
Underfox
@underfox3.bsky.social
Physicist, Telecom Engineering lover, HPC Enthusiast. Prog Rock/Metal fan.
---
Independent tech analyst focused on semiconductors, patent analysis and emerging technologies.
---
Independent tech analyst focused on semiconductors, patent analysis and emerging technologies.

August 29, 2025 at 8:56 AM
Researchers have proposed Mixture of Contexts, a long video generation framework that learns to route each query to the most relevant segments of the video sequence, instead of relying on uniform or static sparse attention or a fixed selection strategy.
arxiv.org/pdf/2508.21058
arxiv.org/pdf/2508.21058




August 29, 2025 at 8:56 AM
Researchers have proposed Mixture of Contexts, a long video generation framework that learns to route each query to the most relevant segments of the video sequence, instead of relying on uniform or static sparse attention or a fixed selection strategy.
arxiv.org/pdf/2508.21058
arxiv.org/pdf/2508.21058
The results show that SwizzlePerf can achieve on a wide range of ML and scientific GPU kernels of up to a 2.1x speedup and 70% L2 hit rate improvement.


August 29, 2025 at 8:35 AM
The results show that SwizzlePerf can achieve on a wide range of ML and scientific GPU kernels of up to a 2.1x speedup and 70% L2 hit rate improvement.
In this paper is presented SwizzlePerf, a LLM workflow that automatically generates spatial optimizations for GPU kernels on disaggregated architectures by giving LLMs explicit hardware-awareness.
arxiv.org/pdf/2508.20258
arxiv.org/pdf/2508.20258



August 29, 2025 at 8:35 AM
In this paper is presented SwizzlePerf, a LLM workflow that automatically generates spatial optimizations for GPU kernels on disaggregated architectures by giving LLMs explicit hardware-awareness.
arxiv.org/pdf/2508.20258
arxiv.org/pdf/2508.20258
This work will be presented at the in 58th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture (MICRO 25), which will be held October 18 - 22, 2025 at Seoul, Korea.

August 29, 2025 at 6:04 AM
This work will be presented at the in 58th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture (MICRO 25), which will be held October 18 - 22, 2025 at Seoul, Korea.
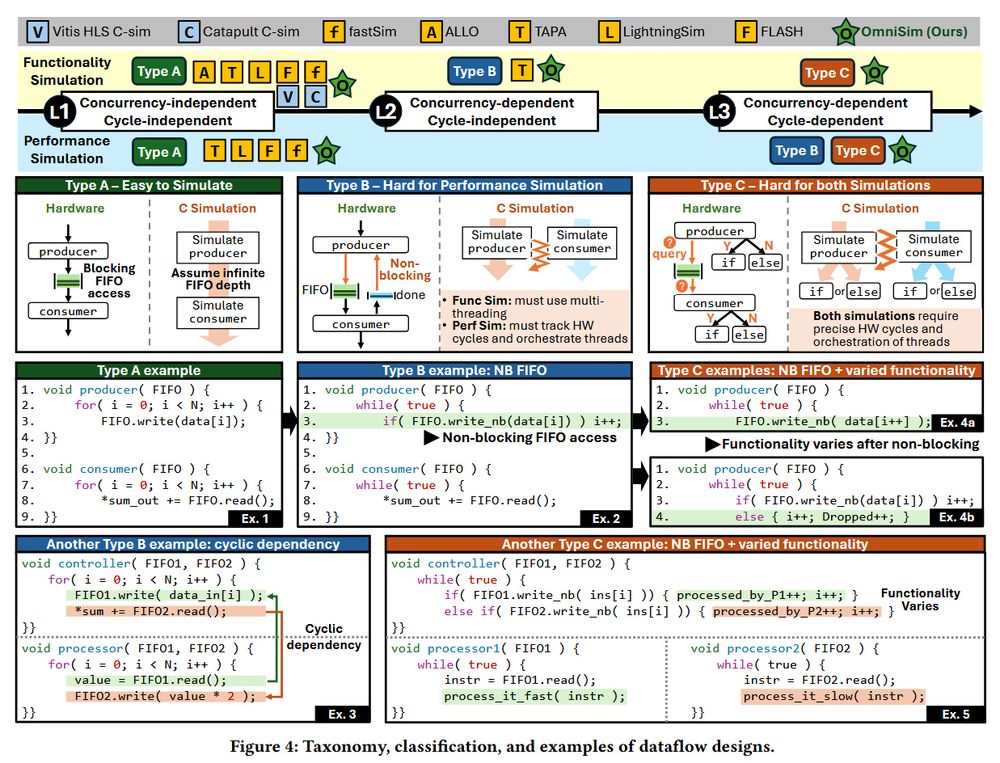
OmniSim is able to successfully simulate 11 designs previously unsupported by any HLS tool, achieving up to 35.9x speedup over traditional C/RTL co-simulation, and up to 6.61x speedup over the state-of-the-art yet less capable simulator, LightningSim, on its own benchmark suite.


August 29, 2025 at 6:04 AM
OmniSim is able to successfully simulate 11 designs previously unsupported by any HLS tool, achieving up to 35.9x speedup over traditional C/RTL co-simulation, and up to 6.61x speedup over the state-of-the-art yet less capable simulator, LightningSim, on its own benchmark suite.
OmniSim carefully orchestrates functionality and performance simulation threads to accurately model hardware-level behavior under arbitrary OS scheduling, achieving near-C simulation speed with near-RTL accuracy for both functionality and performance.



August 29, 2025 at 6:04 AM
OmniSim carefully orchestrates functionality and performance simulation threads to accurately model hardware-level behavior under arbitrary OS scheduling, achieving near-C simulation speed with near-RTL accuracy for both functionality and performance.
In this paper is presented OmniSim, a framework that extend C-level simulation capability of HLS tools by enabling both functionality and performance simulations for those complex dataflow designs that are currently unsupported or considered infeasible.
arxiv.org/pdf/2508.19299
arxiv.org/pdf/2508.19299



August 29, 2025 at 6:04 AM
In this paper is presented OmniSim, a framework that extend C-level simulation capability of HLS tools by enabling both functionality and performance simulations for those complex dataflow designs that are currently unsupported or considered infeasible.
arxiv.org/pdf/2508.19299
arxiv.org/pdf/2508.19299
The implemented proof of concept is capable of demonstrating softmax computation and invertible logic without the need to create a network of probabilistic devices, offering major scalability advantages.



August 29, 2025 at 5:05 AM
The implemented proof of concept is capable of demonstrating softmax computation and invertible logic without the need to create a network of probabilistic devices, offering major scalability advantages.
For the first time, researchers reported the realization of multi-value probabilistic computing by leveraging the thermally activated diffusion of magnetic skyrmions through an effectively non-flat energy landscape defined by a discrete number of sites.
arxiv.org/pdf/2508.19623
arxiv.org/pdf/2508.19623




August 29, 2025 at 5:05 AM
For the first time, researchers reported the realization of multi-value probabilistic computing by leveraging the thermally activated diffusion of magnetic skyrmions through an effectively non-flat energy landscape defined by a discrete number of sites.
arxiv.org/pdf/2508.19623
arxiv.org/pdf/2508.19623
Excerpt from: Y. Wong, G. Zocchi, Spontaneous spiral patterns etched on Germanium, Arxiv, 2025
Link: arxiv.org/pdf/2508.16764
Link: arxiv.org/pdf/2508.16764


August 29, 2025 at 3:59 AM
Excerpt from: Y. Wong, G. Zocchi, Spontaneous spiral patterns etched on Germanium, Arxiv, 2025
Link: arxiv.org/pdf/2508.16764
Link: arxiv.org/pdf/2508.16764
A thin metallic film on germanium, in the presence of water, results in a remarkable pattern-forming system, such as this beautiful spiral spontaneously etched on the surface with a total structure diameter of 680 μm.

August 29, 2025 at 3:59 AM
A thin metallic film on germanium, in the presence of water, results in a remarkable pattern-forming system, such as this beautiful spiral spontaneously etched on the surface with a total structure diameter of 680 μm.
Researchers have demonstrated graphene spin-field-effect junctions where the electric field can control ultrafast spin currents and spin dynamics in thin-film ferromagnets.
PRL link: journals.aps.org/prl/pdf/10.1...
PRL link: journals.aps.org/prl/pdf/10.1...




August 28, 2025 at 11:31 PM
Researchers have demonstrated graphene spin-field-effect junctions where the electric field can control ultrafast spin currents and spin dynamics in thin-film ferromagnets.
PRL link: journals.aps.org/prl/pdf/10.1...
PRL link: journals.aps.org/prl/pdf/10.1...
It is important to note that the proposed experiment in this work also revealed that the topology-aware losses could also contribute to improving the geometry of the interpolated data.




August 28, 2025 at 11:19 PM
It is important to note that the proposed experiment in this work also revealed that the topology-aware losses could also contribute to improving the geometry of the interpolated data.
Given an input sequence of persistence diagrams and a sparse temporal sampling of the corresponding data, the porposed approach inverts the non-keyframe diagrams to produce plausible estimations of the missing data.

August 28, 2025 at 11:19 PM
Given an input sequence of persistence diagrams and a sparse temporal sampling of the corresponding data, the porposed approach inverts the non-keyframe diagrams to produce plausible estimations of the missing data.
In this paper, researchers have developed a neural approach for the topology aware interpolation of scalar fields losses based on persistence diagrams, for constraining the topology and geometry of the output interpolations.
arxiv.org/pdf/2508.17995
arxiv.org/pdf/2508.17995




August 28, 2025 at 11:19 PM
In this paper, researchers have developed a neural approach for the topology aware interpolation of scalar fields losses based on persistence diagrams, for constraining the topology and geometry of the output interpolations.
arxiv.org/pdf/2508.17995
arxiv.org/pdf/2508.17995
Through a proposed single-pass plane sweeping strategy, the present method achieve over 60fps for 90+ views, up to 228 FPS for 45 views using a single RTX 5090.




August 28, 2025 at 5:34 AM
Through a proposed single-pass plane sweeping strategy, the present method achieve over 60fps for 90+ views, up to 228 FPS for 45 views using a single RTX 5090.
Nvidia researchers have developed a unified framework for real-time radiance field rendering on light field displays, supporting a wide range of radiance field representations within a shared architecture based on a single-pass plane sweeping strategy.
arxiv.org/pdf/2508.18540
arxiv.org/pdf/2508.18540




August 28, 2025 at 5:34 AM
Nvidia researchers have developed a unified framework for real-time radiance field rendering on light field displays, supporting a wide range of radiance field representations within a shared architecture based on a single-pass plane sweeping strategy.
arxiv.org/pdf/2508.18540
arxiv.org/pdf/2508.18540
The results show that the proposed approach yields up to 6.20x throughput and 5.93x energy improvements for general workloads and 1.59x and 1.12x improvement to throughput and energy, respectively, for ML workloads on an A100 GPU.


August 28, 2025 at 5:20 AM
The results show that the proposed approach yields up to 6.20x throughput and 5.93x energy improvements for general workloads and 1.59x and 1.12x improvement to throughput and energy, respectively, for ML workloads on an A100 GPU.
The proposed scheduler is based on a new time series-based predictive technique to determine memory footprints of dynamically unanalyzable jobs, while also allowing to schedule these jobs in constrained partitions.

August 28, 2025 at 5:20 AM
The proposed scheduler is based on a new time series-based predictive technique to determine memory footprints of dynamically unanalyzable jobs, while also allowing to schedule these jobs in constrained partitions.
In this paper, researchers have developed a comprehensive framework for managing multi-instance GPU partitions that can significantly improve throughput, power consumption, memory utilization, and task response time.
arxiv.org/pdf/2508.18556
arxiv.org/pdf/2508.18556

August 28, 2025 at 5:20 AM
In this paper, researchers have developed a comprehensive framework for managing multi-instance GPU partitions that can significantly improve throughput, power consumption, memory utilization, and task response time.
arxiv.org/pdf/2508.18556
arxiv.org/pdf/2508.18556
Compared to the state of the art from 2024, the present work have increased the maximum achievable simulation workload by a factor of almost 16, while increasing the walltime by only 35%.



August 28, 2025 at 5:00 AM
Compared to the state of the art from 2024, the present work have increased the maximum achievable simulation workload by a factor of almost 16, while increasing the walltime by only 35%.
The proposed simulation of 42,240 atoms on 37,600 GPUs achieve ultra-short iteration time of∼42 seconds per iteration, excellent parallel efficiency of 82% in weak scaling, and high computational performance of 1.15 Eflop/s.




August 28, 2025 at 5:00 AM
The proposed simulation of 42,240 atoms on 37,600 GPUs achieve ultra-short iteration time of∼42 seconds per iteration, excellent parallel efficiency of 82% in weak scaling, and high computational performance of 1.15 Eflop/s.
In this paper is presented an ab-initio transistor simulation of unprecedented scale including electron-electron interactions within the self-consistent GW approximation, carefully optimized to take advantage of the Alps and Frontier supercomputers. #HPC
arxiv.org/pdf/2508.19138
arxiv.org/pdf/2508.19138




August 28, 2025 at 5:00 AM
In this paper is presented an ab-initio transistor simulation of unprecedented scale including electron-electron interactions within the self-consistent GW approximation, carefully optimized to take advantage of the Alps and Frontier supercomputers. #HPC
arxiv.org/pdf/2508.19138
arxiv.org/pdf/2508.19138
This work will be presented at 32th IEEE International Symposium on High-Performance Computer Architecture (HPCA 2026), which will be held January 31 to February 4, 2026 at Sydney, Australia.

August 27, 2025 at 6:25 AM
This work will be presented at 32th IEEE International Symposium on High-Performance Computer Architecture (HPCA 2026), which will be held January 31 to February 4, 2026 at Sydney, Australia.

