(BioRxiv All) Controlled Delivery and Light-Induced Release of Magic Spot Nucleotides in Escherichia coli: The "magic spot nucleotides" (MSNs) ppGpp and pppGpp (also: (p)ppGpp) are bacterial alarmones central to the conserved stringent response, a stress adaptation mechanism… #BioRxiv #MassSpecRSS
Controlled Delivery and Light-Induced Release of Magic Spot Nucleotides in Escherichia coli
The "magic spot nucleotides" (MSNs) ppGpp and pppGpp (also: (p)ppGpp) are bacterial alarmones central to the conserved stringent response, a stress adaptation mechanism that helps bacteria adapt to stress conditions and hostile environments. Current strategies to manipulate MSN levels rely mainly on genetic or environmental approaches, which are slow and lack temporal control. Chemical tools such as photocaged MSN analogues could provide such temporal control over MSN levels. However, the high negative charge of MSNs prevents spontaneous passage through the complex bacterial cell envelope. Here, we report the synthesis of photocaged, clickable, and isotope-labeled MSN analogues and their delivery into Escherichia coli comparing different approaches. A cyclodextrin-based synthetic nucleotide transporter provides particular advantages. Upon 400nm irradiation, these probes were photo-released inside living cells, where we tracked their conversion from pppGpp to ppGpp by capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry and studied their ability to alter growth in a (p)ppGpp mutant. This work provides the first demonstration that highly charged, photocaged MSNs can traverse the bacterial envelope, be photo-released intracellularly, and be metabolically tracked in real time. These probes lay the foundation for spatially and temporally controlled studies of MSN function and of other highly negatively charged metabolites in bacteria.
dlvr.it
October 23, 2025 at 4:02 AM
Everybody can reply
1 likes
RNase Y + Y-complex initiate rRNA cleavage in B. subtilis, shrinking ribosome pools under stress while ppGpp limits synthesis. => Dual control -> better fitness. Bonus: Y-complex includes YmcA doi.org/10.1101/2025.06.27.661978

October 13, 2025 at 9:43 AM
Everybody can reply
2 reposts
6 likes
In our recent journal club, we discussed an impressive paper published in Nature Microbiology titled “A shared alarmone–GTP switch controls persister formation in bacteria”. A comprehensive work on a (p)ppGpp–GTP antagonism pathway!
Check it out:
doi.org/10.1038/s415...
Check it out:
doi.org/10.1038/s415...

A shared alarmone–GTP switch controls persister formation in bacteria - Nature Microbiology
Alarmone synthesis depletes GTP levels leading to a GTP-dependent switch that controls triggered, spontaneous and antibiotic-induced persister formation in Bacillus subtilis.
doi.org
September 29, 2025 at 5:28 PM
Everybody can reply
1 reposts
1 likes
(not just) Caulophiles take note 👇
no alarmism, but evidence for
direct molecular cross-talk between (p)ppGpp and c-di-GMP nucleotide messengers!
#MicroSky
no alarmism, but evidence for
direct molecular cross-talk between (p)ppGpp and c-di-GMP nucleotide messengers!
#MicroSky
Check out the first preprint from our lab describing a direct molecular cross-talk between (p)ppGpp and c-di-GMP nucleotide messengers! Great work from first-author Corentin Jaboulay who was a postdoc in our lab, and great collaborations! @mmsb-lyon.bsky.social @cnrsbiologie.bsky.social
Cross-regulation of (p)ppGpp and c-di-GMP pathways controls a cell-cycle transition https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2025.08.22.671821v1
September 28, 2025 at 4:18 PM
Everybody can reply
14 likes
Cross-regulation of (p)ppGpp and c-di-GMP pathways controls a cell-cycle transition www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

Cross-regulation of (p)ppGpp and c-di-GMP pathways controls a cell-cycle transition
Bacteria must adapt their physiology to changing environments, a process often orchestrated by nucleotide messengers such as (p)ppGpp and cyclic di-GMP (c-di-GMP). While (p)ppGpp promotes survival und...
www.biorxiv.org
September 10, 2025 at 12:38 PM
Everybody can reply
3 reposts
7 likes
1 saves
Analysis of (p)ppGpp metabolism and signaling using a dynamic luminescent reporter
journals.plos.org/plosgenetics...
journals.plos.org/plosgenetics...

Analysis of (p)ppGpp metabolism and signaling using a dynamic luminescent reporter
Author summary Most bacteria adapt to stressful conditions such as nutrient limitation by synthesizing a signaling molecule, known as ppGpp, that consists of a hyper-phosphorylated GTP. Synthesis of p...
journals.plos.org
August 25, 2025 at 12:45 PM
Everybody can reply
1 reposts
2 likes
(p)ppGpp-dependent activation of gene expression during nutrient limitation | mBio #microsky #ribosome with Hpf and friends journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/...

(p)ppGpp-dependent activation of gene expression during nutrient limitation | mBio
Bacteria often experience nutrient limitation and, in response, attenuate energetically costly metabolic processes like protein synthesis. At the same time, however, they stimulate the expression of a subset of proteins that facilitate survival under ...
journals.asm.org
August 25, 2025 at 12:07 PM
Everybody can reply
1 reposts
Check out the first preprint from our lab describing a direct molecular cross-talk between (p)ppGpp and c-di-GMP nucleotide messengers! Great work from first-author Corentin Jaboulay who was a postdoc in our lab, and great collaborations! @mmsb-lyon.bsky.social @cnrsbiologie.bsky.social
Cross-regulation of (p)ppGpp and c-di-GMP pathways controls a cell-cycle transition https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2025.08.22.671821v1
August 24, 2025 at 7:48 AM
Everybody can reply
15 reposts
3 quotes
33 likes
1 saves
Caulobacter crescentus cell cycle: direct molecular cross-talk between (p)ppGpp and c-di-GMP signaling
bioRxiv👇🏼
bioRxiv👇🏼
Cross-regulation of (p)ppGpp and c-di-GMP pathways controls a cell-cycle transition https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2025.08.22.671821v1
August 24, 2025 at 6:35 AM
Everybody can reply
2 reposts
12 likes
Cross-regulation of (p)ppGpp and c-di-GMP pathways controls a cell-cycle transition https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2025.08.22.671821v1
August 24, 2025 at 4:16 AM
Everybody can reply
1 reposts
3 quotes
10 likes
Cross-regulation of (p)ppGpp and c-di-GMP pathways controls a cell-cycle transition https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2025.08.22.671821v1
August 24, 2025 at 4:16 AM
Everybody can reply
The bacterial alarmone (p)ppGpp mediates pathogenicity of the tomato plant pathogen Clavibacter michiganensis via a dual mechanism that affects both enzyme production and the Tat secretion system. Get the story in #mSystems: asm.social/2yk

August 21, 2025 at 6:03 PM
Everybody can reply
1 reposts
4 likes
(p)ppGpp-dependent activation of gene expression during nutrient limitation
#mBio from Jonathan Dworkin
journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/...
#mBio from Jonathan Dworkin
journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/...
(p)ppGpp-dependent activation of gene expression during nutrient limitation | mBio
Bacteria often experience nutrient limitation and, in response, attenuate energetically costly metabolic processes like protein synthesis. At the same time, however, they stimulate the expression of a subset of proteins that facilitate survival under ...
journals.asm.org
August 19, 2025 at 1:29 PM
Everybody can reply
6 reposts
6 likes
(p)ppGpp-dependent activation of gene expression during nutrient limitation journals.asm.org/doi/full/10.... #jcampubs
August 18, 2025 at 4:30 PM
Everybody can reply
1 likes
The stringent response in S. aureus, controlled by (p)ppGpp, is vital for survival & virulence. A null strain showed reduced virulence in zebrafish; myeloid cell depletion restored it. 🦠💉##idsky
Determining the importance of the stringent response for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus virulence in vivo
AbstractThe stringent response is a stress signalling pathway with links to bacterial virulence. This pathway is controlled by the nucleotide alarmone (p)ppGpp, produced in Staphylococcus aureus by three synthetase enzymes. Here, we used a panel of synthetase mutants to examine the importance of this signalling network for S. aureus survival and virulence in vivo. Using a zebrafish larval infection model, we observed that infection with a (p)ppGpp null strain attenuated virulence. Zebrafish myeloid cell depletion restored the virulence during systemic infection, indicating that (p)ppGpp is important for phagocyte-mediated immune evasion. Primary macrophages infection studies, followed by in vitro tolerance assays and RNA-seq, revealed that (p)ppGpp is required to survive stressors found within the intracellular macrophage environment, with roles for each class of synthetase, and the linked transcription factor CodY, implicated. Taken together, these results define the importance of the stringent response and each class of synthetase for S. aureus infection.
academic.oup.com
August 8, 2025 at 11:00 PM
Everybody can reply
Christopher Hamm (Gray lab): #Ecoli mutants that cannot produce polyphosphate or (p)ppGpp have disrupted Zring positioning, resulting in division and morphological defects #phages2025 🦠
journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/...
journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/...
journals.asm.org
August 5, 2025 at 4:26 PM
Everybody can reply
1 reposts
3 likes
August 5, 2025 at 4:13 PM
Everybody can reply
1 reposts
1 likes
The wonderful dynamics of (p)ppGpp, big thank you to everyone involved with this story
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

(p)ppGpp imposes graded transcriptional changes to impair motility and promote antibiotic tolerance in biofilms - npj Biofilms and Microbiomes
npj Biofilms and Microbiomes - (p)ppGpp imposes graded transcriptional changes to impair motility and promote antibiotic tolerance in biofilms
www.nature.com
August 1, 2025 at 7:15 PM
Everybody can reply
6 reposts
1 quotes
15 likes
Happy to share our lastest story about the Stringent Response ! We show how host-relevant stress disrupts Fe-S cluster stability, tuning (p)ppGpp levels to control bacterial adaptation and trigger virulence.
Read more here 👉 www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Read more here 👉 www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

Stress-Induced Iron-Sulfur Cluster Damage as a Conserved Trigger of the Stringent Response
Pathogenic bacteria rely on the stringent response to adapt to the complex and fluctuating conditions encountered within the host. However, the mechanisms by which the stringent response senses host-i...
www.biorxiv.org
July 30, 2025 at 10:53 AM
Everybody can reply
3 reposts
8 likes
Exicted to present my results at the #FEMS2025 tomorrow morning at Amber 3 & 4. I will present the effect of ppGpp in gene expression of AIEC, but also in host’s gene expression during infection of organoid-derived monolayers. Those are results obtained during my #PostdocBP

July 15, 2025 at 12:18 PM
Everybody can reply
1 likes
Yeh, Kelly, and Misra show that mutations in RNA polymerase (rpoB) mimic the stringent response in the absence of (p)ppGpp and help maintain a healthy proteome under extreme growth temperatures and without molecular chaperones or proteases.
#MicroSky
onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/...
#MicroSky
onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/...
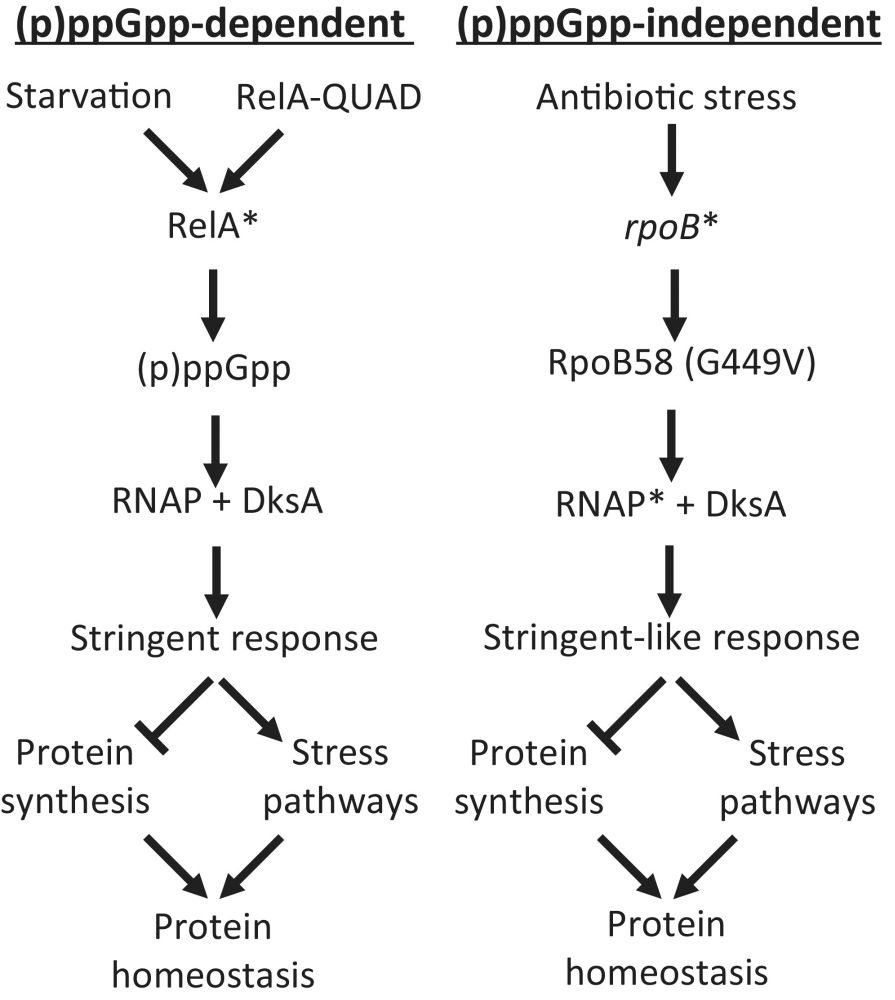
Characterization of a Novel RNA Polymerase Mutant of Escherichia coli That Confers Thermotolerance and Chaperone Independence
Protein homeostasis is perturbed at extremely high growth temperatures and without molecular chaperones or proteases. The protein synthesis-inhibiting branch of the stringent response involves elevat...
onlinelibrary.wiley.com
July 15, 2025 at 11:50 AM
Everybody can reply
1 reposts
1 likes
Functional interplay between (p)ppGpp and RNAP in Acinetobacter baumannii https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2025.07.04.663200v1
July 7, 2025 at 3:19 AM
Everybody can reply
2 reposts
1 likes
Functional interplay between (p)ppGpp and RNAP in Acinetobacter baumannii https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2025.07.04.663200v1
July 7, 2025 at 3:19 AM
Everybody can reply

