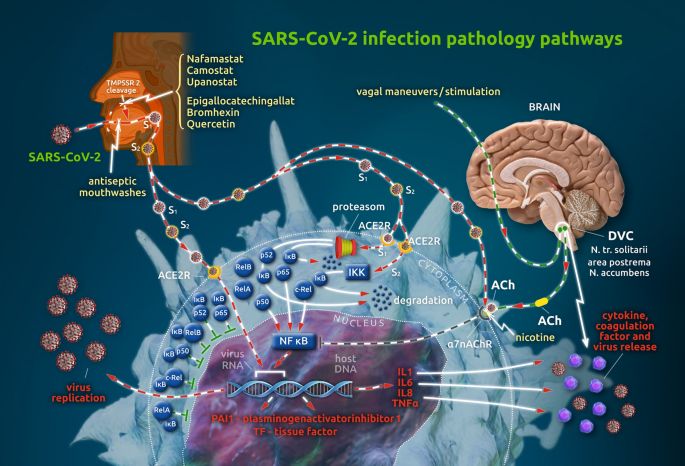
#MedSky
bit.ly/41HwxRH
#PsychSciSky #STS

bit.ly/41HwxRH
#PsychSciSky #STS
#STS
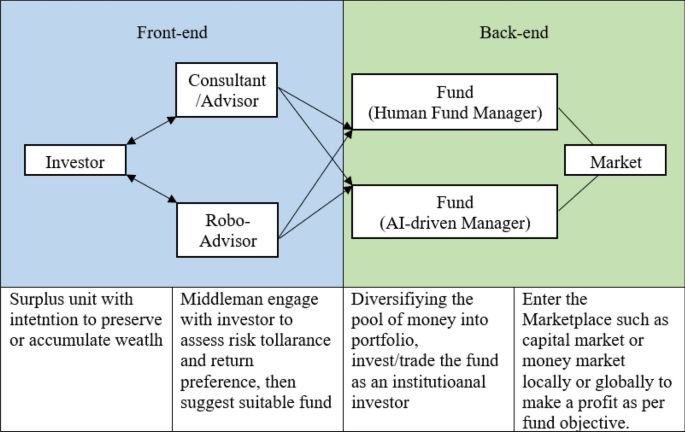
#STS
On #WorldCancerDay, we’re sharing a review by Renaud et al. (2025) on how linking biological insights with clinical practice could help improve cancer care.
bit.ly/4kem5Zz
#MedSky #OncoSky
On #WorldCancerDay, we’re sharing a review by Renaud et al. (2025) on how linking biological insights with clinical practice could help improve cancer care.
bit.ly/4kem5Zz
#MedSky #OncoSky
#MedSky

#MedSky
This case study shows how a Springer Nature collection published in a Discover journal led to WHO citations & worldwide recognition: bit.ly/4hZEyYB
#MedSky

This case study shows how a Springer Nature collection published in a Discover journal led to WHO citations & worldwide recognition: bit.ly/4hZEyYB
#MedSky

#PsychSciSky

#PsychSciSky
bit.ly/3SFtJ1Y
#MedSky
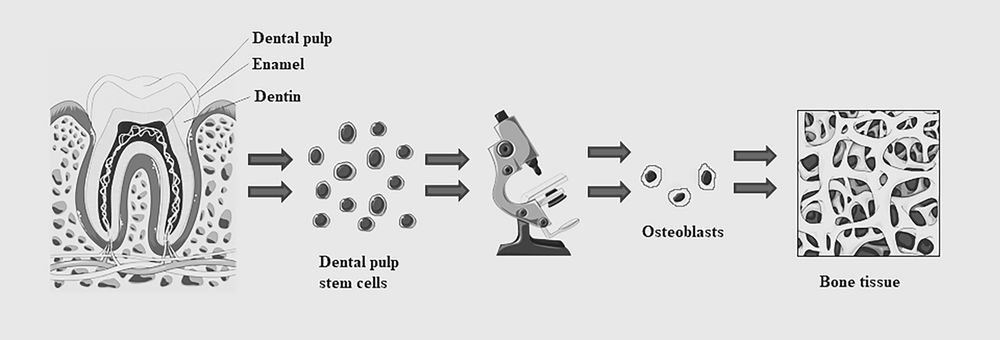
bit.ly/3SFtJ1Y
#MedSky

bit.ly/476oSxs

bit.ly/476oSxs
#MedSky #PsychSciSky

#MedSky #PsychSciSky
bit.ly/44b5e3L

bit.ly/44b5e3L
#OncoSky #epigenetics

#OncoSky #epigenetics
bit.ly/45t4cQu
#STS
bit.ly/45t4cQu
#STS
bit.ly/45MBla7

bit.ly/45MBla7
#STS

#STS

Read the full review by Liao & Xu (2025): bit.ly/461oO2r
#OncoSky #MedSky
Read the full review by Liao & Xu (2025): bit.ly/461oO2r
#OncoSky #MedSky
#STS

#STS
An open-access study by Britwum (2025) examines how well-being, resilience, and connectedness relate to academic achievement among education students in Ghana.
bit.ly/4sW1Wva
#AcademicSky




An open-access study by Britwum (2025) examines how well-being, resilience, and connectedness relate to academic achievement among education students in Ghana.
bit.ly/4sW1Wva
#AcademicSky

